Immune Netw.
2017 Aug;17(4):228-236. 10.4110/in.2017.17.4.228.
Yersinia enterocolitica Exploits Signal Crosstalk between Complement 5a Receptor and Toll-like Receptor 1/2 and 4 to Avoid the Bacterial Clearance in M cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Molecular Biology and Institute for Molecular Biology and Genetics, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju 54896, Korea. yongsuk@jbnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Bioactive Material Sciences and Research Center of Bioactive Materials, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju 54896, Korea.
- KMID: 2388077
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2017.17.4.228
Abstract
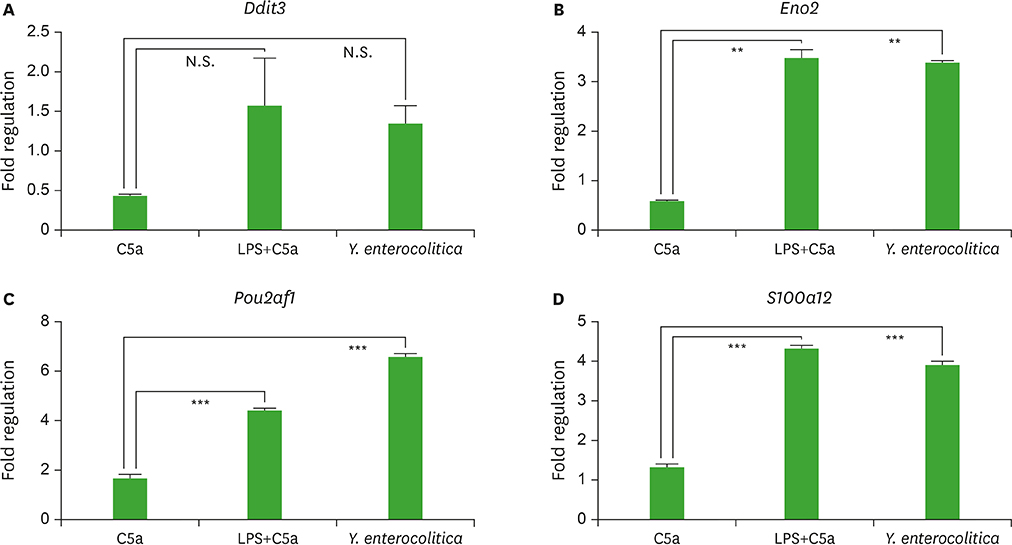
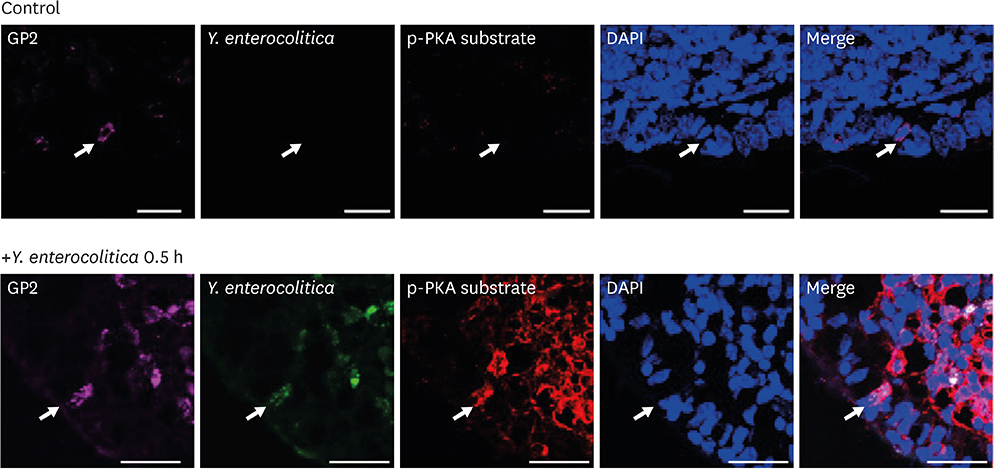
- In the intestinal mucosal surface, microfold cells (M cells) are the representative gateway for the uptake of luminal antigens. At the same time, M cells are the primary infection site for pathogens invading mucosal surface for their infection. Although it is well recognized that many mucosal pathogens exploit the M cells for their infection, the mechanism to infect M cells utilized by pathogens is not clearly understood yet. In this study, we found that M cells expressing complement 5a (C5a) receptor (C5aR) also express Toll-like receptor (TLR) 1/2 and TLR4. Infection of Yersinia enterocolitica, an M cell-invading pathogen, synergistically regulated cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase A (cAMP-PKA) signaling which are involved in signal crosstalk between C5aR and TLRs. In addition, Y. enterocolitica infection into M cells was enhanced by C5a treatment and this enhancement was abrogated by C5a antagonist treatment. Finally, Y. enterocolitica infection into M cells was unsuccessful in C5aR knock-out mice. Collectively, we suggest that exploit the crosstalk between C5aR and TLR signaling is one of infection mechanisms utilized by mucosal pathogens to infect M cells.
MeSH Terms
-
Adenosine
Animals
Complement C5a*
Complement System Proteins*
Cyclic AMP-Dependent Protein Kinases
Mice
Mice, Knockout
Phenobarbital
Receptor, Anaphylatoxin C5a*
Toll-Like Receptors*
Yersinia enterocolitica*
Yersinia*
Adenosine
Complement C5a
Complement System Proteins
Cyclic AMP-Dependent Protein Kinases
Phenobarbital
Receptor, Anaphylatoxin C5a
Toll-Like Receptors
Figure
Reference
-
1. Peterson LW, Artis D. Intestinal epithelial cells: regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014; 14:141–153.
Article2. Kurashima Y, Kiyono H. Mucosal ecological network of epithelium and immune cells for gut homeostasis and tissue healing. Annu Rev Immunol. 2017; 35:119–147.
Article3. Schulz O, Pabst O. Antigen sampling in the small intestine. Trends Immunol. 2013; 34:155–161.
Article4. Mabbott NA, Donaldson DS, Ohno H, Williams IR, Mahajan A. Microfold (M) cells: important immunosurveillance posts in the intestinal epithelium. Mucosal Immunol. 2013; 6:666–677.
Article5. Owen RL. Uptake and transport of intestinal macromolecules and microorganisms by M cells in Peyer's patches--a personal and historical perspective. Semin Immunol. 1999; 11:157–163.
Article6. Sansonetti PJ, Phalipon A. M cells as ports of entry for enteroinvasive pathogens: mechanisms of interaction, consequences for the disease process. Semin Immunol. 1999; 11:193–203.
Article7. Hase K, Kawano K, Nochi T, Pontes GS, Fukuda S, Ebisawa M, Kadokura K, Tobe T, Fujimura Y, Kawano S, et al. Uptake through glycoprotein 2 of FimH(+) bacteria by M cells initiates mucosal immune response. Nature. 2009; 462:226–230.
Article8. Kim SH, Jung DI, Yang IY, Kim J, Lee KY, Nochi T, Kiyono H, Jang YS. M cells expressing the complement C5a receptor are efficient targets for mucosal vaccine delivery. Eur J Immunol. 2011; 41:3219–3229.
Article9. Hajishengallis G, Lambris JD. Microbial manipulation of receptor crosstalk in innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011; 11:187–200.
Article10. Nakayama M, Underhill DM, Petersen TW, Li B, Kitamura T, Takai T, Aderem A. Paired Ig-like receptors bind to bacteria and shape TLR-mediated cytokine production. J Immunol. 2007; 178:4250–4259.
Article11. Bergman MP, Engering A, Smits HH, van Vliet SJ, van Bodegraven AA, Wirth HP, Kapsenberg ML, Vandenbroucke-Grauls CM, van Kooyk Y, Appelmelk BJ. Helicobacter pylori modulates the T helper cell 1/T helper cell 2 balance through phase-variable interaction between lipopolysaccharide and DC-SIGN. J Exp Med. 2004; 200:979–990.
Article12. Geijtenbeek TB, Van Vliet SJ, Koppel EA, Sanchez-Hernandez M, Vandenbroucke-Grauls CM, Appelmelk B, Van Kooyk Y. Mycobacteria target DC-SIGN to suppress dendritic cell function. J Exp Med. 2003; 197:7–17.
Article13. Gringhuis SI, den Dunnen J, Litjens M, van Het Hof B, van Kooyk Y, Geijtenbeek TB. C-type lectin DC-SIGN modulates Toll-like receptor signaling via Raf-1 kinase-dependent acetylation of transcription factor NF-kappaB. Immunity. 2007; 26:605–616.
