Asia Pac Allergy.
2017 Jul;7(3):148-155. 10.5415/apallergy.2017.7.3.148.
A review of 42 asthmatic children with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Vallabhbhai Patel Chest Institute, University of Delhi, Delhi 110 007, India. ashokshah99@yahoo.com
- KMID: 2396938
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5415/apallergy.2017.7.3.148
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) in children with asthma, not associated with cystic fibrosis, is yet to receive the recognition it deserves.
OBJECTIVE
To highlight the presentation of ABPA in children with asthma.
METHODS
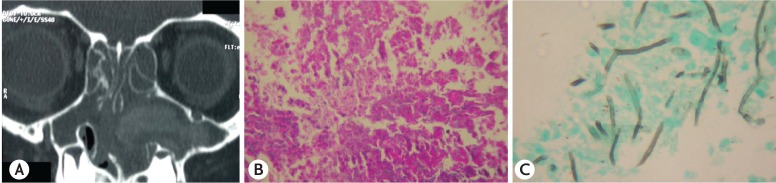
This retrospective review documents the occurrence of pediatric ABPA over a period of 31 years in one unit. Children with asthma, eosinophilia and infiltrates on chest radiograph were screened for ABPA. In these patients, demonstration of immediate hypersensitivity response against Aspergillus species along with serological profile and pulmonary function testing were done. Bronchography/computed tomography (CT) of the chest demonstrated central bronchiectasis (CB). CT of the paranasal sinuses was done in patients with upper airways symptoms. In those suspected with allergic Aspergillus sinusitis (AAS) consent was sought from the parents for the invasive procedure needed for the diagnosis of AAS.
RESULTS
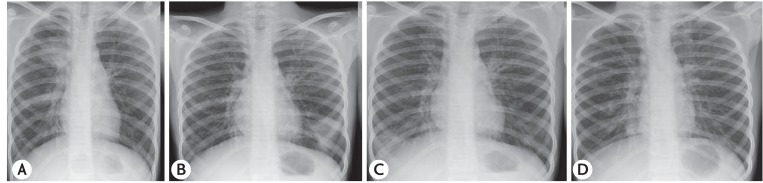
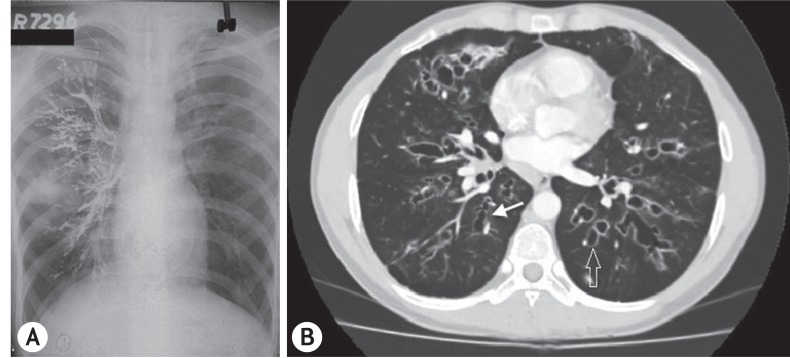
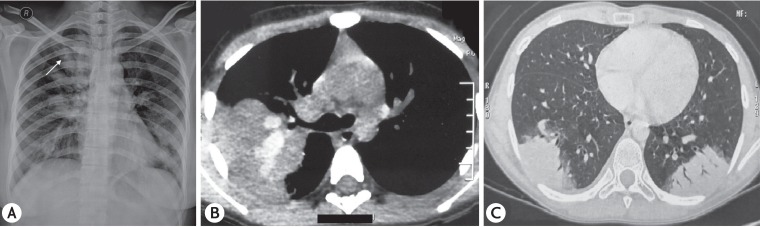
Of the 349 patients with ABPA diagnosed, 42 (12.03%) were in the pediatric age group. The mean age on presentation was 12.9 ± 4 years with a male preponderance. All patients had asthma and positive intradermal/skin prick test against Aspergillus species. Ring shadows, the most common radiological presentation, were seen in 28 of 42 patients. Bronchography/CT of the chest demonstrated CB, a feature pathognomic of ABPA, in 32 of 42 patients. High attenuation mucus plugs was observed in 7 of 36 patients while ABPA-seropositive was diagnosed in 10 of 42 patients. On imaging, sinusitis was seen in 20 of 30 patients with upper airways symptoms of whom eight had suspected AAS. Three parents consented for surgery, which confirmed the diagnosis.
