Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2017 May;21(3):293-300. 10.4196/kjpp.2017.21.3.293.
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ is essential for secretion of ANP induced by prostaglandin D₂ in the beating rat atrium
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, Yanbian University, Yanji 133-002, China. cuixun@ybu.edu.cn 15526770645@163.com
- 2Key Laboratory of Organism Functional Factors of the Changbai Mountain, Ministry of Education, Yanbian University, Yanji 133-002, China.
- 3Cellular Function Research Center, Yanbian University, Yanji 133-002, China.
- 4Institue of Clinical Medicine, Yanbian University, Yanji 133-002, China.
- KMID: 2376957
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2017.21.3.293
Abstract
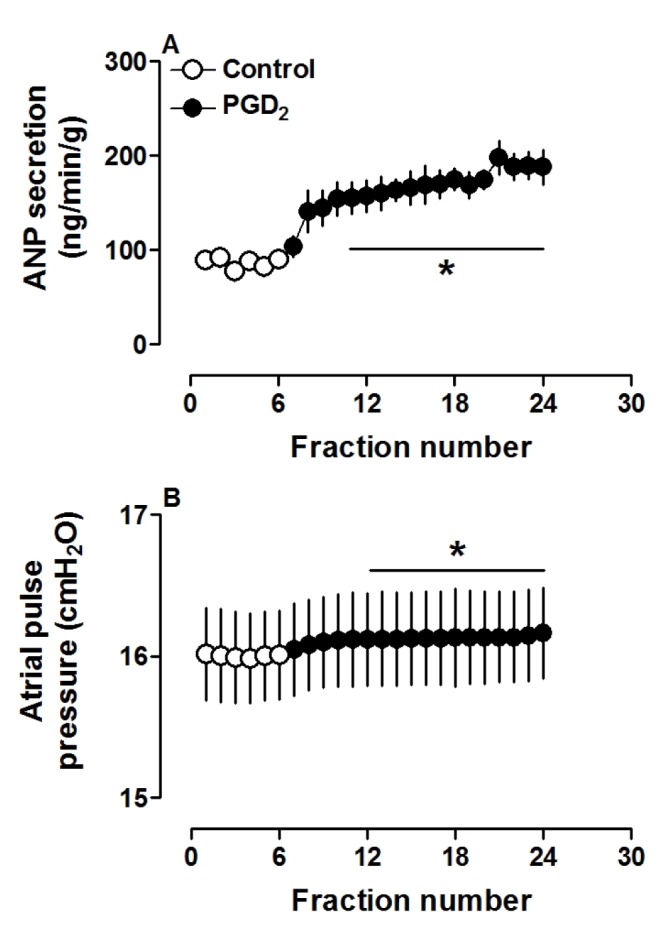
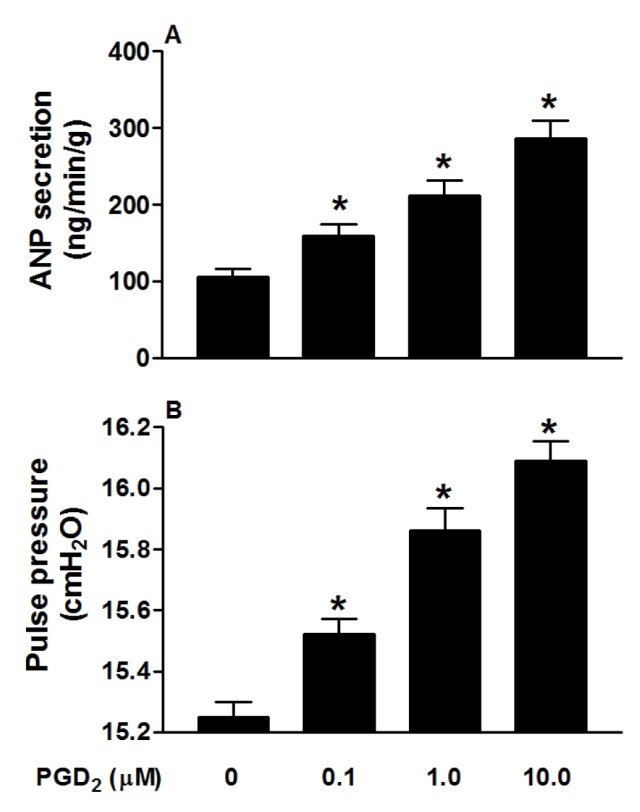
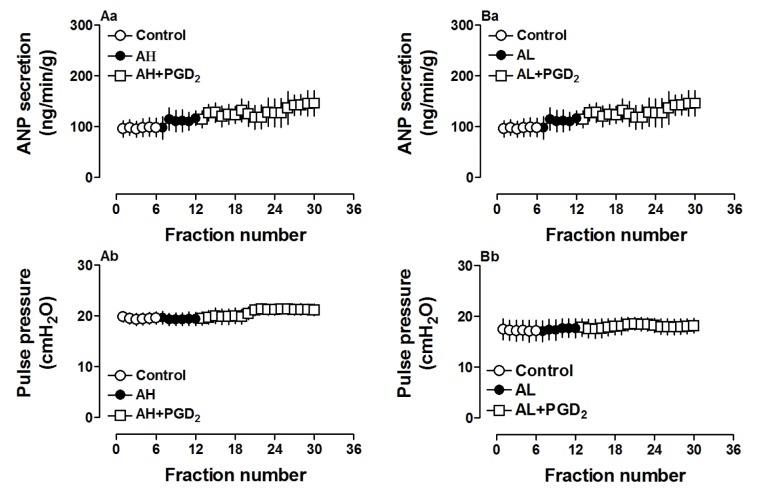
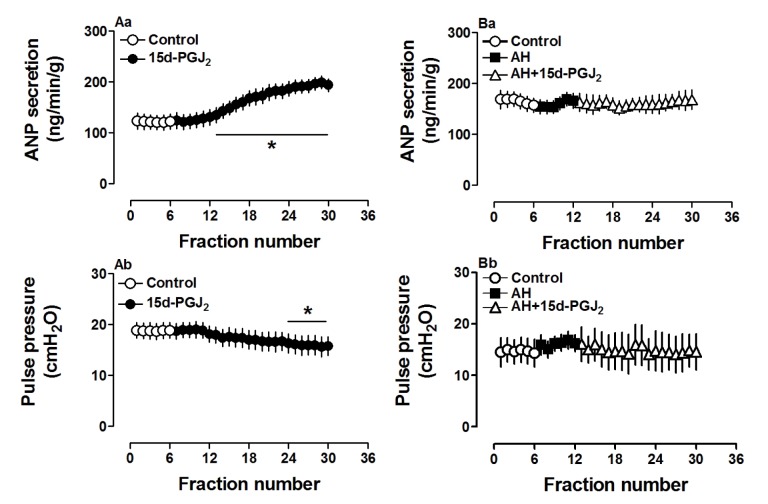
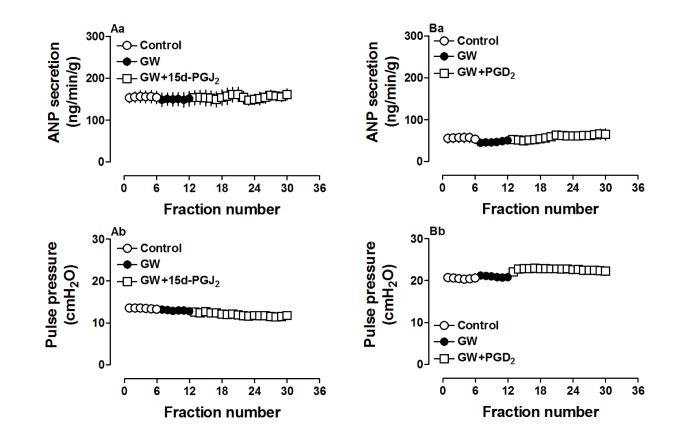
- Prostaglandin Dâ‚‚ (PGDâ‚‚) may act against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury and play an anti-inflammatory role in the heart. Although the effect of PGDâ‚‚ in regulation of ANP secretion of the atrium was reported, the mechanisms involved are not clearly identified. