J Rheum Dis.
2017 Jun;24(3):165-168. 10.4078/jrd.2017.24.3.165.
Hypereosinophilic Syndrome Associated with the Onset of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea.
- 2Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chonbuk National University Medical School and Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea. ywhim@jbnu.ac.kr
- 3Division of Pulmonology and Allergy, Department of Internal Medicine, Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2385345
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2017.24.3.165
Abstract
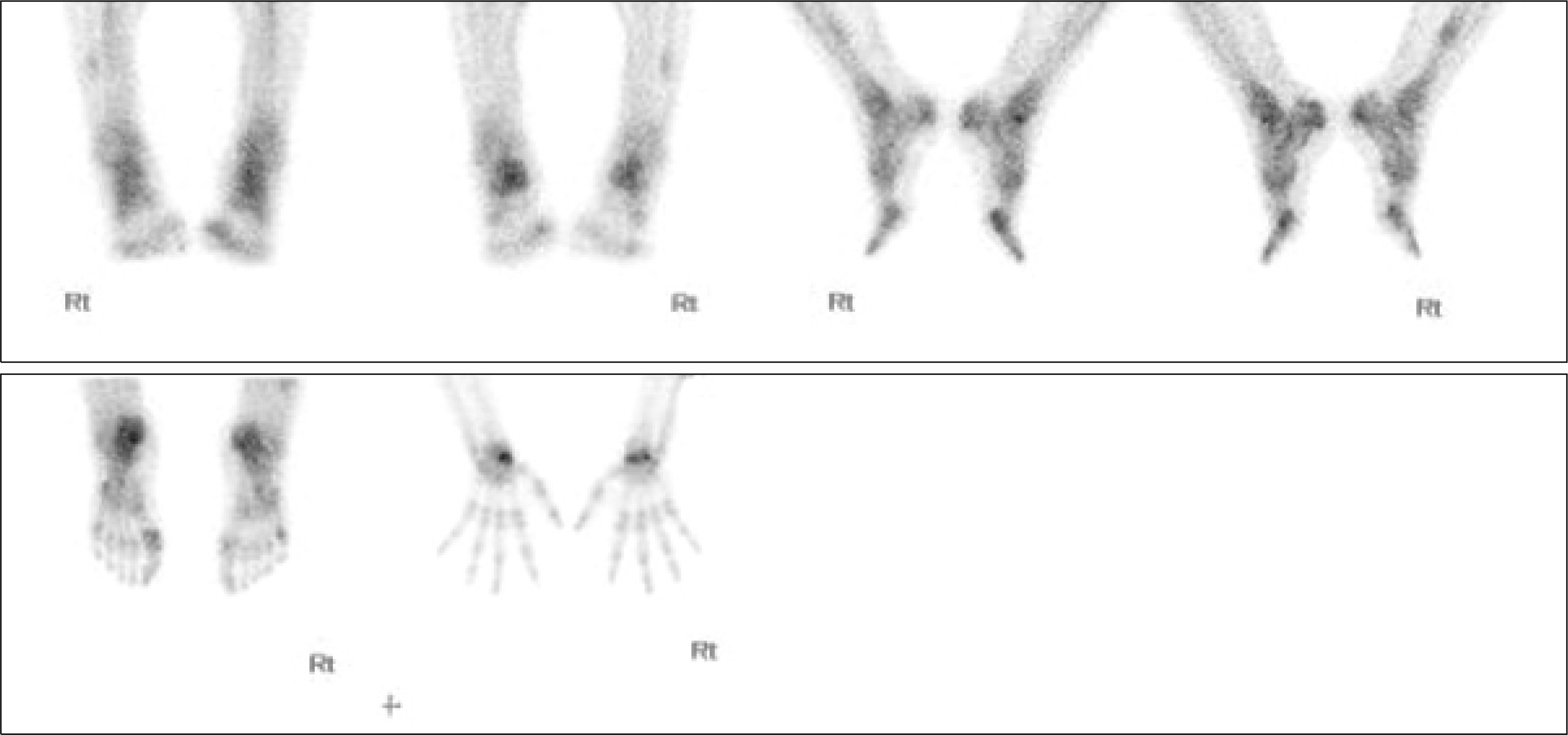
- Idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) is a disorder characterized by the sustained overproduction of eosinophils and multiple organ damage. Rheumatologic manifestations of HES are infrequent, but persistent eosinophilia is observed in approximately 10% to 40% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This finding may be a result of the RA itself and is often associated with active disease and the presence of extra-articular features. We describe the case of a 48-year-old man affected by HES who subsequently developed RA. Both HES and RA responded rapidly to the corticosteroid and methotrexate therapy. In this patient, the initiation of RA and HES was related, suggesting a common pathogenetic link between these two diseases.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Case of Idiopathic Hypereosinophilic Syndrome with Articular Involvement
Ji Hyoun Kim, You-Jung Ha, Eun Ha Kang, Yeong Wook Song, Yun Jong Lee
J Rheum Dis. 2018;25(3):207-211. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2018.25.3.207.
Reference
-
1. Weller PF, Bubley GJ. The idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Blood. 1994; 83:2759–79.
Article2. Chaudhuri K, Dubey S, Zaphiropoulos G. Idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome in a patient with longstanding rheumatoid arthritis: a case report. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002; 41:349–50.
Article3. Winchester RJ, Koffler D, Litwin SD, Kunkel HG. Observations on the eosinophilia of certain patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1971; 14:650–65.
Article4. Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO 3rd, et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/ European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 62:2569–81.5. Roufosse FE, Goldman M, Cogan E. Hypereosinophilic syndromes. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007; 2:37.
Article6. Bain BJ. Eosinophilia–idiopathic or not? N Engl J Med. 1999; 341:1141–3.7. Seifert M, Gerth J, Gajda M, Pester F, Pfeifer R, Wolf G. Eosinophilia–a challenging differential diagnosis. Med Klin (Munich). 2008; 103:591–7.8. Brogadir SP, Goldwein MI, Schumacher HR. A hypereosinophilic syndrome mimicking rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1980; 69:799–802.
Article9. Prattichizzo FA, Bernini L. An idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome mimicking seronegative rheumatoid arthritis: 20-year follow-up with clinical and laboratory findings. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1992; 10:79–81.10. Martín-Santos JM, Mulero J, Andréu JL, de Villa LF, Bernaldo-de Quirós L, et al. Arthritis in idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1988; 31:120–5.11. Tay C. Eosinophilic arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 1999; 38:1188–94.
Article12. Bonanno D, Fedele R, Minciullo P, Quattrocchi P, Ferlazzo B. Idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome associated with rheumatoid arthritis. A case report. Reumatismo. 2003; 55:181–3.
Article13. Rosenstein RK, Panush RS, Kramer N, Rosenstein ED. Hypereosinophilia and seroconversion of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2014; 33:1685–8.
Article14. Boomars KA, van Velzen-Blad H, Mulder PG, Koenderman L, Lammers JW, van den Bosch JM. Eosinophil cationic protein and immunoglobulin levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid obtained from patients with chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. Eur Respir J. 1996; 9:2488–93.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis with Idiopathic Hypereosinophilic Syndrome
- A Case Of Rheumatoid Arthritis Accompanied By Severe Eosinophilia
- Case of Idiopathic Hypereosinophilic Syndrome with Articular Involvement
- A Case of Rheumatoid Arthritis Associated with Klinefelter's Syndrome
- A Case of Sweet's Syndrome associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis