J Nutr Health.
2017 Aug;50(4):391-401. 10.4163/jnh.2017.50.4.391.
Estimated flavonoid intakes according to socioeconomic status of Korean adults based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007~2012
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Public Health, Graduate School of Public Health, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Korea. hjjoung@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Clinical Nutrition, Research Institute & Hospital, National Cancer Center, Goyang-si 10408, Korea.
- 3Institute of Environmental Medicine, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul 03080, Korea.
- 4Department of Preventive Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 03080, Korea.
- 5Department of Economics and Finance, Hanyang Cyber University, Seoul 04763, Korea.
- 6Institute of Health and Environment, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Korea.
- KMID: 2389555
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4163/jnh.2017.50.4.391
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to estimate the dietary flavonoid intakes of Korean adults according to socioeconomic status.
METHODS
Using data from the 2007~2012 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, a total of 31,112 subjects aged over 19 years were included in this study. We estimated individuals' daily intakes of total flavonoids and seven flavonoid subclasses, including flavonols, flavones, flavanones, flavan-3-ols, anthocyanins, proanthocyanidin, and isoflavones,by linking food consumption data with the flavonoids database for commonly consumed Korean foods. We compared intakes of flavonoids according to the levels of household income and education.
RESULTS
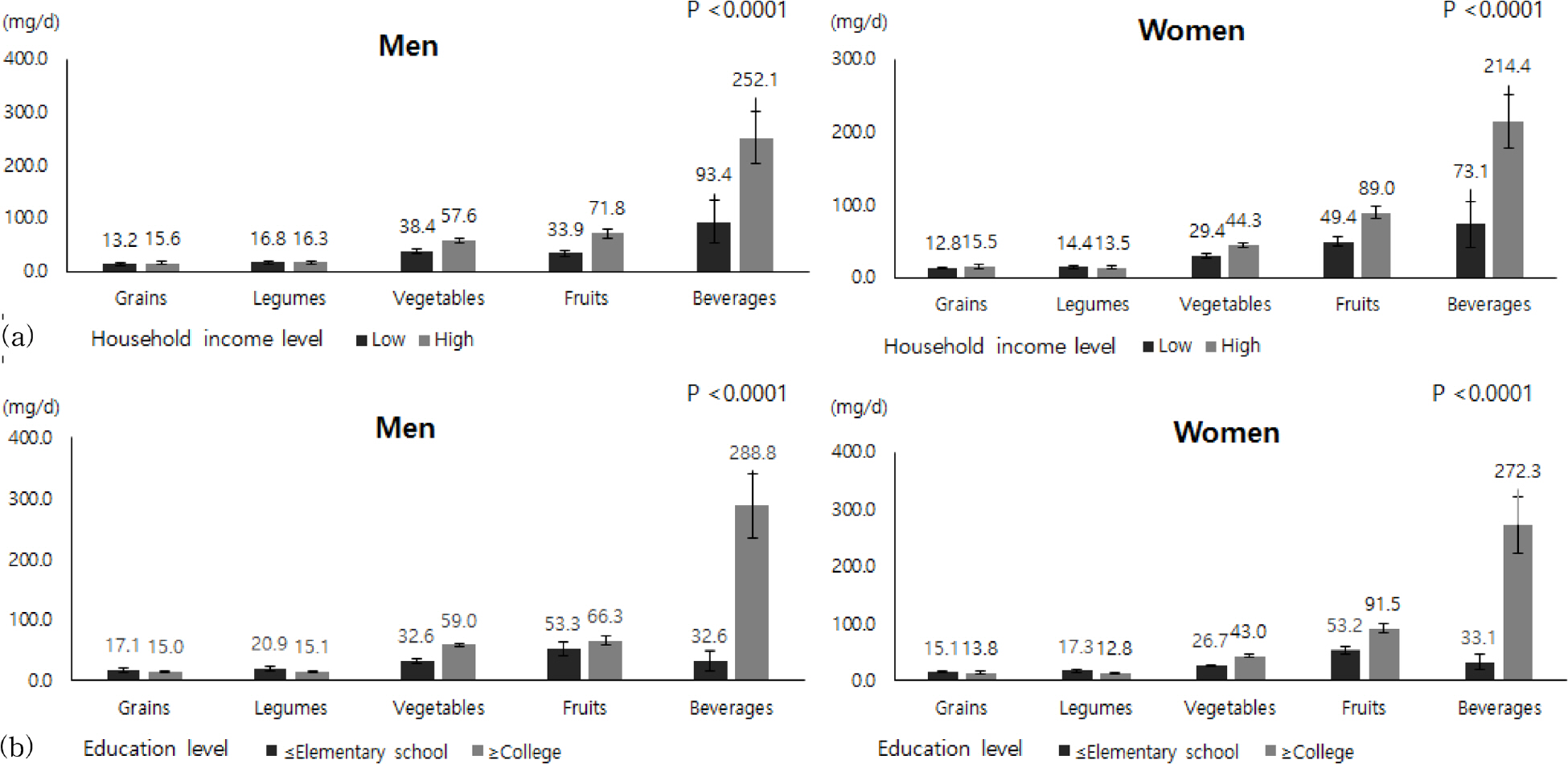
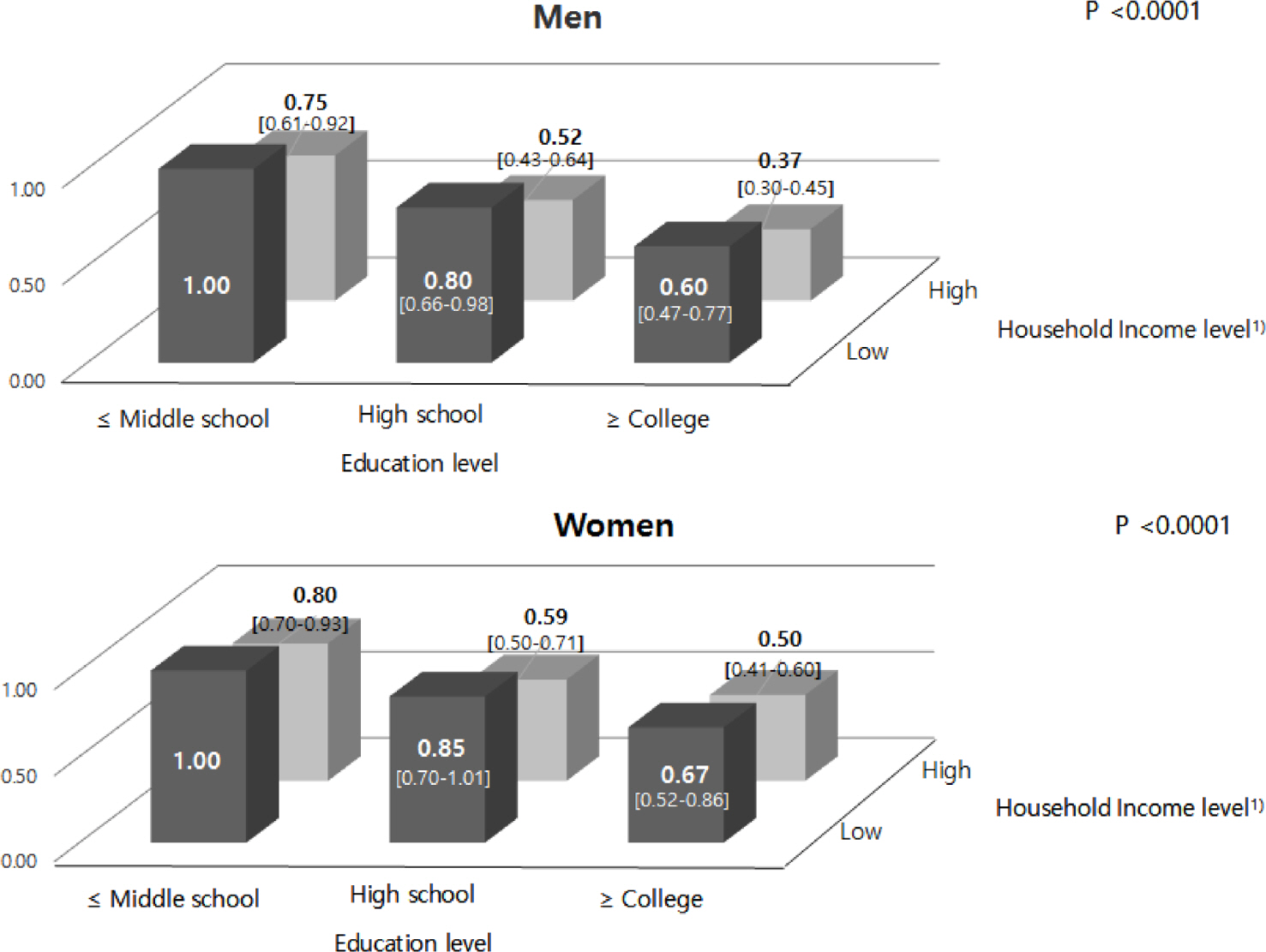
Average dietary flavonoid intakes of the study subjects were 321.8 mg/d in men and 308.3 mg/d in women. Daily flavonoid intakes were positively associated with household income level (p < 0.0001) and education level (p < 0.0001). The subjects in the highest household income and highest education level group (OR 0.37, 95% CI 0.30~0.45, p < 0.0001 in men, OR 0.50, 95% CI 0.41~0.60, p < 0.0001 in women) had a lower likelihood of having low total flavonoid intake (less than 25 percentile) compared to the lowest household income and lowest education level group. The food group that contributed to total flavonoid intake with the biggest difference between the lowest and highest groups for both household income level and education level was beverages.
CONCLUSION
This study shows that socioeconomic status was positively associated with flavonoid intake in a representative Korean population. Further research is needed to analyze the association of flavonoid intake with health outcomes according to socioeconomic status such as household income and education level.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. James WP, Nelson M, Ralph A, Leather S. Socioeconomic determinants of health. The contribution of nutrition to inequalities in health. BMJ. 1997; 314(7093):1545–1549.
Article2. Smith GD, Brunner E. Socioeconomic differentials in health: the role of nutrition. Proc Nutr Soc. 1997; 56(1A):75–90.
Article3. Janssen I, Boyce WF, Simpson K, Pickett W. Influence of individual-and area-level measures of socioeconomic status on obesity, unhealthy eating, and physical inactivity in Canadian adolescents. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006; 83(1):139–145.4. Giskes K, Turrell G, Patterson C, Newman B. Socioeconomic differences among Australian adults in consumption of fruit and vegetables and intakes of vitamins A, C and folate. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2002; 15(5):375–385.
Article5. Mishra G, Ball K, Arbuckle J, Crawford D. Dietary patterns of Australian adults and their association with socioeconomic status: results from the 1995 National Nutrition Survey. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2002; 56(7):687–693.
Article6. Kaplan GA, Keil JE. Socioeconomic factors and cardiovascular disease: a review of the literature. Circulation. 1993; 88(4 Pt 1):1973–1998.
Article7. Kim BH, Lee JW, Lee Y, Lee HS, Jang YA, Kim CI. Food and nutrient consumption patterns of the Korean adult population by income level: 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey. Korean J Community Nutr. 2005; 10(6):952–962.8. Jun S, Hong E, Joung H. Flavonoid intake according to food security in Korean adults: based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2012. J Nutr Health. 2015; 48(6):507–518.
Article9. Kim SA, Jun S, Joung H. Estimated dietary intake of vitamin A in Korean adults: based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2012. J Nutr Health. 2016; 49(4):258–268.
Article10. Bravo L. Polyphenols: chemistry, dietary sources, metabolism, and nutritional significance. Nutr Rev. 1998; 56(11):317–333.
Article11. Hertog MG, Feskens EJ, Hollman PC, Katan MB, Kromhout D. Dietary antioxidant flavonoids and risk of coronary heart disease: the Zutphen elderly study. Lancet. 1993; 342(8878):1007–1011.
Article12. Wang H, Cao G, Prior RL. Total antioxidant capacity of fruits. J Agric Food Chem. 1996; 44(3):701–705.
Article13. Byers T, Perry G. Dietary carotenes, vitamin C, and vitamin E as protective antioxidants in human cancers. Annu Rev Nutr. 1992; 12(1):139–159.
Article14. Stephens NG, Parsons A, Schofield PM, Kelly F, Cheeseman K, Mitchinson MJ. Randomised controlled trial of vitamin E in patients with coronary disease: Cambridge Heart Antioxidant Study (CHAOS). Lancet. 1996; 347(9004):781–786.
Article15. Marlett JA, McBurney MI, Slavin JL. American Dietetic Association. Position of the American Dietetic Association: health implications of dietary fiber. J Am Diet Assoc. 2002; 102(7):993–1000.16. Ames BN, Shigenaga MK, Hagen TM. Oxidants, antioxidants, and the degenerative diseases of aging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993; 90(17):7915–7922.
Article17. Chun OK, Kim DO, Smith N, Schroeder D, Han JT, Lee CY. Daily consumption of phenolics and total antioxidant capacity from fruit and vegetables in the American diet. J Sci Food Agric. 2005; 85(10):1715–1724.
Article18. Chun OK, Chung SJ, Song WO. Estimated dietary flavonoid intake and major food sources of U.S. adults. J Nutr. 2007; 137(5):1244–1252.
Article19. Middleton E Jr, Kandaswami C, Theoharides TC. The effects of plant flavonoids on mammalian cells: implications for inflammation, heart disease, and cancer. Pharmacol Rev. 2000; 52(4):673–751.20. Graf BA, Milbury PE, Blumberg JB. Flavonols, flavones, flava-nones, and human health: epidemiological evidence. J Med Food. 2005; 8(3):281–290.
Article21. Kris-Etherton PM, Keen CL. Evidence that the antioxidant flavonoids in tea and cocoa are beneficial for cardiovascular health. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2002; 13(1):41–49.
