Diabetes Metab J.
2017 Jun;41(3):170-178. 10.4093/dmj.2017.41.3.170.
Comparison of Antidiabetic Regimens in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Uncontrolled by Combination Therapy of Sulfonylurea and Metformin: Results of the MOHAS Disease Registry in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. janghak@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2392491
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.3.170
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The aim of this study was to investigate the glucose-lowering efficacy of antidiabetic treatments in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) uncontrolled by sulfonylurea plus metformin.
METHODS
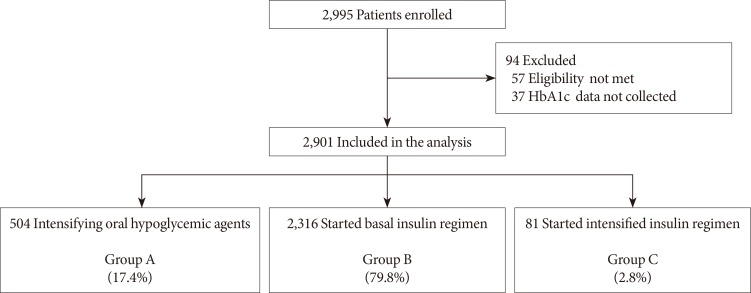
This open-label, multicenter, prospective, observational study was conducted in 144 centers in Korea, from June 2008 to July 2010, and included patients with T2DM who had received sulfonylurea and metformin for at least 3 months and had levels of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) >7.0% in the last month. Data of clinical and biochemical characteristics were collected at baseline and 6 months after treatment. The treatment option was decided at the physician's discretion. Subjects were classified into the following three groups: intensifying oral hypoglycemic agents (group A), adding basal insulin (group B), or starting intensified insulin therapy (group C).
RESULTS
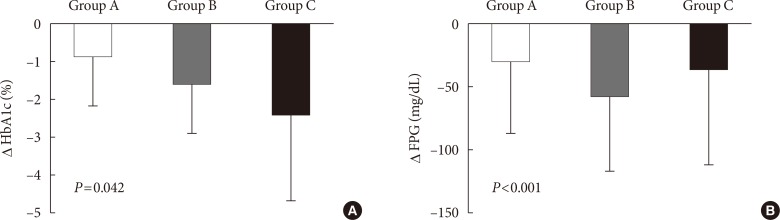
Of 2,995 patients enrolled, 2,901 patients were evaluated, and 504 (17.4%), 2,316 (79.8%), and 81 patients (2.8%) were classified into groups A, B, and C, respectively. Subjects in group C showed relatively higher baseline levels of HbA1c and longer duration of diabetes. The mean decrease in HbA1c level was higher in the insulin treated groups (−0.9%±1.3%, −1.6%±1.3%, and −2.4%±2.3% in groups A, B, and C, respectively, P=0.042). The proportion of patients who achieved target HbA1c <7.0% was comparable among the groups; however, intensified insulin therapy seemed to be the most effective in achieving the target HbA1c of 6.5%.
CONCLUSION
These findings suggest that insulin-based therapy will be an important option in the improved management of Korean patients with T2DM whose glycemic control is not sufficient with sulfonylurea and metformin.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas. 6th ed. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation;2013.2. Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea 2012. Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association/Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2012.3. Kim DJ. The epidemiology of diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:303–308. PMID: 21977448.
Article4. Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea 2013. Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association;2013.5. Yeung RO, Zhang Y, Luk A, Yang W, Sobrepena L, Yoon KH, Aravind SR, Sheu W, Nguyen TK, Ozaki R, Deerochanawong C, Tsang CC, Chan WB, Hong EG, Do TQ, Cheung Y, Brown N, Goh SY, Ma RC, Mukhopadhyay M, Ojha AK, Chakraborty S, Kong AP, Lau W, Jia W, Li W, Guo X, Bian R, Weng J, Ji L, Reyes-dela Rosa M, Toledo RM, Himathongkam T, Yoo SJ, Chow CC, Ho LL, Chuang LM, Tutino G, Tong PC, So WY, Wolthers T, Ko G, Lyubomirsky G, Chan JC. Metabolic profiles and treatment gaps in young-onset type 2 diabetes in Asia (the JADE programme): a cross-sectional study of a prospective cohort. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014; 2:935–943. PMID: 25081582.
Article6. Weir GC, Bonner-Weir S. Five stages of evolving beta-cell dysfunction during progression to diabetes. Diabetes. 2004; 53(Suppl 3):S16–S21. PMID: 15561905.
Article7. American Diabetes Association. 7 Approaches to glycemic treatment. Diabetes Care. 2016; 39(Suppl 1):S52–S59. PMID: 26696682.8. Korean Diabetes Association. Treatment guideline for diabetes. 5th ed. Seoul: Gold' Planning and Development;2015.9. Garber AJ, Abrahamson MJ, Barzilay JI, Blonde L, Bloomgarden ZT, Bush MA, Dagogo-Jack S, Davidson MB, Einhorn D, Garber JR, Garvey WT, Grunberger G, Handelsman Y, Hirsch IB, Jellinger PS, McGill JB, Mechanick JI, Rosenblit PD, Umpierrez G, Davidson MH. AACE/ACE comprehensive diabetes management algorithm 2015. Endocr Pract. 2015; 21:438–447. PMID: 25877012.
