Nutr Res Pract.
2017 Feb;11(1):11-16. 10.4162/nrp.2017.11.1.11.
Anti-bacterial effects of enzymatically-isolated sialic acid from glycomacropeptide in a Helicobacter pylori-infected murine model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medical Nutrition, Kyung Hee University, 1732, Deogyeong-daero, Giheung-gu, Yongin-si, Gyeonggi 17104, Korea. jlee2007@khu.ac.kr
- 2College of Veterinary Medicine, Chonnam National University, Gwangju 61186, Korea.
- 3Medinutrol Co. Ltd., Jeonnam 57024, Korea.
- KMID: 2395288
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2017.11.1.11
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) colonization of the stomach mucosa and duodenum is the major cause of acute and chronic gastroduodenal pathology in humans. Efforts to find effective anti-bacterial strategies against H. pylori for the non-antibiotic control of H. pylori infection are urgently required. In this study, we used whey to prepare glycomacropeptide (GMP), from which sialic acid (G-SA) was enzymatically isolated. We investigated the anti-bacterial effects of G-SA against H. pylori in vitro and in an H. pylori-infected murine model.
MATERIALS/METHODS
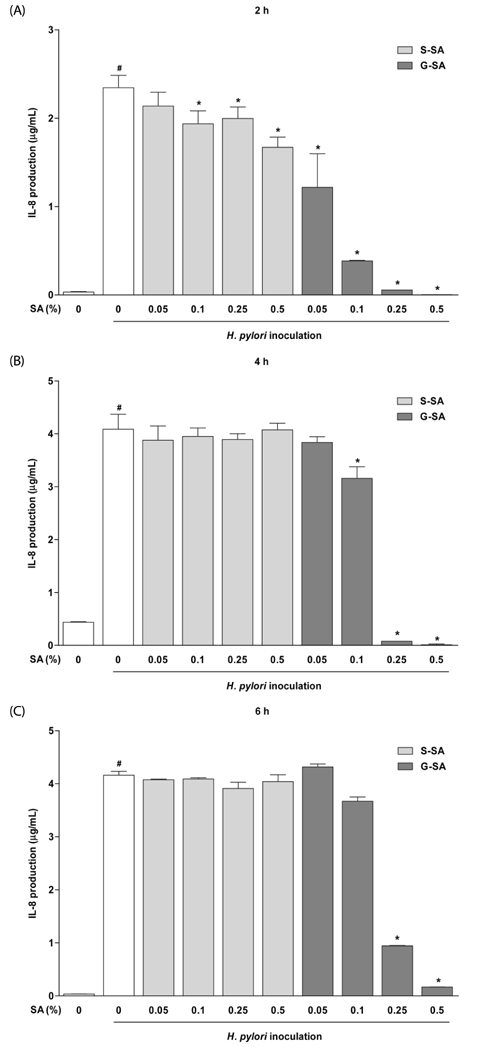
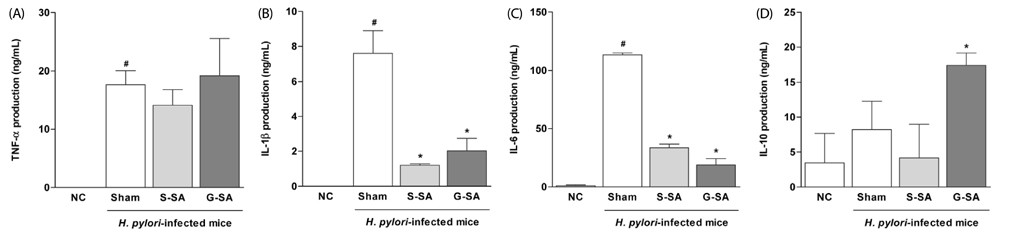
The anti-bacterial activity of G-SA was measured in vitro using the macrodilution method, and interleukin-8 (IL-8) production was measured in H. pylori and AGS cell co-cultures by ELISA. For in vivo study, G-SA 5 g/kg body weight (bw)/day and H. pylori were administered to mice three times over one week. After one week, G-SA 5 g/kg bw/day alone was administered every day for one week. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-10 levels were measured by ELISA to determine the anti-inflammatory effects of G-SA. In addition, real-time PCR was performed to measure the genetic expression of cytotoxin-associated gene A (cagA).
RESULTS
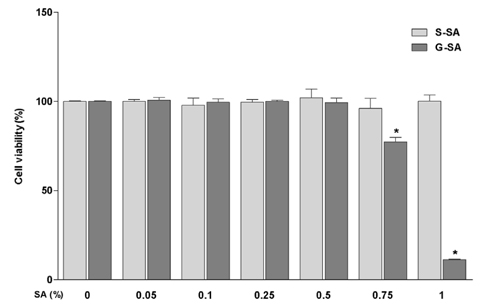
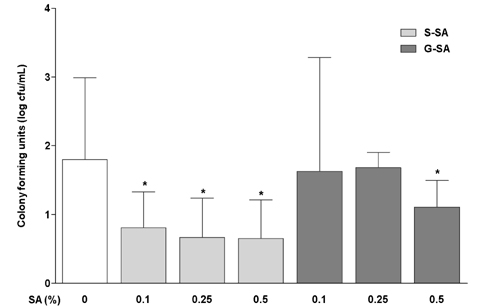
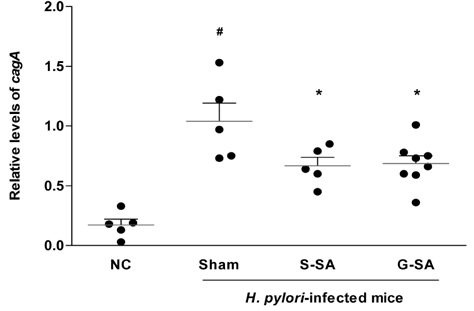
G-SA inhibited the growth of H. pylori and suppressed IL-8 production in H. pylori and in AGS cell co-cultures in vitro. In the in vivo assay, administration of G-SA reduced levels of IL-1β and IL-6 pro-inflammatory cytokines whereas IL-10 level increased. Also, G-SA suppressed the expression of cagA in the stomach of H. pylori-infected mice.
CONCLUSION
G-SA possesses anti-H. pylori activity as well as an anti-H. pylori-induced gastric inflammatory effect in an experimental H. pylori-infected murine model. G-SA has potential as an alternative to antibiotics for the prevention of H. pylori infection and H. pylori-induced gastric disease prevention.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Body Weight
Coculture Techniques
Colon
Cytokines
Duodenum
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter*
Humans
In Vitro Techniques
Interleukin-10
Interleukin-6
Interleukin-8
Methods
Mice
Mucous Membrane
N-Acetylneuraminic Acid*
Necrosis
Pathology
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
Stomach
Stomach Diseases
Whey
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Cytokines
Interleukin-10
Interleukin-6
Interleukin-8
N-Acetylneuraminic Acid
Figure
Reference
-
1. Suerbaum S, Michetti P. Helicobacter pylori infection. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:1175–1186.2. Venerito M, Vasapolli R, Rokkas T, Malfertheiner P. Helicobacter pylori and gastrointestinal malignancies. Helicobacter. 2015; 20:Suppl 1. 36–39.
Article3. Cover TL, Blaser MJ. Helicobacter pylori infection, a paradigm for chronic mucosal inflammation: pathogenesis and implications for eradication and prevention. Adv Intern Med. 1996; 41:85–117.4. Borén T, Falk P, Roth KA, Larson G, Normark S. Attachment of Helicobacter pylori to human gastric epithelium mediated by blood group antigens. Science. 1993; 262:1892–1895.
Article5. Kobayashi Y, Okazaki K, Murakami K. Adhesion of Helicobacter pylori to gastric epithelial cells in primary cultures obtained from stomachs of various animals. Infect Immun. 1993; 61:4058–4063.
Article6. Bodger K, Crabtree JE. Helicobacter pylori and gastric inflammation. Br Med Bull. 1998; 54:139–150.7. Huang J, O'Toole PW, Doig P, Trust TJ. Stimulation of interleukin-8 production in epithelial cell lines by Helicobacter pylori. Infect Immun. 1995; 63:1732–1738.
Article8. Harris PR, Mobley HL, Perez-Perez GI, Blaser MJ, Smith PD. Helicobacter pylori urease is a potent stimulus of mononuclear phagocyte activation and inflammatory cytokine production. Gastroenterology. 1996; 111:419–425.
Article9. Jones KR, Whitmire JM, Merrell DS. A tale of two toxins: Helicobacter pylori CagA and VacA modulate host pathways that impact disease. Front Microbiol. 2010; 1:115.
Article10. Kaji T, Ishihara S, Ashizawa N, Hamamoto N, Endo H, Fukuda R, Adachi K, Watanabe M, Nakao M, Kinoshita Y. Adherence of Helicobacter pylori to gastric epithelial cells and mucosal inflammation. J Lab Clin Med. 2002; 139:244–250.
Article11. Varki NM, Varki A. Diversity in cell surface sialic acid presentations: implications for biology and disease. Lab Invest. 2007; 87:851–857.
Article12. Vimr ER, Kalivoda KA, Deszo EL, Steenbergen SM. Diversity of microbial sialic acid metabolism. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2004; 68:132–153.
Article13. Carson CF, Riley TV. Non-antibiotic therapies for infectious diseases. Commun Dis Intell Q Rep. 2003; 27:Suppl. S143–S146.14. Kamiji MM, de Oliveira RB. Non-antibiotic therapies for Helicobacter pylori infection. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005; 17:973–981.
Article15. Yang JC, Shun CT, Chien CT, Wang TH. Effective prevention and treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection using a combination of catechins and sialic acid in AGS cells and BALB/c mice. J Nutr. 2008; 138:2084–2090.
Article16. Wang YC. Medicinal plant activity on Helicobacter pylori related diseases. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:10368–10382.17. Ando T, Kusugami K, Ohsuga M, Shinoda M, Sakakibara M, Saito H, Fukatsu A, Ichiyama S, Ohta M. Interleukin-8 activity correlates with histological severity in Helicobacter pylori-associated antral gastritis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996; 91:1150–1156.18. Lee A, O'Rourke J, De Ungria MC, Robertson B, Daskalopoulos G, Dixon MF. A standardized mouse model of Helicobacter pylori infection: introducing the Sydney strain. Gastroenterology. 1997; 112:1386–1397.
Article19. Shimoyama T, Crabtree JE. Bacterial factors and immune pathogenesis in Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut. 1998; 43:Suppl 1. S2–S5.20. Simon PM, Goode PL, Mobasseri A, Zopf D. Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori binding to gastrointestinal epithelial cells by sialic acid-containing oligosaccharides. Infect Immun. 1997; 65:750–757.
Article21. Kudo T, Lu H, Wu JY, Ohno T, Wu MJ, Genta RM, Graham DY, Yamaoka Y. Pattern of transcription factor activation in Helicobacter pylori-infected Mongolian gerbils. Gastroenterology. 2007; 132:1024–1038.
Article22. Yamamoto T, Kita M, Ohno T, Iwakura Y, Sekikawa K, Imanishi J. Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma in Helicobacter pylori infection. Microbiol Immunol. 2004; 48:647–654.
Article23. Thalmaier U, Lehn N, Pfeffer K, Stolte M, Vieth M, Schneider-Brachert W. Role of tumor necrosis factor alpha in Helicobacter pylori gastritis in tumor necrosis factor receptor 1-deficient mice. Infect Immun. 2002; 70:3149–3155.
Article24. Bodger K, Wyatt JI, Heatley RV. Gastric mucosal secretion of interleukin-10: relations to histopathology, Helicobacter pylori status, and tumour necrosis factor-alpha secretion. Gut. 1997; 40:739–744.
Article25. Bodger K, Bromelow K, Wyatt JI, Heatley RV. Interleukin 10 in Helicobacter pylori associated gastritis: immunohistochemical localisation and in vitro effects on cytokine secretion. J Clin Pathol. 2001; 54:285–292.
Article26. Berg DJ, Lynch NA, Lynch RG, Lauricella DM. Rapid development of severe hyperplastic gastritis with gastric epithelial dedifferentiation in Helicobacter felis-infected IL-10(-/-) mice. Am J Pathol. 1998; 152:1377–1386.27. Lindén SK, Wickström C, Lindell G, Gilshenan K, Carlstedt I. Four modes of adhesion are used during Helicobacter pylori binding to human mucins in the oral and gastric niches. Helicobacter. 2008; 13:81–93.
Article28. Nakayama J. Helicobacter pylori growth assay for glycans. In : Taniguchi N, Suzuki A, Ito Y, Narimatsu H, Kawasaki T, Hase S, editors. Experimental Glycoscience. Tokyo: Springer;2008. p. 227–229.29. Lee H, Wang P, Hoshino H, Ito Y, Kobayashi M, Nakayama J, Seeberger PH, Fukuda M. α1,4GlcNAc-capped mucin-type O-glycan inhibits cholesterol α-glucosyltransferase from Helicobacter pylori and suppresses H. pylori growth. Glycobiology. 2008; 18:549–558.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- In Vitro and In Vivo Investigation and Verification of the Substances with Anti-Helicobacter pylori Activity
- Anti-Helicobacter pylori activity of crude N-acetylneuraminic acid isolated from glycomacropeptide of whey
- Absence of vertical transmission of Helicobacter pylori in an experimental murine model
- Helicobacter pylori and Gastric Microbiota
- The Effects of Probiotics on the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Eradication