J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Jul;31(7):1143-1149. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.7.1143.
Progression of Hip Displacement during Radiographic Surveillance in Patients with Cerebral Palsy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, 21th Century Hospital, Wonju, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. chungcy55@gmail.com
- 4Yeollin Orthopedic Clinic, Suwon, Korea.
- 5Department of Mathematics, College of Natural Science, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2373736
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.7.1143
Abstract
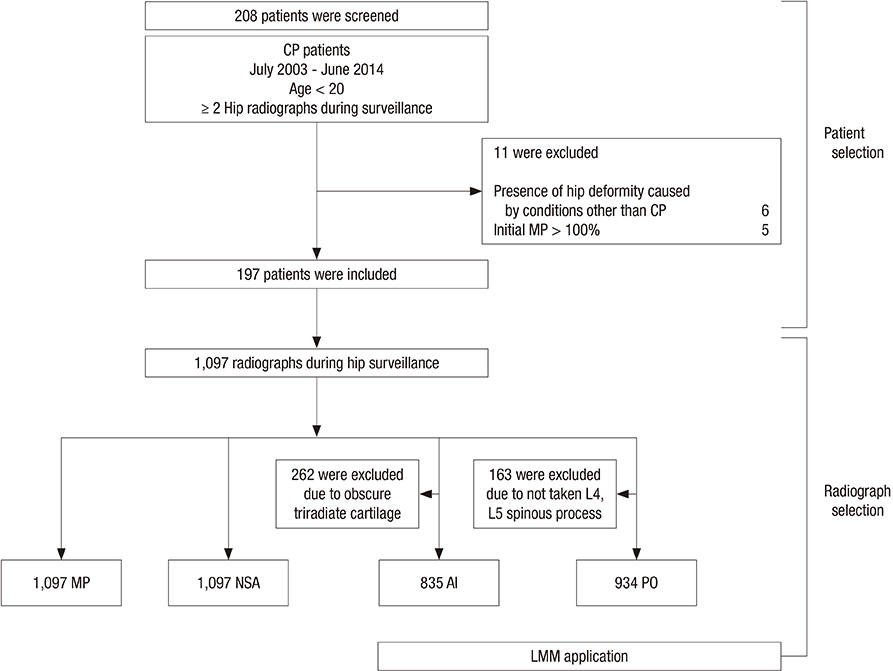
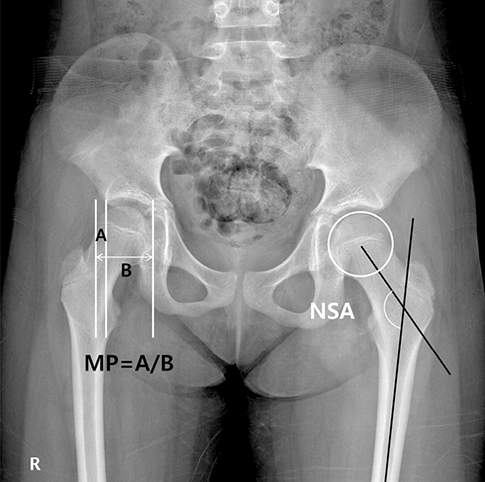
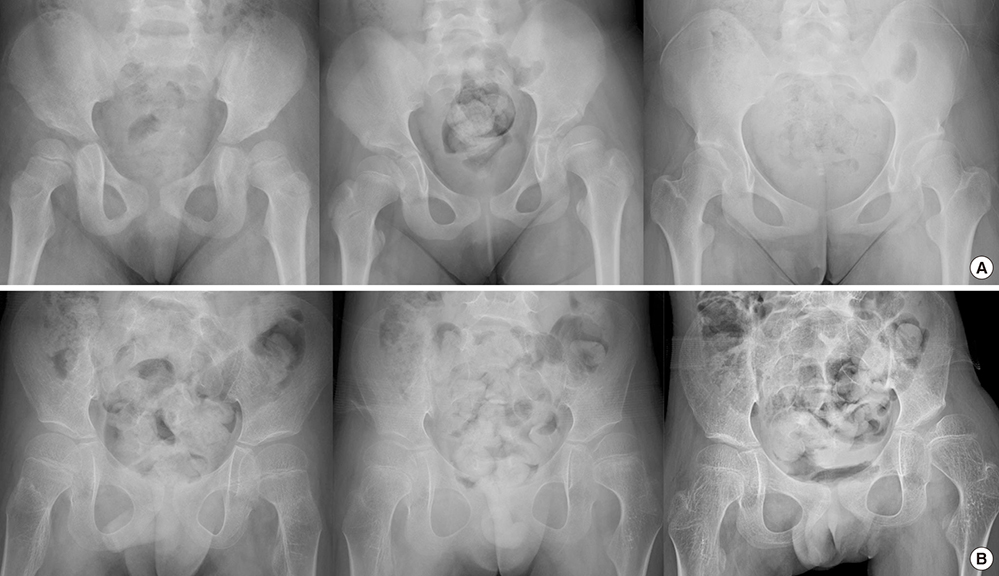
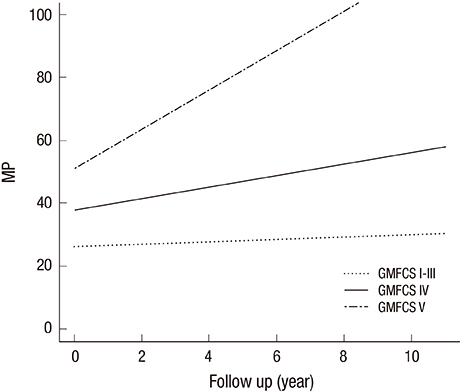
- Progression of hip displacement is common in patients with cerebral palsy (CP). We aimed to investigate the rate of progression of hip displacement in patients with CP by assessing changes in radiographic indices according to Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS) level during hip surveillance. We analyzed the medical records of patients with CP aged < 20 years who underwent at least 6 months interval of serial hip radiographs before any surgical hip intervention, including reconstructive surgery. After panel consensus and reliability testing, radiographic measurements of migration percentage (MP), neck-shaft angle (NSA), acetabular index (AI), and pelvic obliquity (PO) were obtained during hip surveillance. For each GMFCS level, annual changes in radiographic indices were analyzed and adjusted for affecting factors, such as sex, laterality, and type of CP. A total of 197 patients were included in this study, and 1,097 radiographs were evaluated. GMFCS classifications were as follows: 100 patients were level I-III, 48 were level IV, and 49 were level V. MP increased significantly over the duration of hip surveillance in patients with GMFCS levels I-III, IV, and V by 0.3%/year (P < 0.001), 1.9%/year (P < 0.001), and 6.2%/year (P < 0.001), respectively. In patients with GMFCS level IV, NSA increased significantly by 3.4°/year (P < 0.001). Our results suggest that periodic monitoring and radiographic hip surveillance is warranted for patients with CP, especially those with GMFCS level IV or V. Furthermore, physicians can predict and inform parents or caregivers regarding the progression of hip displacement in patients with CP.