Cancer Res Treat.
2017 Oct;49(4):869-879. 10.4143/crt.2016.378.
Laminin Modulates the Stem Cell Population in LM05-E Murine Breast Cancer Cells through the Activation of the MAPK/ERK Pathway
- Affiliations
-
- 1Research Area, Instituto de OncologÃa “Angel H. Roffoâ€, Ciudad de Buenos Aires, Argentina.
- 2Members of the Research Career, Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones CientÃficas y Técnicas, Ciudad de Buenos Aires, Argentina. marina.simian@galuzzi.com
- 3Instituto de Nanosistemas, Universidad Nacional de San MartÃn, Campus Miguelete, San MartÃn, Argentina.
- KMID: 2394806
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2016.378
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We investigated the effects of laminin on the fraction of cells with self-renewing capacity in the estrogen-dependent, tamoxifen-sensitive LM05-E breast cancer cell line. We also determined whether laminin affected the response to tamoxifen.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The LM05-E breast cancer cell line was used as a model for all experiments. Aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) activity, clonogenic and mammosphere assays were performed to measure the effects of laminin on modulation of the stem cell subpopulation. Pluripotent gene expression was analyzed by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. The involvement of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/ERK pathway was determined using specific inhibitors. The effects of laminin on the response to tamoxifenwere determined and the involvement of α6 integrin was investigated.
RESULTS
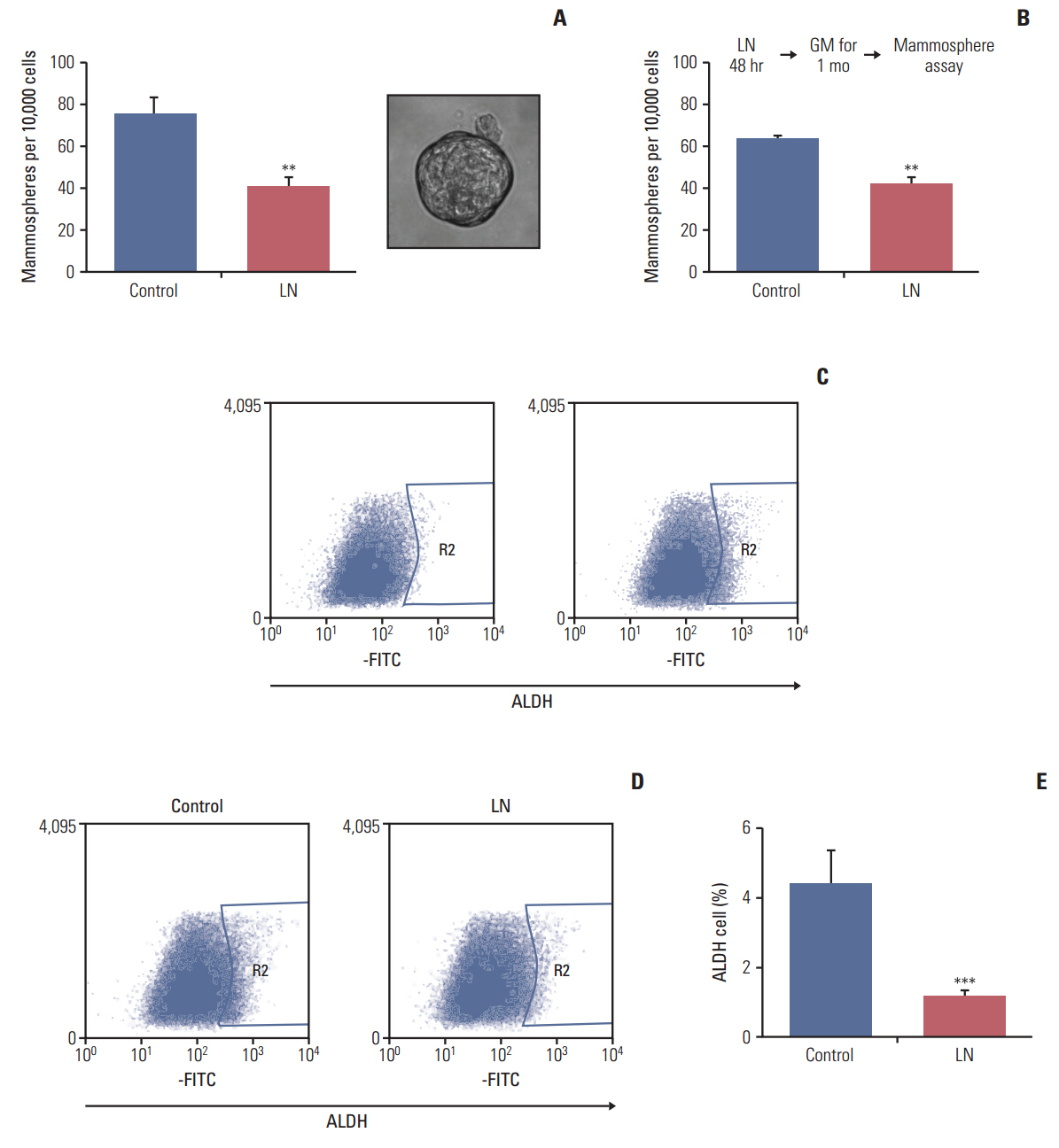
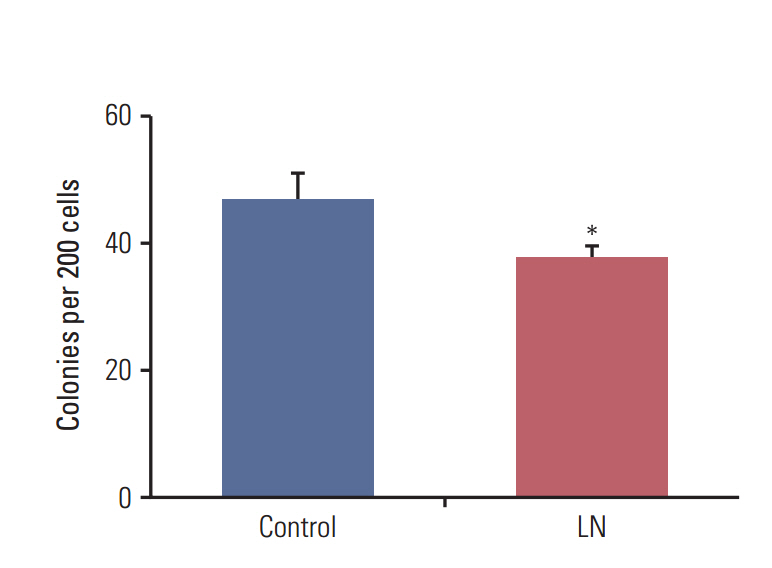
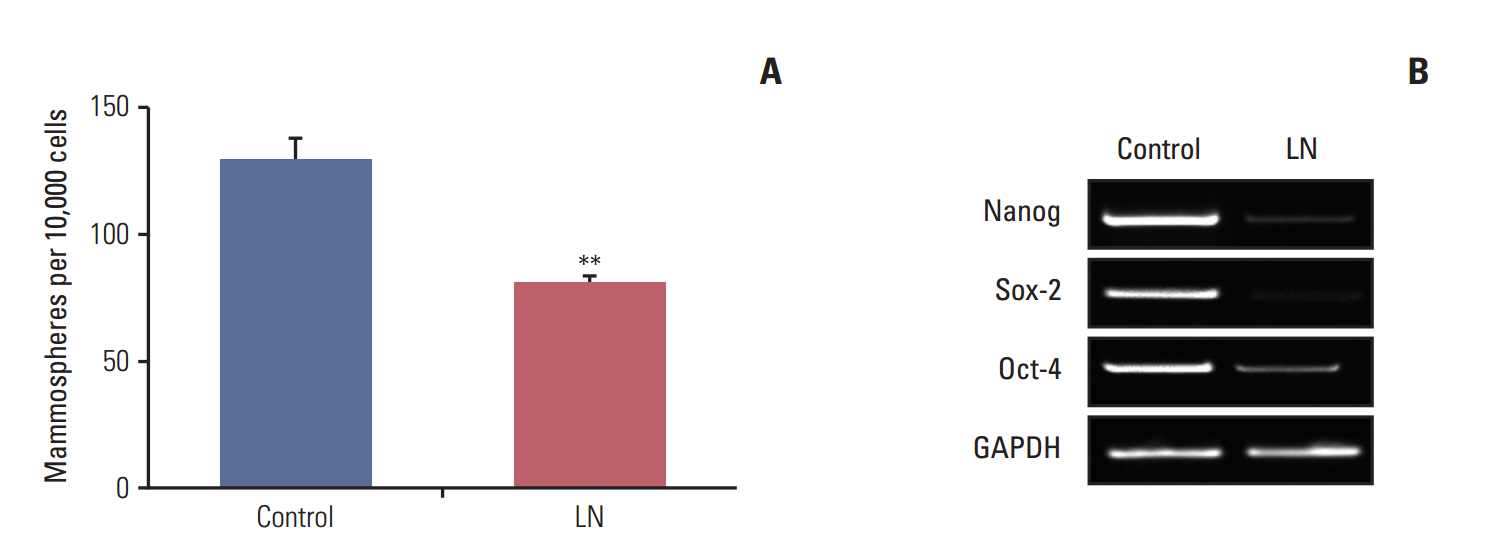
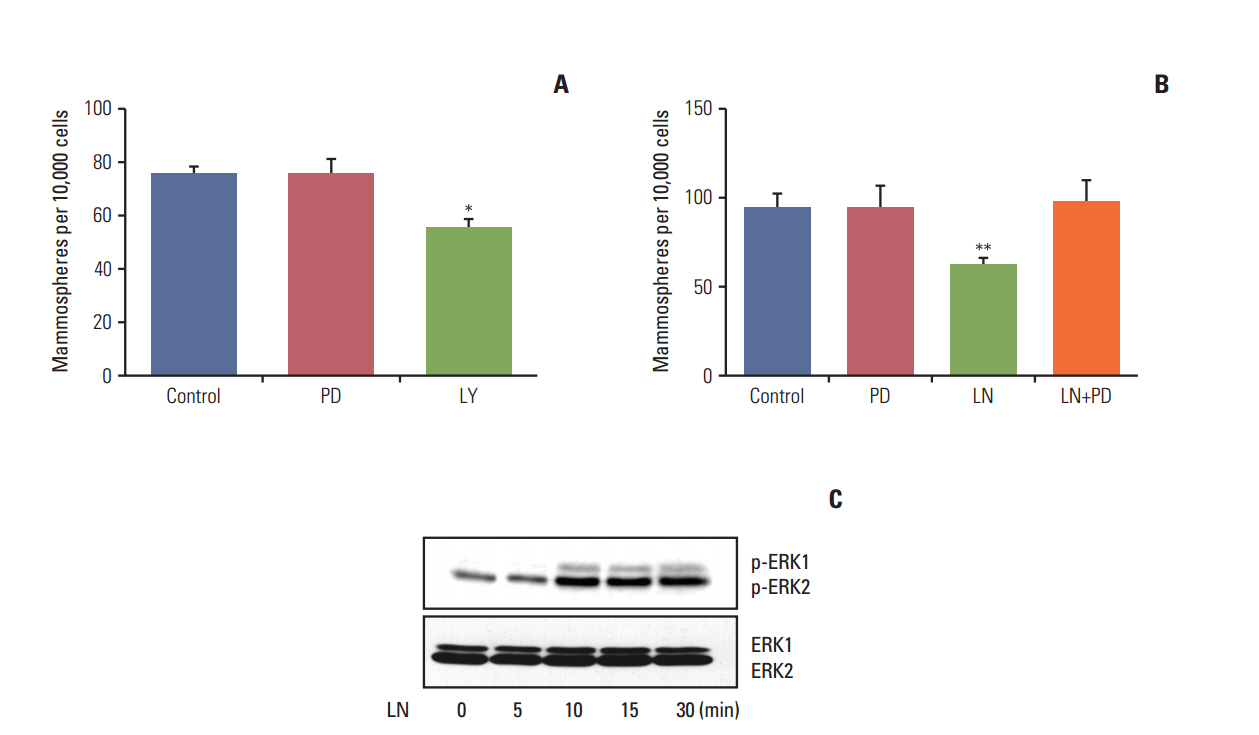
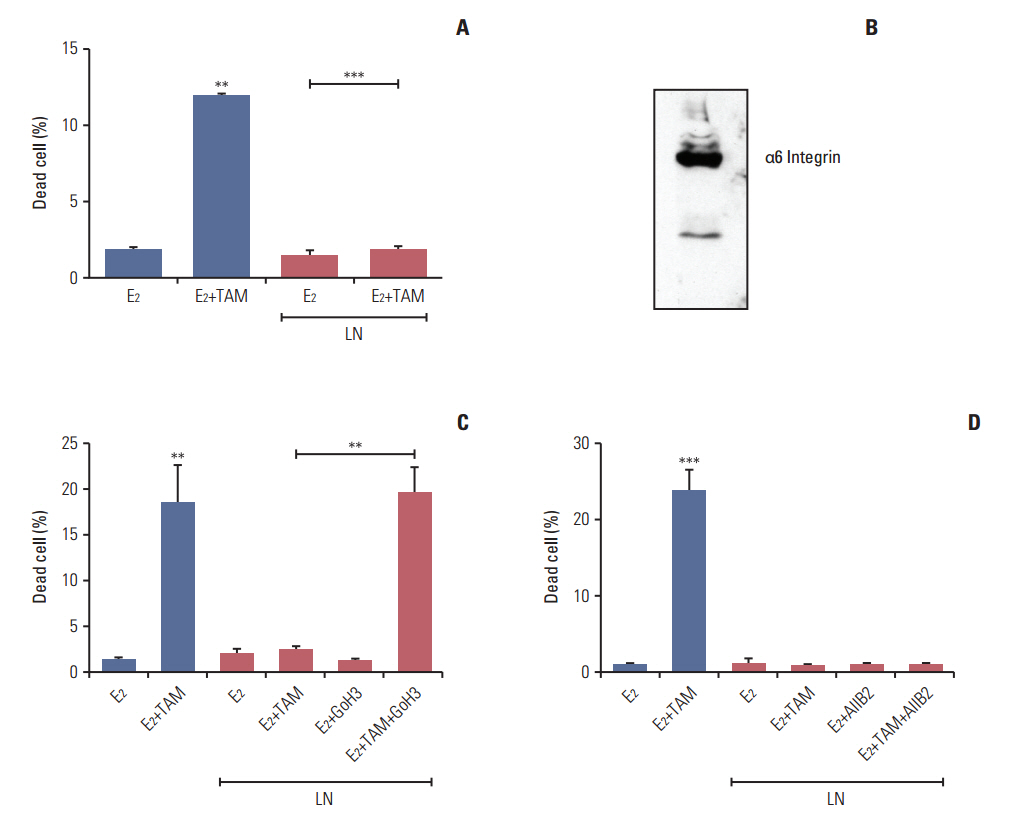
We found that pretreatment with laminin leads to a decrease in cells with the ability to form mammospheres that was accompanied by a decrease in ALDH activity. Moreover, exposure of mammospheres to laminin reduced the capacity to form secondary mammospheres and decreased the expression of Sox-2, Nanog, and Oct-4. We previously reported that 4-OH-tamoxifen leads to an increase in the expression of these genes in LM05-E cells. Treatment with signaling pathway inhibitors revealed that the MAPK/ERK pathway mediates the effects of laminin. Finally, laminin induced tamoxifen resistance in LM05-E cells through α6 integrin.
