Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2017 Sep;20(3):198-203. 10.5223/pghn.2017.20.3.198.
Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disorder Presenting as Intractable Vomiting and Ascites in a Young Girl
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. izzihn@gmail.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Colorectal Surgery, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2390552
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2017.20.3.198
Abstract
- Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorder (EGID) is a rare disease in children that affects the bowel wall, with eosinophilic infiltration in the absence of any other causes for eosinophilia. The etiology remains unknown, but allergies and immunological imbalance are suspected triggers. We encountered a case of serosal EGID presenting as intractable vomiting and ascites in a 9-year-old girl, after influenza virus infection. Peripheral eosinophilia was not present. The diagnosis was confirmed by biopsy of the bowel wall through laparotomy and endoscopy, and controlled by 2 courses of steroid therapy due to recurring symptoms. Influenza virus infection was assumed to play a role in the onset of EGID through a Th2 response that stimulated eosinophilic infiltration in the GI tract. We therefore report this case along with a literature review.
MeSH Terms
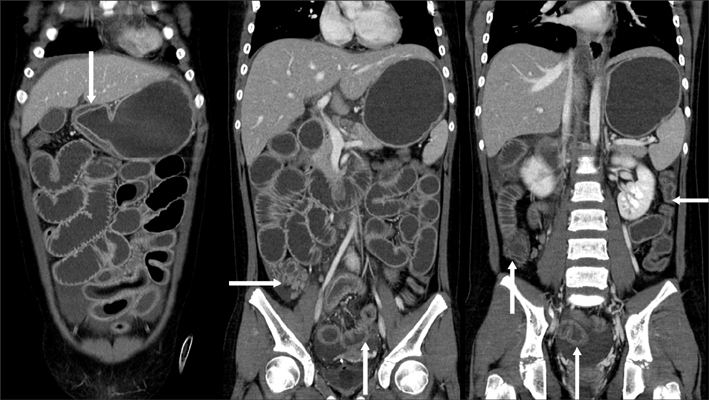
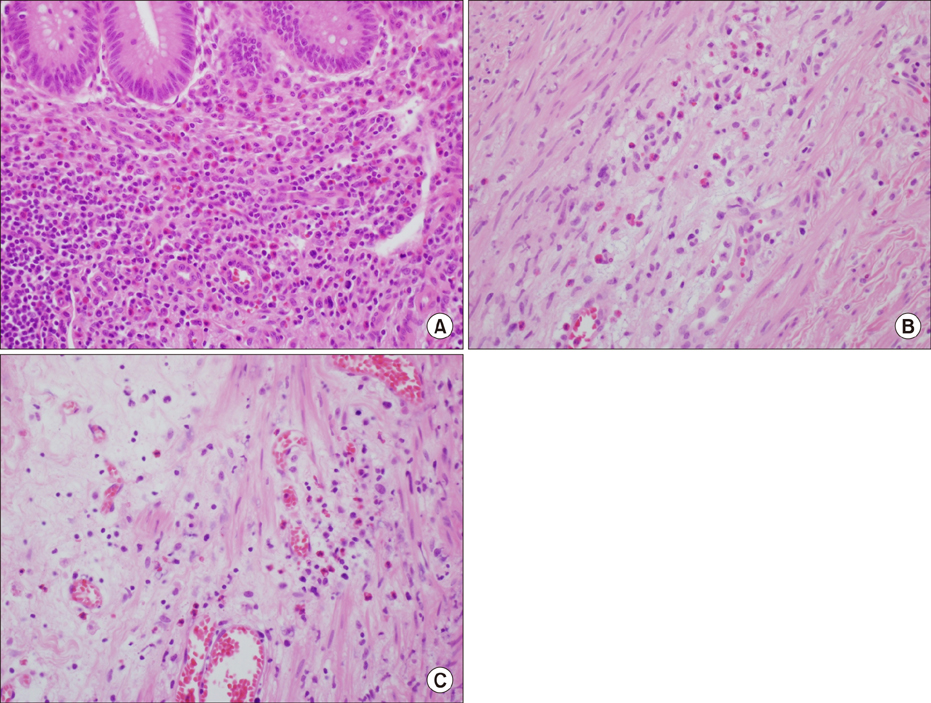
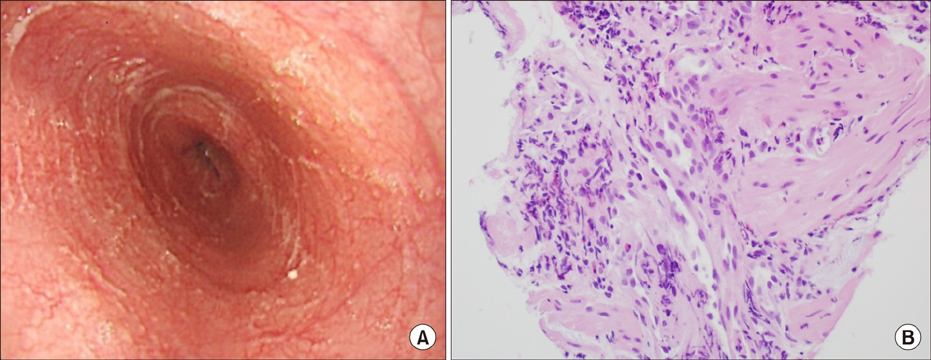
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Fecal Calprotectin as a Useful Non-Invasive Screening Marker for Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disorder in Korean Children
In Hyuk Yoo, Jin Min Cho, Jung Yeon Joo, Hye Ran Yang
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(17):e120. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e120.Eosinophilic Enteritis Presenting as Massive Ascites after Influenza A Virus Infection in a Young Female
Myung Jin Kim, Myung Jin Oh
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2019;74(3):163-167. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2019.74.3.163.