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether PGDâ‚‚ can regulate ANP secretion in the isolated perfused beating rat atrium, and its underlying mechanisms. PGDâ‚‚ (0.1 to 10 µM) significantly increased atrial ANP secretion concomitantly with positive inotropy in a dose-dependent manner. Effects of PGDâ‚‚ on atrial ANP secretion and mechanical dynamics were abolished by AH-6809 (1.0 µM) and AL-8810 (1.0 µM), PGDâ‚‚ and prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) receptor antagonists, respectively. Moreover, PGDâ‚‚ clearly upregulated atrial peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) and the PGDâ‚‚ metabolite 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-PGJâ‚‚ (15d-PGJâ‚‚, 0.1 µM) dramatically increased atrial ANP secretion. Increased ANP secretions induced by PGDâ‚‚ and 15d-PGJâ‚‚ were completely blocked by the PPARγ antagonist GW9662 (0.1 µM). PD98059 (10.0 µM) and LY294002 (1.0 µM), antagonists of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) signaling, respectively, significantly attenuated the increase of atrial ANP secretion by PGDâ‚‚. These results indicated that PGDâ‚‚ stimulated atrial ANP secretion and promoted positive inotropy by activating PPARγ in beating rat atria. MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways were each partially involved in regulating PGDâ‚‚-induced atrial ANP secretion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kalra BS, Roy V. Efficacy of metabolic modulators in ischemic heart disease: an overview. J Clin Pharmacol. 2012; 52:292–305. PMID: 21383339.