CONCLUSION
This study highlights the need to evaluate asthmatic children for ABPA as also to exclude AAS.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Aerobiology in Asian airway allergic diseases
Bernard Yu-Hor Thong
Asia Pac Allergy. 2017;7(3):119-120. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2017.7.3.119.Allergic bronchopulmonary mycosis – pathophysiology, histology, diagnosis, and treatment
Koichiro Asano, Katsuhiko Kamei, Akira Hebisawa
Asia Pac Allergy. 2018;8(3):e24. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2018.8.e24.Allergic bronchopulmonary mycosis – pathophysiology, histology, diagnosis, and treatment
Koichiro Asano, Katsuhiko Kamei, Akira Hebisawa
Asia Pac Allergy. 2018;8(3):. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2018.8.e24.
Reference
-
1. Shah A, Panjabi C. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: a perplexing clinical entity. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2016; 8:282–297. PMID: 27126721.
Article2. Hinson KF, Moon AJ, Plummer NS. Broncho-pulmonary aspergillosis; a review and a report of eight new cases. Thorax. 1952; 7:317–333. PMID: 13015523.3. Mann B, Pasha MA. Allergic primary pulmonary aspergillosis and Schonlein-Henoch purpura. Br Med J. 1959; 1:282–283. PMID: 13618621.
Article4. Geller DE, Kaplowitz H, Light MJ, Colin AA. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in cystic fibrosis: reported prevalence, regional distribution, and patient characteristics. Scientific Advisory Group, Investigators, and Coordinators of the Epidemiologic Study of Cystic Fibrosis. Chest. 1999; 116:639–646. PMID: 10492265.5. Sharma VK, Raj D, Xess I, Lodha R, Kabra SK. Prevalence and risk factors for allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in Indian children with cystic fibrosis. Indian Pediatr. 2014; 51:295–297. PMID: 24825267.
Article6. Slavin RG, Laird TS, Cherry JD. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in a child. J Pediatr. 1970; 76:416–421. PMID: 4984017.
Article7. Berger I, Phillips WL, Shenker IR. Pulmonary aspergillosis in childhood A case report and discussion. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1972; 11:178–182. PMID: 4553322.8. Imbeau SA, Cohen M, Reed CE. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in infants. Am J Dis Child. 1977; 131:1127–1130. PMID: 910766.
Article9. Wang JL, Patterson R, Mintzer R, Roberts M, Rosenberg M. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in pediatric practice. J Pediatr. 1979; 94:376–381. PMID: 423017.
Article10. Chetty A, Bhargava S, Jain RK. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in Indian children with bronchial asthma. Ann Allergy. 1985; 54:46–49. PMID: 3966689.11. Singh M, Das S, Chauhan A, Paul N, Sodhi KS, Mathew J, Chakrabarti A. The diagnostic criteria for allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in children with poorly controlled asthma need to be re-evaluated. Acta Paediatr. 2015; 104:e206–e209. PMID: 25620428.
Article12. De H, Azad SM, Giri PP, Pal P, Ghosh A, Maitra A. Two cases of non-cystic fibrosis (CF) bronchiectasis with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Respir Med Case Rep. 2016; 20:68–71. PMID: 28053855.
Article13. Shah A, Pant CS, Bhagat R, Panchal N. CT in childhood allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Pediatr Radiol. 1992; 22:227–228. PMID: 1508597.
Article14. Shah A, Bhagat R, Panchal N. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis with clubbing and cavitation. Indian Pediatr. 1993; 30:248–251. PMID: 8375890.15. Shah A, Panchal N, Agarwal AK. Concomitant allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis and allergic Aspergillus sinusitis: a review of an uncommon association*. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001; 31:1896–1905. PMID: 11737042.16. Shah A, Kala J, Sahay S. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis with hilar adenopathy in a 42-month-old boy. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2007; 42:747–748. PMID: 17598173.
Article17. Shah A, Kala J, Sahay S, Panjabi C. Frequency of familial occurrence in 164 patients with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008; 101:363–369. PMID: 18939723.