Reference
-
1. Daneshjoo R, J Talley N. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2002; 4:366–372.
Article2. Klein NC, Hargrove RL, Sleisenger MH, Jeffries GH. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Medicine (Baltimore). 1970; 49:299–319.
Article3. Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGID). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 113:11–28.
Article4. Takeyama J, Abukawa D, Miura K. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis with cytomegalovirus infection in an immunocompetent child. World J Gastroenterol. 2007; 13:4653–4654.
Article5. Koga M, Fujiwara M, Hotta N, Matsubara T, Suzuki E, Furukawa S. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection in a young boy. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2001; 33:610–612.
Article6. Minodier L, Charrel RN, Ceccaldi PE, van der, Blanchon T, Hanslik T, et al. Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with influenza, clinical significance, and pathophysiology of human influenza viruses in faecal samples: what do we know? Virol J. 2015; 12:215.
Article7. Vivar KL, Uyeki TM. Influenza virus infection mimicking an acute abdomen in a female adolescent. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2014; 8:140–141.
Article8. Wohlleben G, Müller J, Tatsch U, Hambrecht C, Herz U, Renz H, et al. Influenza A virus infection inhibits the efficient recruitment of Th2 cells into the airways and the development of airway eosinophilia. J Immunol. 2003; 170:4601–4611.
Article9. Kristjansson S, Bjarnarson SP, Wennergren G, Palsdottir AH, Arnadottir T, Haraldsson A, et al. Respiratory syncytial virus and other respiratory viruses during the first 3 months of life promote a local Th2-like response. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005; 116:805–811.
Article10. Yu X, Zhang X, Zhao B, Wang J, Zhu Z, Teng Z, et al. Intensive cytokine induction in pandemic H1N1 influenza virus infection accompanied by robust production of IL-10 and IL-6. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e28680 .
Article11. Terai M, Honda T, Yamamoto S, Yoshida M, Tsuchiya N, Moriyama Y, et al. Early induction of interleukin-5 and peripheral eosinophilia in acute pneumonia in Japanese children infected by pandemic 2009 influenza A in the Tokyo area. Microbiol Immunol. 2011; 55:341–346.
Article12. Choi JS, Choi SJ, Lee KJ, Kim A, Yoo JK, Yang HR, et al. Clinical manifestations and treatment outcomes of eosinophilic gastroenteritis in children. Pediatr Gastro-Enterol Hepatol Nut. 2015; 18:253–260.
Article13. Yi ES, Kim MJ, Ha SY, Lee YM, Choi KE, Choe YH. A case of non-IgE-mediated eosinophilic gastroenteritis presenting as ascites. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011; 14:181–186.
Article14. Yun KT, Jeon YC, Son YW, Sohn JH, Yoon BC, Choi HS, et al. A case of eosinophilic enteritis with ascites. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2000; 35:507–511.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis Presenting with Peritoneal Eosinpophilic Infiltration
- A Case of Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis
- Eosinophilic Enteritis Presenting as Massive Ascites after Influenza A Virus Infection in a Young Female
- Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis Involving Entire Gastrointestinal Tract with Eosinophilic Ascites
- A Case of Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis in a Child