Article2. Ryu SK, Mallat Z, Benessiano J, Tedgui A, Olsson AG, Bao W, Schwartz GG, Tsimikas S. Myocardial Ischemia Reduction With Aggressive Cholesterol Lowering (MIRACL) Trial Investigators. Phospholipase A2 enzymes, high-dose atorvastatin, and prediction of ischemic events after acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 2012; 125:757–766. PMID: 22230483.3. Gross GJ, Falck JR, Gross ER, Isbell M, Moore J, Nithipatikom K. Cytochrome P450 and arachidonic acid metabolites: role in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury revisited. Cardiovasc Res. 2005; 68:18–25. PMID: 15993870.4. Qiu H, Liu JY, Wei D, Li N, Yamoah EN, Hammock BD, Chiamvimonvat N. Cardiac-generated prostanoids mediate cardiac myocyte apoptosis after myocardial ischaemia. Cardiovasc Res. 2012; 95:336–345. PMID: 22707158.
Article5. Ricciotti E, FitzGerald GA. Prostaglandins and inflammation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011; 31:986–1000. PMID: 21508345.6. Taba Y, Sasaguri T, Miyagi M, Abumiya T, Miwa Y, Ikeda T, Mitsumata M. Fluid shear stress induces lipocalin-type prostaglandin D(2) synthase expression in vascular endothelial cells. Circ Res. 2000; 86:967–973. PMID: 10807869.7. Zhang X, Young HA. PPAR and immune system--what do we know? Int Immunopharmacol. 2002; 2:1029–1044. PMID: 12349941.
Article8. Lim HJ, Lee KS, Lee S, Park JH, Choi HE, Go SH, Kwak HJ, Park HY. 15d-PGJ2 stimulates HO-1 expression through p38 MAP kinase and Nrf-2 pathway in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2007; 223:20–27. PMID: 17631927.
Article9. Lee SJ, Kim MS, Park JY, Woo JS, Kim YK. 15-Deoxy-delta 12,14-prostaglandin J2 induces apoptosis via JNK-mediated mitochondrial pathway in osteoblastic cells. Toxicology. 2008; 248:121–129. PMID: 18450357.10. Jung WK, Park IS, Park SJ, Yea SS, Choi YH, Oh S, Park SG, Choi IW. The 15-deoxy-Delta12,14-prostaglandin J2 inhibits LPS-stimulated AKT and NF-kappaB activation and suppresses interleukin-6 in osteoblast-like cells MC3T3E-1. Life Sci. 2009; 85:46–53. PMID: 19409914.11. Giri S, Rattan R, Singh AK, Singh I. The 15-deoxy-delta12,14-prostaglandin J2 inhibits the inflammatory response in primary rat astrocytes via down-regulating multiple steps in phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt-NF-kappaB-p300 pathway independent of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. J Immunol. 2004; 173:5196–5208. PMID: 15470065.12. Bai G, Gao S, Shah A, Yuan K, Park WH, Kim SH. Regulation of ANP secretion from isolated atria by prostaglandins and cyclooxygenase-2. Peptides. 2009; 30:1720–1728. PMID: 19539681.