CONCLUSION
Our results suggest that the final number of cells with self-renewing capacity in estrogen-dependent breast tumors may result from the combined effects of endocrine treatment and microenvironmental cues.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Harvey JM, Clark GM, Osborne CK, Allred DC. Estrogen receptor status by immunohistochemistry is superior to the ligand-binding assay for predicting response to adjuvant endocrine therapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1999; 17:1474–81.
Article2. Graham JD, Yeates C, Balleine RL, Harvey SS, Milliken JS, Bilous AM, et al. Characterization of progesterone receptor A and B expression in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1995; 55:5063–8.3. Sengupta S, Jordan VC. Selective estrogen modulators as an anticancer tool: mechanisms of efficiency and resistance. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008; 630:206–19.4. Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL. Biological determinants of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009; 9:631–43.
Article5. Bissell MJ, Radisky D. Putting tumours in context. Nat Rev Cancer. 2001; 1:46–54.
Article6. Tlsty T. Cancer: whispering sweet somethings. Nature. 2008; 453:604–5.7. Pontiggia O, Sampayo R, Raffo D, Motter A, Xu R, Bissell MJ, et al. The tumor microenvironment modulates tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer: a role for soluble stromal factors and fibronectin through beta1 integrin. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012; 133:459–71.8. Bergamaschi A, Tagliabue E, Sorlie T, Naume B, Triulzi T, Orlandi R, et al. Extracellular matrix signature identifies breast cancer subgroups with different clinical outcome. J Pathol. 2008; 214:357–67.
Article9. Finak G, Bertos N, Pepin F, Sadekova S, Souleimanova M, Zhao H, et al. Stromal gene expression predicts clinical outcome in breast cancer. Nat Med. 2008; 14:518–27.
Article10. Helleman J, Jansen MP, Ruigrok-Ritstier K, van Staveren IL, Look MP, Meijer-van Gelder ME, et al. Association of an extracellular matrix gene cluster with breast cancer prognosis and endocrine therapy response. Clin Cancer Res. 2008; 14:5555–64.
Article11. Jansen MP, Foekens JA, van Staveren IL, Dirkzwager-Kiel MM, Ritstier K, Look MP, et al. Molecular classification of tamoxifen-resistant breast carcinomas by gene expression profiling. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:732–40.
Article12. Cariati M, Naderi A, Brown JP, Smalley MJ, Pinder SE, Caldas C, et al. Alpha-6 integrin is necessary for the tumourigenicity of a stem cell-like subpopulation within the MCF7 breast cancer cell line. Int J Cancer. 2008; 122:298–304.
Article13. Phillips TM, McBride WH, Pajonk F. The response of CD24 (-/low)/CD44+ breast cancer-initiating cells to radiation. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006; 98:1777–85.14. Raffo D, Berardi DE, Pontiggia O, Todaro L, de Kier Joffe EB, Simian M. Tamoxifen selects for breast cancer cells with mammosphere forming capacity and increased growth rate. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013; 142:537–48.
Article15. Taylor-Weiner H, Schwarzbauer JE, Engler AJ. Defined extracellular matrix components are necessary for definitive endoderm induction. Stem Cells. 2013; 31:2084–94.
Article16. Liu J, He X, Corbett SA, Lowry SF, Graham AM, Fassler R, et al. Integrins are required for the differentiation of visceral endoderm. J Cell Sci. 2009; 122(Pt 2):233–42.