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bax M, Goldstein M, Rosenbaum P, Leviton A, Paneth N, Dan B, Jacobsson B, Damiano D; Executive Committee for the Definition of Cerebral Palsy. Proposed definition and classification of cerebral palsy, April 2005. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2005; 47:571–576.2. Odding E, Roebroeck ME, Stam HJ. The epidemiology of cerebral palsy: incidence, impairments and risk factors. Disabil Rehabil. 2006; 28:183–191.3. Park MS, Kim SJ, Chung CY, Kwon DG, Choi IH, Lee KM. Prevalence and lifetime healthcare cost of cerebral palsy in South Korea. Health Policy. 2011; 100:234–238.4. Lonstein JE, Beck K. Hip dislocation and subluxation in cerebral palsy. J Pediatr Orthop. 1986; 6:521–526.5. Renshaw TS, Green NE, Griffin PP, Root L. Cerebral palsy: orthopaedic management. Instr Course Lect. 1996; 45:475–490.6. Gamble JG, Rinsky LA, Bleck EE. Established hip dislocations in children with cerebral palsy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990; 90–99.7. Hägglund G, Lauge-Pedersen H, Wagner P. Characteristics of children with hip displacement in cerebral palsy. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2007; 8:101.8. Gordon GS, Simkiss DE. A systematic review of the evidence for hip surveillance in children with cerebral palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006; 88:1492–1496.9. Hägglund G, Andersson S, Düppe H, Lauge-Pedersen H, Nordmark E, Westbom L. Prevention of dislocation of the hip in children with cerebral palsy. The first ten years of a population-based prevention programme. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87:95–101.10. Soo B, Howard JJ, Boyd RN, Reid SM, Lanigan A, Wolfe R, Reddihough D, Graham HK. Hip displacement in cerebral palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88:121–129.11. Terjesen T. Development of the hip joints in unoperated children with cerebral palsy: a radiographic study of 76 patients. Acta Orthop. 2006; 77:125–131.12. Howard CB, McKibbin B, Williams LA, Mackie I. Factors affecting the incidence of hip dislocation in cerebral palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1985; 67:530–532.13. Kay RM, Jaki KA, Skaggs DL. The effect of femoral rotation on the projected femoral neck-shaft angle. J Pediatr Orthop. 