Article13. Koyani CN, Windischhofer W, Rossmann C, Jin G, Kickmaier S, Heinzel FR, Groschner K, Alavian-Ghavanini A, Sattler W, Malle E. 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-PGJ2 promotes inflammation and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes via the DP2/MAPK/TNFα axis. Int J Cardiol. 2014; 173:472–480. PMID: 24698234.14. Sawyer N, Cauchon E, Chateauneuf A, Cruz RP, Nicholson DW, Metters KM, O'Neill GP, Gervais FG. Molecular pharmacology of the human prostaglandin D2 receptor, CRTH2. Br J Pharmacol. 2002; 137:1163–1172. PMID: 12466225.15. Cho KW, Lee SJ, Wen JF, Kim SH, Seul KH, Lee HS. Mechanical control of extracellular space in rabbit atria: an intimate modulator of the translocation of extracellular fluid and released atrial natriuretic peptide. Exp Physiol. 2002; 87:185–194. PMID: 11856963.16. Katsumata Y, Shinmura K, Sugiura Y, Tohyama S, Matsuhashi T, Ito H, Yan X, Ito K, Yuasa S, Ieda M, Urade Y, Suematsu M, Fukuda K, Sano M. Endogenous prostaglandin D2 and its metabolites protect the heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury by activating Nrf2. Hypertension. 2014; 63:80–87. PMID: 24101662.17. Kim KH, Sadikot RT, Xiao L, Christman JW, Freeman ML, Chan JY, Oh YK, Blackwell TS, Joo M. Nrf2 is essential for the expression of lipocalin-prostaglandin D synthase induced by prostaglandin D2. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013; 65:1134–1142. PMID: 24029383.
Article18. Zhang QL, Cui BR, Li HY, Li P, Hong L, Liu LP, Ding DZ, Cui X. MAPK and PI3K pathways regulate hypoxia-induced atrial natriuretic peptide secretion by controlling HIF-1 alpha expression in beating rabbit atria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013; 438:507–512. PMID: 23916614.
Article19. Liu LP, Hong L, Yu L, Li HY, Ding DZ, Jin SJ, Cui X. Ouabain stimulates atrial natriuretic peptide secretion via the endothelin-1/ET(B) receptor-mediated pathway in beating rabbit atria. Life Sci. 2012; 90:793–798. PMID: 22521291.
Article20. Mitaka C, Si MK, Tulafu M, Yu Q, Uchida T, Abe S, Kitagawa M, Ikeda S, Eishi Y, Tomita M. Effects of atrial natriuretic peptide on inter-organ crosstalk among the kidney, lung, and heart in a rat model of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2014; 2:28. PMID: 26266925.
Article21. Hong L, Xi J, Zhang Y, Tian W, Xu J, Cui X, Xu Z. Atrial natriuretic peptide prevents the mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening by inactivating glycogen synthase kinase 3β via PKG and PI3K in cardiac H9c2 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012; 695:13–19. PMID: 22975711.
Article22. Kiemer AK, Hartung T, Vollmar AM. cGMP-mediated inhibition of TNF-alpha production by the atrial natriuretic peptide in murine macrophages. J Immunol. 2000; 165:175–181. PMID: 10861050.23. Kiemer AK, Weber NC, Fürst R, Bildner N, Kulhanek-Heinze S, Vollmar AM. Inhibition of p38 MAPK activation via induction of MKP-1: atrial natriuretic peptide reduces TNF-alpha-induced actin polymerization and endothelial permeability. Circ Res. 2002; 90:874–881. PMID: 11988488.24. Ladetzki-Baehs K, Keller M, Kiemer AK, Koch E, Zahler S, Wendel A, Vollmar AM. Atrial natriuretic peptide, a regulator of nuclear factor-kappaB activation in vivo. Endocrinology. 2007; 148:332–336. PMID: 17008392.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptors (PPARs) in Diabetic Nephropathy
- The WNT/Ca2+ pathway promotes atrial natriuretic peptide secretion by activating protein kinase C/transforming growth factor-β activated kinase 1/activating transcription factor 2 signaling in isolated beating rat atria
- Characteristics of hypoxia-induced ANP Secretion in Perfused Beating Atria
- Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor-delta (PPAR-delta)
- Comparative effects of angiotensin II and angiotensin-(4-8) on blood pressure and ANP secretion in rats