Article14. Wang M, Krauss JL, Domon H, Hosur KB, Liang S, Magotti P, Triantafilou M, Triantafilou K, Lambris JD, Hajishengallis G. Microbial hijacking of complement-toll-like receptor crosstalk. Sci Signal. 2010; 3:ra11.
Article15. Keely S, Glover LE, Weissmueller T, MacManus CF, Fillon S, Fennimore B, Colgan SP. Hypoxia-inducible factor-dependent regulation of platelet-activating factor receptor as a route for gram-positive bacterial translocation across epithelia. Mol Biol Cell. 2010; 21:538–546.
Article16. Shafique M, Wilschut J, de Haan A. Induction of mucosal and systemic immunity against respiratory syncytial virus by inactivated virus supplemented with TLR9 and NOD2 ligands. Vaccine. 2012; 30:597–606.
Article17. Kim SH, Seo KW, Kim J, Lee KY, Jang YS. The M cell-targeting ligand promotes antigen delivery and induces antigen-specific immune responses in mucosal vaccination. J Immunol. 2010; 185:5787–5795.
Article18. Zanassi P, Paolillo M, Feliciello A, Avvedimento EV, Gallo V, Schinelli S. cAMP-dependent protein kinase induces cAMP-response element-binding protein phosphorylation via an intracellular calcium release/ERK-dependent pathway in striatal neurons. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:11487–11495.
Article19. Vazquez-Torres A, Jones-Carson J, Mastroeni P, Ischiropoulos H, Fang FC. Antimicrobial actions of the NADPH phagocyte oxidase and inducible nitric oxide synthase in experimental salmonellosis. I. Effects on microbial killing by activated peritoneal macrophages in vitro. J Exp Med. 2000; 192:227–236.
Article20. Kishikawa S, Sato S, Kaneto S, Uchino S, Kohsaka S, Nakamura S, Kiyono H. Allograft inflammatory factor 1 is a regulator of transcytosis in M cells. Nat Commun. 2017; 8:14509.
Article21. Monk PN, Scola AM, Madala P, Fairlie DP. Function, structure and therapeutic potential of complement C5a receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 2007; 152:429–448.
Article22. Shrestha A, Shi L, Tanase S, Tsukamoto M, Nishino N, Tokita K, Yamamoto T. Bacterial chaperone protein, Skp, induces leukocyte chemotaxis via C5a receptor. Am J Pathol. 2004; 164:763–772.
Article23. Shushakova N, Skokowa J, Schulman J, Baumann U, Zwirner J, Schmidt RE, Gessner JE. C5a anaphylatoxin is a major regulator of activating versus inhibitory FcgammaRs in immune complex-induced lung disease. J Clin Invest. 2002; 110:1823–1830.
Article24. Teitell MA. OCA-B regulation of B-cell development and function. Trends Immunol. 2003; 24:546–553.
Article25. Zhou H, Brekman A, Zuo WL, Ou X, Shaykhiev R, Agosto-Perez FJ, Wang R, Walters MS, Salit J, Strulovici-Barel Y, et al. POU2AF1 functions in the human airway epithelium to regulate expression of host defense genes. J Immunol. 2016; 196:3159–3167.
Article26. de Lau W, Kujala P, Schneeberger K, Middendorp S, Li VS, Barker N, Martens A, Hofhuis F, DeKoter RP, Peters PJ, et al. Peyer's patch M cells derived from Lgr5(+) stem cells require SpiB and are induced by RankL in cultured “miniguts”. Mol Cell Biol. 2012; 32:3639–3647.
Article27. Zhou Y, Liu X, Xu L, Hunter ZR, Cao Y, Yang G, Carrasco R, Treon SP. Transcriptional repression of plasma cell differentiation is orchestrated by aberrant over-expression of the ETS factor SPIB in Waldenström macroglobulinaemia. Br J Haematol. 2014; 166:677–689.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- In-vitro cell invasiveness and cytotoxicity of CRMOX-posive and- negative strains of yersinia enterocolitica grown at 26'C and 37'C
- Terminal Ileitis Caused by Yersinia enterocolitica and Presents with Intussusception Mimicking Crohn's Disease
- Biotype, serotype and antimicrobial susceptibility of yersinia enterocolitica isolated from cattle
- Study on the Development of a Rapid Detection Method for Pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis by Nested Polymerase Chain Reaction
- Yersinia enterocolitica typing by restriction enzyme analysis of plasmid DNA