Nutr Res Pract.
2017 Oct;11(5):381-387. 10.4162/nrp.2017.11.5.381.
Protection of the brain through supplementation with larch arabinogalactan in a rat model of vascular dementia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biochemistry, School of Medicine, Catholic University of Daegu, 33 Duryugongwon-ro 17-gil, Nam-gu, Daegu 42472, Korea. leejw@cu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2390130
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2017.11.5.381
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES
Vascular dementia (VaD) caused by reduced blood supply to the brain manifests as white matter lesions accompanying demyelination and glial activation. We previously showed that arabinoxylan consisting of arabinose and xylose, and arabinose itself attenuated white matter injury in a rat model of VaD. Here, we investigated whether larch arabinogalactan (LAG) consisting of arabinose and galactose could also reduce white matter injury.
MATERIALS/METHODS
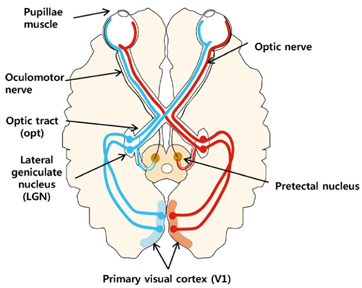
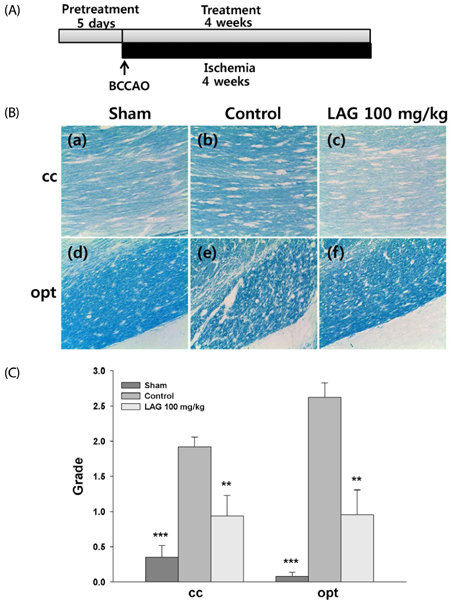
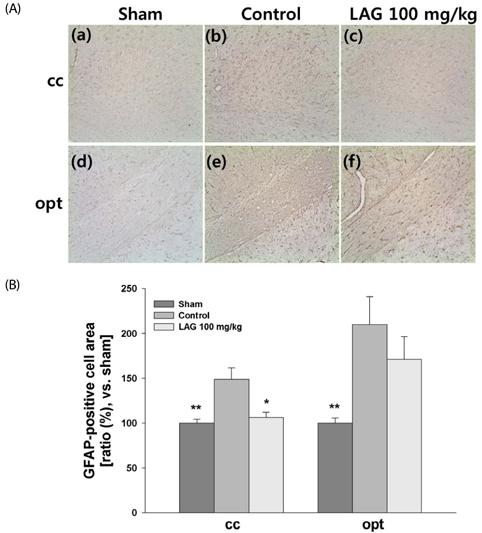
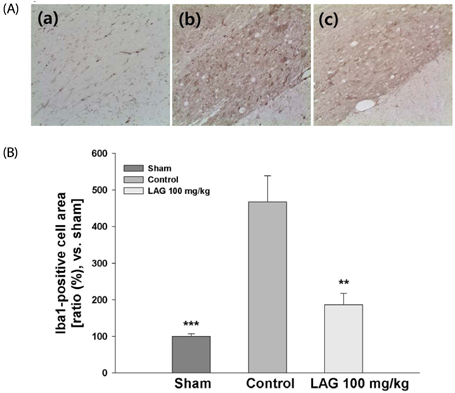
We used a rat model of bilateral common carotid artery occlusion (BCCAO), in which the bilateral common carotid arteries were exposed and ligated permanently with silk sutures. The rats were fed a modified AIN-93G diet supplemented with LAG (100 mg/kg/day) for 5 days before and 4 weeks after being subjected to BCCAO. Four weeks after BCCAO, the pupillary light reflex (PLR) was measured to assess functional consequences of injury in the corpus callosum (cc). Additionally, Luxol fast blue staining and immunohistochemical staining were conducted to assess white matter injury, and astrocytic and microglial activation, respectively.
RESULTS
We showed that white matter injury in the the cc and optic tract (opt) was attenuated in rats fed diet supplemented with LAG. Functional consequences of injury reduction in the opt manifested as improved PLR. Overall, these findings indicate that LAG intake protects against white matter injury through inhibition of glial activation.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study support our hypothesis that cell wall polysaccharides consisting of arabinose are effective at protecting white matter injury, regardless of their origin. Moreover, LAG has the potential for development as a functional food to prevent vascular dementia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Supplementation with psyllium seed husk reduces myocardial damage in a rat model of ischemia/reperfusion
Sun Ha Lim, Jongwon Lee
Nutr Res Pract. 2019;13(3):205-213. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2019.13.3.205.
Reference
-
1. Venkat P, Chopp M, Chen J. Models and mechanisms of vascular dementia. Exp Neurol. 2015; 272:97–108.
Article2. O'Brien JT, Thomas A. Vascular dementia. Lancet. 2015; 386:1698–1706.3. Iadecola C. The pathobiology of vascular dementia. Neuron. 2013; 80:844–866.
Article4. Jiwa NS, Garrard P, Hainsworth AH. Experimental models of vascular dementia and vascular cognitive impairment: a systematic review. J Neurochem. 2010; 115:814–828.
Article5. Yamauchi H, Fukuyama H, Harada K, Nabatame H, Ogawa M, Ouchi Y, Kimura J, Konishi J. Callosal atrophy parallels decreased cortical oxygen metabolism and neuropsychological impairment in Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1993; 50:1070–1074.
Article6. Lin CJ, Chang FC, Chou KH, Tu PC, Lee YH, Lin CP, Wang PN, Lee IH. Intervention versus aggressive medical therapy for cognition in severe asymptomatic carotid stenosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016; 37:1889–1897.
Article7. Terelak-Borys B, Skonieczna K, Grabska-Liberek I. Ocular ischemic syndrome - a systematic review. Med Sci Monit. 2012; 18:RA138–RA144.
Article8. Stevens WD, Fortin T, Pappas BA. Retinal and optic nerve degeneration after chronic carotid ligation: time course and role of light exposure. Stroke. 2002; 33:1107–1112.
Article9. Román GC, Erkinjuntti T, Wallin A, Pantoni L, Chui HC. Subcortical ischaemic vascular dementia. Lancet Neurol. 2002; 1:426–436.
Article10. Han HS, Jang JH, Jang JH, Choi JS, Kim YJ, Lee C, Lim SH, Lee HK, Lee J. Water extract of Triticum aestivum L. and its components demonstrate protective effect in a model of vascular dementia. J Med Food. 2010; 13:572–578.
Article11. Lim SH, Lee J. Hot water extract of wheat bran attenuates white matter injury in a rat model of vascular dementia. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2014; 19:145–155.
Article12. Fincher GB, Sawyer WH, Stone BA. Chemical and physical properties of an arabinogalactan-peptide from wheat endosperm. Biochem J. 1974; 139:535–545.
Article13. Van den Bulck K, Swennen K, Loosveld AM, Courtin C, Brijs K, Proost P, Van Damme J, Van Campenhout S, Mort A, Delcour J. Isolation of cereal arabinogalactan-peptides and structural comparison of their carbohydrate and peptide moieties. J Cereal Sci. 2005; 41:59–67.
Article14. Lim SH, Kim MY, Lee J. Apple pectin, a dietary fiber, ameliorates myocardial injury by inhibiting apoptosis in a rat model of ischemia/reperfusion. Nutr Res Pract. 2014; 8:391–397.
Article15. Nishimura N, Tanabe H, Sasaki Y, Makita Y, Ohata M, Yokoyama S, Asano M, Yamamoto T, Kiriyama S. Pectin and high-amylose maize starch increase caecal hydrogen production and relieve hepatic ischaemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Br J Nutr. 2012; 107:485–492.
Article16. Wakita H, Tomimoto H, Akiguchi I, Kimura J. Glial activation and white matter changes in the rat brain induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion: an immunohistochemical study. Acta Neuropathol. 1994; 87:484–492.
Article17. Farkas E, Donka G, de Vos RA, Mihály A, Bari F, Luiten PG. Experimental cerebral hypoperfusion induces white matter injury and microglial activation in the rat brain. Acta Neuropathol. 2004; 108:57–64.
Article18. Tykhomyrov AA, Pavlova AS, Nedzvetsky VS. Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP): on the 45th anniversary of its discovery. Neurophysiology. 2016; 48:54–71.
Article19. Imai Y, Kohsaka S. Intracellular signaling in M-CSF-induced microglia activation: role of Iba1. Glia. 2002; 40:164–174.
Article20. Farkas E, Luiten PG, Bari F. Permanent, bilateral common carotid artery occlusion in the rat: a model for chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-related neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Rev. 2007; 54:162–180.
Article21. López-Valdés HE, Martínez-Coria H. The role of neuroinflammation in age-related dementias. Rev Invest Clin. 2016; 68:40–48.22. Rosenberg GA, Bjerke M, Wallin A. Multimodal markers of inflammation in the subcortical ischemic vascular disease type of vascular cognitive impairment. Stroke. 2014; 45:1531–1538.
Article23. Liu Z, Chopp M. Astrocytes, therapeutic targets for neuroprotection and neurorestoration in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol. 2016; 144:103–120.
Article24. Saggu R, Schumacher T, Gerich F, Rakers C, Tai K, Delekate A, Petzold GC. Astroglial NF-kB contributes to white matter damage and cognitive impairment in a mouse model of vascular dementia. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2016; 4:76.
Article25. McDougal DH, Gamlin PD. Autonomic control of the eye. Compr Physiol. 2015; 5:439–473.
Article26. Lavinsky D, Arterni NS, Achaval M, Netto CA. Chronic bilateral common carotid artery occlusion: a model for ocular ischemic syndrome in the rat. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2006; 244:199–204.
Article27. Gunes A, Demirci S, Umul A. Vision loss and RNFL thinning after internal carotid arter occlusion and middle cerebral artery infarction. Acta Inform Med. 2014; 22:413–414.
Article28. Klijn CJ, Kappelle LJ. Haemodynamic stroke: clinical features, prognosis, and management. Lancet Neurol. 2010; 9:1008–1017.
Article29. Pretegiani E, Rosini F, Dotti MT, Bianchi S, Federico A, Rufa A. Visual system involvement in CADASIL. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013; 22:1377–1384.
Article30. Parisi V, Pierelli F, Coppola G, Restuccia R, Ferrazzoli D, Scassa C, Bianco F, Parisi L, Fattapposta F. Reduction of optic nerve fiber layer thickness in CADASIL. Eur J Neurol. 2007; 14:627–631.
Article31. Rufa A, Malandrini A, Dotti MT, Berti G, Salvadori C, Federico A. Typical pathological changes of CADASIL in the optic nerve. Neurol Sci. 2005; 26:271–274.
Article32. Fabri M, Pierpaoli C, Barbaresi P, Polonara G. Functional topography of the corpus callosum investigated by DTI and fMRI. World J Radiol. 2014; 6:895–906.
Article33. Paul LK, Erickson RL, Hartman JA, Brown WS. Learning and memory in individuals with agenesis of the corpus callosum. Neuropsychologia. 2016; 86:183–192.
Article34. Tomimoto H, Lin JX, Matsuo A, Ihara M, Ohtani R, Shibata M, Miki Y, Shibasaki H. Different mechanisms of corpus callosum atrophy in Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia. J Neurol. 2004; 251:398–406.
Article35. Jung WB, Mun CW, Kim YH, Park JM, Lee BD, Lee YM, Moon E, Jeong HJ, Chung YI. Cortical atrophy, reduced integrity of white matter and cognitive impairment in subcortical vascular dementia of Binswanger type. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2014; 68:821–832.
Article36. Lin L, Xue Y, Duan Q, Sun B, Lin H, Chen X, Luo L, Wei X, Zhang Z. Microstructural white matter abnormalities and cognitive dysfunction in subcortical ischemic vascular disease: an atlas-based diffusion tensor analysis study. J Mol Neurosci. 2015; 56:363–370.
Article37. Best T, Howe P, Bryan J, Buckley J, Scholey A. Acute effects of a dietary non-starch polysaccharide supplement on cognitive performance in healthy middle-aged adults. Nutr Neurosci. 2015; 18:76–86.
Article38. Lim SH, Kim Y, Yun KN, Kim JY, Jang JH, Han MJ, Lee J. Plant-based foods containing cell wall polysaccharides rich in specific active monosaccharides protect against myocardial injury in rat myocardial infarction models. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:38728.
Article39. Zhang P, Zhang Q, Whistler RL. L-arabinose release from arabinoxylan and arabinogalactan under potential gastric acidities. Cereal Chem. 2003; 80:252–254.
Article40. Bach Knudsen KE. Microbial degradation of whole-grain complex carbohydrates and impact on short-chain fatty acids and health. Adv Nutr. 2015; 6:206–213.
Article41. Koropatkin NM, Cameron EA, Martens EC. How glycan metabolism shapes the human gut microbiota. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012; 10:323–335.
Article42. Yano JM, Yu K, Donaldson GP, Shastri GG, Ann P, Ma L, Nagler CR, Ismagilov RF, Mazmanian SK, Hsiao EY. Indigenous bacteria from the gut microbiota regulate host serotonin biosynthesis. Cell. 2015; 161:264–276.
Article43. Fitzpatrick A, Roberts A, Witherly S. Larch arabinogalactan: a novel and multifunctional natural product. Agro Food Ind Hi Tech. 2004; 15:30–32.44. Dion C, Chappuis E, Ripoll C. Does larch arabinogalactan enhance immune function? A review of mechanistic and clinical trials. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2016; 13:28.
Article45. Groman EV, Enriquez PM, Jung C, Josephson L. Arabinogalactan for hepatic drug delivery. Bioconjug Chem. 1994; 5:547–556.
Article46. Robinson RR, Feirtag J, Slavin JL. Effects of dietary arabinogalactan on gastrointestinal and blood parameters in healthy human subjects. J Am Coll Nutr. 2001; 20:279–285.
Article47. Nair AB, Jacob S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J Basic Clin Pharm. 2016; 7:27–31.
Article