Article17. Saha S, Lo PK, Duan X, Chen H, Wang Q. Breast tumour initiating cell fate is regulated by microenvironmental cues from an extracellular matrix. Integr Biol (Camb). 2012; 4:897–904.
Article18. Simian M, Manzur T, Rodriguez V, de Kier Joffe EB, Klein S. A spontaneous estrogen dependent, tamoxifen sensitive mouse mammary tumor: a new model system to study hormone-responsiveness in immune competent mice. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009; 113:1–8.
Article19. Pontiggia O, Rodriguez V, Fabris V, Raffo D, Bumaschny V, Fiszman G, et al. Establishment of an in vitro estrogen-dependent mouse mammary tumor model: a new tool to understand estrogen responsiveness and development of tamoxifen resistance in the context of stromal-epithelial interactions. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009; 116:247–55.20. Piva M, Domenici G, Iriondo O, Rabano M, Simoes BM, Comaills V, et al. Sox2 promotes tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells. EMBO Mol Med. 2014; 6:66–79.
Article21. Simoes BM, Piva M, Iriondo O, Comaills V, Lopez-Ruiz JA, Zabalza I, et al. Effects of estrogen on the proportion of stem cells in the breast. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011; 129:23–35.
Article22. Yang XH, Flores LM, Li Q, Zhou P, Xu F, Krop IE, et al. Disruption of laminin-integrin-CD151-focal adhesion kinase axis sensitizes breast cancer cells to ErbB2 antagonists. Cancer Res. 2010; 70:2256–63.
Article23. Zhang L, Luo YB, Bou G, Kong QR, Huan YJ, Zhu J, et al. Overexpression Nanog activates pluripotent genes in porcine fetal fibroblasts and nuclear transfer embryos. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2011; 294:1809–17.
Article24. Ginestier C, Hur MH, Charafe-Jauffret E, Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown M, et al. ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell Stem Cell. 2007; 1:555–67.
Article25. Dontu G, Abdallah WM, Foley JM, Jackson KW, Clarke MF, Kawamura MJ, et al. In vitro propagation and transcriptional profiling of human mammary stem/progenitor cells. Genes Dev. 2003; 17:1253–70.
Article26. Prowse AB, Chong F, Gray PP, Munro TP. Stem cell integrins: implications for ex-vivo culture and cellular therapies. Stem Cell Res. 2011; 6:1–12.
Article27. Domogatskaya A, Rodin S, Boutaud A, Tryggvason K. Laminin-511 but not -332, -111, or -411 enables mouse embryonic stem cell self-renewal in vitro. Stem Cells. 2008; 26:2800–9.
Article28. Hunt GC, Singh P, Schwarzbauer JE. Endogenous production of fibronectin is required for self-renewal of cultured mouse embryonic stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 2012; 318:1820–31.
Article29. Benton G, Crooke E, George J. Laminin-1 induces E-cadherin expression in 3-dimensional cultured breast cancer cells by inhibiting DNA methyltransferase 1 and reversing promoter methylation status. FASEB J. 2009; 23:3884–95.
Article30. Pujuguet P, Radisky D, Levy D, Lacza C, Bissell MJ. Trichostatin A inhibits beta-casein expression in mammary epithelial cells. J Cell Biochem. 2001; 83:660–70.31. Novaro V, Roskelley CD, Bissell MJ. Collagen-IV and laminin-1 regulate estrogen receptor alpha expression and function in mouse mammary epithelial cells. J Cell Sci. 2003; 116(Pt 14):2975–86.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hederacoside C Modulates EGF-Induced MUC5AC Mucin Gene Expression by Regulating the MAPK Signaling Pathway in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
- Induction of Integrin Signaling by Steroid Sulfatase in Human Cervical Cancer Cells
- Molecular assembly of mitogen-activated protein kinase module in ras-transformed NIH3T3 cell line
- IGF-1 Induces Osteogenic Differentiation of Rat Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Promoting SOX4 via the MAPK/ERK Pathway
- Cancer Stem Cells