Article22. Rein D, Paglieroni TG, Wun T, Pearson DA, Schmitz HH, Gosselin R, Keen CL. Cocoa inhibits platelet activation and function. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000; 72(1):30–35.
Article23. Yao LH, Jiang YM, Shi J, Tomás-Barberán FA, Datta N, Singanu-song R, Chen SS. Flavonoids in food and their health benefits. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2004; 59(3):113–122.
Article24. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea Health Statistics 2007: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES IV-1) [Internet]. Cheongwon: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2008. [cited 2016 Nov 20]. Available from:. https://knhanes.cdc.go.kr/knhanes/index.do.knhanes.cdc.go.kr/knhanes/index.do.25. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea Health Statistics 2008: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES IV-2) [Internet]. Cheongwon: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2009. [cited 2016 Nov 20]. Available from:. https://knhanes.cdc.go.kr/knhanes/index.do.26. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.Korea Health Statistics 2009: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES IV-3) [Internet]. Cheongwon: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2010. [cited 2016 Nov 20]. Available from:. https://knhanes.cdc.go.kr/knhanes/index.do.27. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea Health Statistics 2010: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V-1) [Internet]. Cheongwon: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2011. [cited 2016 Nov 20]. Available from:. https://knhanes.cdc.go.kr/knhanes/index.do.28. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea Health Statistics 2011: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V-2) [Internet]. Cheongwon: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2012. [cited 2016 Nov 20]. Available from:. https://knhanes.cdc.go.kr/knhanes/index.do.29. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea Health Statistics 2012: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V-3) [Internet]. Cheongwon: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2013. [cited 2016 Nov 20]. Available from:. https://knhanes.cdc.go.kr/knhanes/index.do.30. Jun S, Shin S, Joung H. Estimation of dietary flavonoid intake and major food sources of Korean adults. Br J Nutr. 2016; 115(3):480–489.
Article31. Casey PH, Szeto K, Lensing S, Bogle M, Weber J. Children in food-insufficient, low-income families: prevalence, health, and nutrition status. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2001; 155(4):508–514.32. Ball K, Crawford D, Mishra G. Socioeconomic inequalities in women's fruit and vegetable intakes: a multilevel study of individual, social and environmental mediators. Public Health Nutr. 2006; 9(5):623–630.
Article33. Kirkpatrick S, Tarasuk V. The relationship between low income and household food expenditure patterns in Canada. Public Health Nutr. 2003; 6(6):589–597.
Article34. Dibsdall LA, Lambert N, Bobbin RF, Frewer LJ. Low-income consumers'attitudes and behaviour towards access, availability and motivation to eat fruit and vegetables. Public Health Nutr. 2003; 6(2):159–168.35. Steptoe A, Perkins-Porras L, McKay C, Rink E, Hilton S, Cappuccio FP. Psychological factors associated with fruit and vegetable intake and with biomarkers in adults from a low-income neighborhood. Health Psychol. 2003; 22(2):148–155.
Article36. Arai Y, Watanabe S, Kimira M, Shimoi K, Mochizuki R, Kinae N. Dietary intakes of flavonols, flavones and isoflavones by Japanese women and the inverse correlation between quercetin intake and plasma LDL cholesterol concentration. J Nutr. 2000; 130(9):2243–2250.
Article37. Lee HS, Cho YH, Park J, Shin HR, Sung MK. Dietary intake of phytonutrients in relation to fruit and vegetable consumption in Korea. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2013; 113(9):1194–1199.
Article38. Cho SW, Kim JH, Lee SM, Lee SM, Choi EJ, Jeong J, Park YK. Effect of 8-week nutrition counseling to increase phytochemical rich fruit and vegetable consumption in Korean breast cancer patients: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Nutr Res. 2014; 3(1):39–47.
Article39. Park S, Ham JO, Lee BK. Effects of total vitamin A, vitamin C, and fruit intake on risk for metabolic syndrome in Korean women and men. Nutrition. 2015; 31(1):111–118.
Article40. Ham D, Jun S, Kang M, Shin S, Wie GA, Baik HW, Joung H. Association of total dietary antioxidant capacity with oxidative stress and metabolic markers among patients with metabolic syndrome. J Nutr Health. 2017; 50(3):246–256.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Flavonoid intake according to food security in Korean adults: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007~2012
- Estimated dietary intake of vitamin A in Korean adults: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007~2012
- Nutritional Status and Food Insufficiency of Korean Population through the Life-Course by Education Level Based on 2005 National Health and Nutrition Survey
- Evaluation of Nutritional Status of Vitamins and Minerals According to Consumption of Dietary Supplements in Korean Adults and the Elderly: Report Based on 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
- Estimated dietary flavonoids intake of Korean adolescent: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007~2012