Article10. Kadowaki T, Ohtani T, Naito Y, Odawara M. Potential formula for the calculation of starting and incremental insulin glargine doses: ALOHA subanalysis. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e41358. PMID: 22870214.
Article11. Kostev K, Dippel FW. Predictors for the initiation of a basal supported oral therapy (BOT) in type 2 diabetic patients under real-life conditions in Germany. Prim Care Diabetes. 2012; 6:329–335. PMID: 22749713.
Article12. Ratanawongsa N, Crosson JC, Schillinger D, Karter AJ, Saha CK, Marrero DG. Getting under the skin of clinical inertia in insulin initiation: the Translating Research Into Action for Diabetes (TRIAD) Insulin Starts Project. Diabetes Educ. 2012; 38:94–100. PMID: 22222513.13. Weng J, Li Y, Xu W, Shi L, Zhang Q, Zhu D, Hu Y, Zhou Z, Yan X, Tian H, Ran X, Luo Z, Xian J, Yan L, Li F, Zeng L, Chen Y, Yang L, Yan S, Liu J, Li M, Fu Z, Cheng H. Effect of intensive insulin therapy on beta-cell function and glycaemic control in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a multicentre randomised parallel-group trial. Lancet. 2008; 371:1753–1760. PMID: 18502299.14. TODAY Study Group. Zeitler P, Hirst K, Pyle L, Linder B, Copeland K, Arslanian S, Cuttler L, Nathan DM, Tollefsen S, Wilfley D, Kaufman F. A clinical trial to maintain glycemic control in youth with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:2247–2256. PMID: 22540912.
Article15. Riedel AA, Heien H, Wogen J, Plauschinat CA. Loss of glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who were receiving initial metformin, sulfonylurea, or thiazolidinedione monotherapy. Pharmacotherapy. 2007; 27:1102–1110. PMID: 17655510.
Article16. Riedel AA, Heien H, Wogen J, Plauschinat CA. Secondary failure of glycemic control for patients adding thiazolidinedione or sulfonylurea therapy to a metformin regimen. Am J Manag Care. 2007; 13:457–463. PMID: 17685826.17. Fonseca V, Gill J, Zhou R, Leahy J. An analysis of early insulin glargine added to metformin with or without sulfonylurea: impact on glycaemic control and hypoglycaemia. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011; 13:814–822. PMID: 21481127.
Article18. Stratton IM, Adler AI, Neil HA, Matthews DR, Manley SE, Cull CA, Hadden D, Turner RC, Holman RR. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): prospective observational study. BMJ. 2000; 321:405–412. PMID: 10938048.
Article19. Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10-Year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:1577–1589. PMID: 18784090.
Article20. Li C, Ford ES, Zhao G, Tsai J, Balluz LS, Giles WH. Trends of insulin use among US adults with type 2 diabetes: the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, 1995-2007. J Diabetes Complications. 2012; 26:17–22. PMID: 22226485.
Article21. Khunti K, Damci T, Meneghini L, Pan CY, Yale JF, Group SS. Study of Once Daily Levemir (SOLVE): insights into the timing of insulin initiation in people with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes in routine clinical practice. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012; 14:654–661. PMID: 22443213.
Article22. Cryer PE. Hypoglycemia is the limiting factor in the management of diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 1999; 15:42–46. PMID: 10398545.23. Baser O, Tangirala K, Wei W, Xie L. Real-world outcomes of initiating insulin glargine-based treatment versus premixed analog insulins among US patients with type 2 diabetes failing oral antidiabetic drugs. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2013; 5:497–505. PMID: 24124384.
Article24. Jia W, Xiao X, Ji Q, Ahn KJ, Chuang LM, Bao Y, Pang C, Chen L, Gao F, Tu Y, Li P, Yang J. Comparison of thrice-daily premixed insulin (insulin lispro premix) with basal-bolus (insulin glargine once-daily plus thrice-daily prandial insulin lispro) therapy in east Asian patients with type 2 diabetes insufficiently controlled with twice-daily premixed insulin: an open-label, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015; 3:254–262. PMID: 25754414.
Article25. Hwang YC, Kang JG, Ahn KJ, Cha BS, Ihm SH, Lee S, Kim M, Lee BW. The glycemic efficacies of insulin analogue regimens according to baseline glycemic status in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes: sub-analysis from the A(1)chieve((R)) study. Int J Clin Pract. 2014; 68:1338–1344. PMID: 25284679.26. Kim SS, Kim IJ, Kim YK, Yoon KH, Son HY, Park SW, Sung YA, Baek HS. Insulin initiation in insulin-naive Korean type 2 diabetic patients inadequately controlled on oral antidiabetic drugs in real-world practice: the modality of insulin treatment evaluation study. Diabetes Metab J. 2015; 39:481–488. PMID: 26616594.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Combination Therapy of Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Cancer Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes on Antidiabetic Monotherapy: A Population Based Cohort Study Using National Insurance Health Service Database
- Efficacy of Sitagliptin When Added to Ongoing Therapy in Korean Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- The Effect of Metformin in Obese Pediatric Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Comparison of the Effects of Various Antidiabetic Medication on Bone Mineral Density in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus