Asia Pac Allergy.
2014 Jul;4(3):172-176. 10.5415/apallergy.2014.4.3.172.
Poor positive predictive value of serum immunoglobulin G4 concentrations in the diagnosis of immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Immunology, Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Camperdown, NSW 2050, Australia. james.j.yun@gmail.com
- KMID: 2397095
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5415/apallergy.2014.4.3.172
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-related sclerosing disease is a recently described clinicopathological entity with diverse manifestations including, amongst others, autoimmune pancreatitis, sclerosing cholangitis, sclerosing sialadenitis and retroperitoneal fibrosis. Elevated serum IgG4 concentration has been described as the hallmark of this condition with reported good sensitivity and specificity.
OBJECTIVE
We sought to establish the utility of serum IgG4 concentrations in the diagnosis of IgG4-related sclerosing disease by determining how many serum samples with elevated IgG4 from an unselected population would originate from patients who fulfilled criteria for this diagnosis.
METHODS
The clinical features and laboratory characteristics of patients whose serum IgG4 concentration was greater than 1.30 g/L were analysed retrospectively from a total of 1,258 IgG subclass measurements performed in a tertiary hospital diagnostic laboratory.
RESULTS
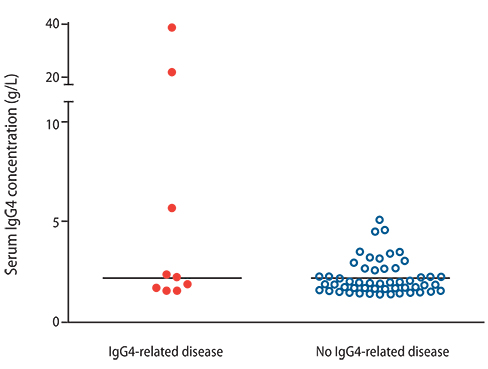
Eighty patients (6.4%) had elevated IgG4 concentrations greater than 1.30 g/L. Nine of 61 patients had the diagnosis of IgG4-related sclerosing disease, giving a poor positive predictive value of 15%. The median serum IgG4 concentrations of those with and without IgG4-related sclerosing disease were 2.16 g/L and 1.86 g/L, respectively (p = 0.22).
CONCLUSION
Serum IgG4 concentration has poor positive predictive value in the diagnosis of IgG4-related sclerosing disease and, therefore, the clinical significance of elevated serum IgG4 concentration alone must be interpreted with caution.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, Fukushima M, Nikaido T, Nakayama K, Usuda N, Kiyosawa K. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:732–738.
Article2. Neild GH, Rodriguez-Justo M, Wall C, Connolly JO. Hyper-IgG4 disease: report and characterisation of a new disease. BMC Med. 2006; 4:23.
Article3. Kamisawa T, Nakajima H, Egawa N, Funata N, Tsuruta K, Okamoto A. IgG4-related sclerosing disease incorporating sclerosing pancreatitis, cholangitis, sialadenitis and retroperitoneal fibrosis with lymphadenopathy. Pancreatology. 2006; 6:132–137.
Article4. Umemura T, Zen Y, Hamano H, Ichijo T, Kawa S, Nakanuma Y, Kiyosawa K. IgG4 associated autoimmune hepatitis: a differential diagnosis for classical autoimmune hepatitis. Gut. 2007; 56:1471–1472.
Article5. Zen Y, Kasahara Y, Horita K, Miyayama S, Miura S, Kitagawa S, Nakanuma Y. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the breast in a patient with a high serum IgG4 level: histologic similarity to sclerosing pancreatitis. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005; 29:275–278.6. Takato H, Yasui M, Ichikawa Y, Fujimura M, Nakao S, Zen Y, Minato H. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia with abundant IgG4-positive cells infiltration, which was thought as pulmonary involvement of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. Intern Med. 2008; 47:291–294.
Article7. Kasashima S, Zen Y. IgG4-related inflammatory abdominal aortic aneurysm. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011; 23:18–23.
Article8. Morselli-Labate AM, Pezzilli R. Usefulness of serum IgG4 in the diagnosis and follow up of autoimmune pancreatitis: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 24:15–36.
Article9. Tabata T, Kamisawa T, Takuma K, Anjiki H, Egawa N, Kurata M, Honda G, Tsuruta K, Setoguchi K, Obayashi T, Sasaki T. Serum IgG4 concentrations and IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2009; 408:25–28.
Article10. Yamamoto M, Ohara M, Suzuki C, Naishiro Y, Yamamoto H, Takahashi H, Imai K. Elevated IgG4 concentrations in serum of patients with Mikulicz's disease. Scand J Rheumatol. 2004; 33:432–433.
Article11. Ghazale A, Chari ST, Smyrk TC, Levy MJ, Topazian MD, Takahashi N, Clain JE, Pearson RK, Pelaez-Luna M, Petersen BT, Vege SS, Farnell MB. Value of serum IgG4 in the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis and in distinguishing it from pancreatic cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102:1646–1653.
Article12. Sadler R, Chapman RW, Simpson D, Soonawalla ZF, Waldegrave EL, Burden JM, Misbah SA, Ferry BL. The diagnostic significance of serum IgG4 levels in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis: a UK study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 23:139–145.13. Ngwa TN, Law R, Murray D, Chari ST. Serum immunoglobulin g4 level is a poor predictor of immunoglobulin g4-related disease. Pancreas. 2014; 43:704–707.
Article14. Carruthers MN, Khosroshahi A, Augustin T, Deshpande V, Stone JH. The diagnostic utility of serum IgG4 concentrations in IgG4-related disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014; 03. 20. [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204907.
Article15. Zen Y, Onodera M, Inoue D, Kitao A, Matsui O, Nohara T, Namiki M, Kasashima S, Kawashima A, Matsumoto Y, Katayanagi K, Murata T, Ishizawa S, Hosaka N, Kuriki K, Nakanuma Y. Retroperitoneal fibrosis: a clinicopathologic study with respect to immunoglobulin G4. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009; 33:1833–1839.
Article16. Kanari H, Kagami S, Kashiwakuma D, Oya Y, Furuta S, Ikeda K, Suto A, Suzuki K, Hirose K, Watanabe N, Okamoto Y, Yamamoto S, Iwamoto I, Nakajima H. Role of Th2 cells in IgG4-related lacrimal gland enlargement. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2010; 152:Suppl 1. 47–53.
Article17. Shakib F, Stanworth DR, Smalley CA, Brown GA. Elevated serum IgG4 levels in cystic fibrosis patients. Clin Allergy. 1976; 6:237–240.
Article18. Aalberse RC, van der Gaag R, van Leeuwen J. Serologic aspects of IgG4 antibodies. I. Prolonged immunization results in an IgG4-restricted response. J Immunol. 1983; 130:722–726.19. Lin G, Li J. Elevation of serum IgG subclass concentration in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2010; 30:837–840.
Article20. Saeki T, Saito A, Yamazaki H, Emura I, Imai N, Ueno M, Nishi S, Miyamura S, Gejyo F. Tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with IgG4-related systemic disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2007; 11:168–173.
Article21. Mendes FD, Jorgensen R, Keach J, Katzmann JA, Smyrk T, Donlinger J, Chari S, Lindor KD. Elevated serum IgG4 concentration in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:2070–2075.
Article22. Schauer U, Stemberg F, Rieger CH, Borte M, Schubert S, Riedel F, Herz U, Renz H, Wick M, Carr-Smith HD, Bradwell AR, Herzog W. IgG subclass concentrations in certified reference material 470 and reference values for children and adults determined with the binding site reagents. Clin Chem. 2003; 49:1924–1929.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing cholangitis
- A Case of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sclerosing Disease Mimicking Lung Cancer
- A Case of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sclerosing Disease of the Paranasal Sinus Mimicking Nasal Malignancy
- Two Cases of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sclerosing Disease Mimicking Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
- Immunoglobulin G4-Related Systemic Sclerosing Disease: A Case Involving the Ureter and Kidney