Article18. Shah A, Gera K, Panjabi C. Childhood allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis presenting as a middle lobe syndrome. Asia Pac Allergy. 2016; 6:67–69. PMID: 26844222.
Article19. Rosenberg M, Patterson R, Mintzer R, Cooper BJ, Roberts M, Harris KE. Clinical and immunologic criteria for the diagnosis of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Ann Intern Med. 1977; 86:405–414. PMID: 848802.
Article20. Wang JL, Patterson R, Rosenberg M, Roberts M, Cooper BJ. Serum IgE and IgG antibody activity against Aspergillus fumigatus as a diagnostic aid in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978; 117:917–927. PMID: 350109.21. Shah A, Khan ZU, Chaturvedi S, Malik GB, Randhawa HS. Concomitant allergic Aspergillus sinusitis and allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis associated with familial occurrence of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Ann Allergy. 1990; 64:507–512. PMID: 2346236.22. Shah A, Khan ZU, Sircar M, Chaturvedi S, Malik GB, Randhawa HS. Allergic Aspergillus sinusitis: an Indian report. Respir Med. 1990; 84:249–251. PMID: 2218009.23. Bhagat R, Shah A, Jaggi OP, Khan ZU. Concomitant allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis and allergic Aspergillus sinusitis with an operated aspergilloma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1993; 91:1094–1096. PMID: 8491942.24. Shah A, Bhagat R, Panchal N, Jaggi OP, Khan ZU. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis with middle lobe syndrome and allergic Aspergillus sinusitis. Eur Respir J. 1993; 6:917–918. PMID: 8339813.25. deShazo RD, Swain RE. Diagnostic criteria for allergic fungal sinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995; 96:24–35. PMID: 7622760.
Article26. Shah A. Allergic bronchopulmonary and sinus aspergillosis: the co-occurrence. Chest (India). 2001; 2:234–235.27. Maurya V, Gugnani HC, Sarma PU, Madan T, Shah A. Sensitization to Aspergillus antigens and occurrence of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in patients with asthma. Chest. 2005; 127:1252–1259. PMID: 15821202.28. Agarwal R, Gupta D, Aggarwal AN, Behera D, Jindal SK. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: lessons from 126 patients attending a chest clinic in north India. Chest. 2006; 130:442–448. PMID: 16899843.29. Chetty A, Menon RK, Malviya AN. Allergic bronchopulmon ary aspergillosis in children. Indian J Pediatr. 1982; 49:203–205. PMID: 6752013.30. Mastella G, Rainisio M, Harms HK, Hodson ME, Koch C, Navarro J, Strandvik B, McKenzie SG. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in cystic fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 2001; 17:1052–1053. PMID: 11488309.
Article31. Kabra SK, Kabra M, Lodha R, Shastri S. Cystic fibrosis in India. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2007; 42:1087–1094. PMID: 17968991.
Article32. Mandal A, Kabra SK, Lodha R. Cystic fibrosis in India: past, present and future. J Pulm Med Respir Res. 2015; 1:002.33. Greenberger PA. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002; 110:685–692. PMID: 12417875.
Article34. Shah A, Panjabi C. Allergic aspergillosis of the respiratory tract. Eur Respir Rev. 2014; 23:8–29. PMID: 24591658.
Article35. Shah A, Agarwal AK, Chugh IM. Hilar adenopathy in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1999; 82:504–506. PMID: 10353584.
Article36. Scadding JG. The bronchi in allergic aspergillosis. Scand J Respir Dis. 1967; 48:372–377.37. Agarwal R, Gupta D, Aggarwal AN, Saxena AK, Chakrabarti A, Jindal SK. Clinical significance of hyperattenuating mucoid impaction in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: an analysis of 155 patients. Chest. 2007; 132:1183–1190. PMID: 17646221.38. Panjabi C, Shah A. Allergic Aspergillus sinusitis and its association with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Asia Pac Allergy. 2011; 1:130–137. PMID: 22053309.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis
- Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis Presenting as Recurrent Mass-like Consolidation
- Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis Coupled with Broncholithiasis in a Non-asthmatic Patient
- A Case of Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis
- Asymptomatic Developments of Pulmonary Infiltrates and Central Bronchiectasis in a Patient with Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis