J Korean Soc Radiol.
2013 Jul;69(1):53-56. 10.3348/jksr.2013.69.1.53.
A Case of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sclerosing Disease Mimicking Lung Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. ykradio@medimail.co.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2002890
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2013.69.1.53
Abstract
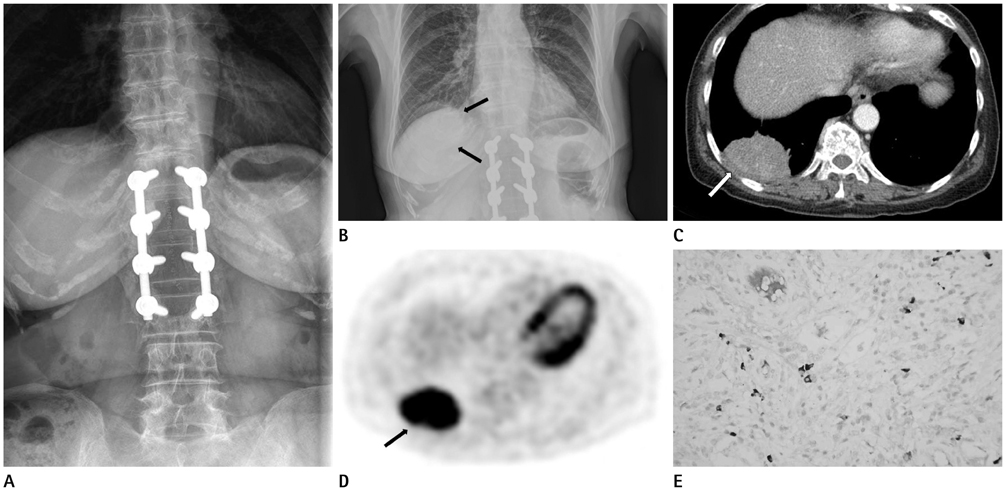
- Immunoglobulin (Ig) G4-related sclerosing disease is a recently described systemic fibro-inflammatory disease associated with an elevated circulating level of IgG4 and extensive IgG4-positive lymphoplasmacytic infiltration, resulting in sclerosing inflammation involving various body organs. We experienced one case where surgery confirmed IgG4-related sclerosing disease as a solitary lung mass mimicking lung cancer. We report radiologic findings including chest computed tomography and positron emission tomography computed tomography, with clinical manifestations of IgG4-related sclerosing disease.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Neild GH, Rodriguez-Justo M, Wall C, Connolly JO. Hyper-IgG4 disease: report and characterisation of a new disease. BMC Med. 2006; 4:23.2. de Jong WK, Kluin PM, Groen HM. Overlapping immunoglobulin G4-related disease and Rosai-Dorfman disease mimicking lung cancer. Eur Respir Rev. 2012; 21:365–367.3. Kamisawa T, Okamoto A. IgG4-related sclerosing disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14:3948–3955.4. Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:732–738.5. Hirano K, Kawabe T, Komatsu Y, Matsubara S, Togawa O, Arizumi T, et al. High-rate pulmonary involvement in autoimmune pancreatitis. Intern Med J. 2006; 36:58–61.6. Zen Y, Inoue D, Kitao A, Onodera M, Abo H, Miyayama S, et al. IgG4-related lung and pleural disease: a clinicopathologic study of 21 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009; 33:1886–1893.7. Chari ST, Smyrk TC, Levy MJ, Topazian MD, Takahashi N, Zhang L, et al. Diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis: the Mayo Clinic experience. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006; 4:1010–1016. quiz 934.8. Ryu JH, Sekiguchi H, Yi ES. Pulmonary manifestations of immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing disease. Eur Respir J. 2012; 39:180–186.9. Taniguchi T, Ko M, Seko S, Nishida O, Inoue F, Kobayashi H, et al. Interstitial pneumonia associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut. 2004; 53:770. author reply 770-771.10. Inoue D, Zen Y, Abo H, Gabata T, Demachi H, Kobayashi T, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-related lung disease: CT findings with pathologic correlations. Radiology. 2009; 251:260–270.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Immunoglobulin G4-Related Lung Disease Mimicking Lung Cancer: Two Case Reports
- Immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing cholangitis
- Two Cases of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sclerosing Disease Mimicking Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
- A Case of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sclerosing Disease of the Paranasal Sinus Mimicking Nasal Malignancy
- Immunoglobulin G4-Related Systemic Sclerosing Disease: A Case Involving the Ureter and Kidney