2000; 20:736–739.14. Bauer F. The functional treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip-joint: (section of orthopaedics). Proc R Soc Med. 1941; 34:215–217.15. Mose K. Methods of measuring in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease with special regard to the prognosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980; 103–109.16. Pidcock FS, Fish DE, Johnson-Greene D, Borras I, McGready J, Silberstein CE. Hip migration percentage in children with cerebral palsy treated with botulinum toxin type A. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005; 86:431–435.17. Senaran H, Shah SA, Glutting JJ, Dabney KW, Miller F. The associated effects of untreated unilateral hip dislocation in cerebral palsy scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2006; 26:769–772.18. Southwick WO. Osteotomy through the lesser trochanter for slipped capital femoral epiphysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1967; 49:807–835.19. Werner CM, Ramseier LE, Ruckstuhl T, Stromberg J, Copeland CE, Turen CH, Rufibach K, Bouaicha S. Normal values of Wiberg's lateral center-edge angle and Lequesne's acetabular index--a coxometric update. Skeletal Radiol. 2012; 41:1273–1278.20. Eklöf O, Ringertz H, Samuelsson L. The percentage of migration as indicator of femoral head position. Acta Radiol. 1988; 29:363–366.21. Bonett DG. Sample size requirements for estimating intraclass correlations with desired precision. Stat Med. 2002; 21:1331–1335.22. Park MS, Kim SJ, Chung CY, Choi IH, Lee SH, Lee KM. Statistical consideration for bilateral cases in orthopaedic research. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010; 92:1732–1737.23. Lee KM, Lee J, Chung CY, Ahn S, Sung KH, Kim TW, Lee HJ, Park MS. Pitfalls and important issues in testing reliability using intraclass correlation coefficients in orthopaedic research. Clin Orthop Surg. 2012; 4:149–155.24. Shrout PE, Fleiss JL. Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull. 1979; 86:420–428.25. Foroohar A, McCarthy JJ, Yucha D, Clarke S, Brey J. Head-shaft angle measurement in children with cerebral palsy. J Pediatr Orthop. 2009; 29:248–250.26. Robin J, Graham HK, Selber P, Dobson F, Smith K, Baker R. Proximal femoral geometry in cerebral palsy: a population-based cross-sectional study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008; 90:1372–1379.27. Reimers J, Bialik V. Influence of femoral rotation on the radiological coverage of the femoral head in children. Pediatr Radiol. 1981; 10:215–218.28. Dobson F, Boyd RN, Parrott J, Nattrass GR, Graham HK. Hip surveillance in children with cerebral palsy. Impact on the surgical management of spastic hip disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84:720–726.29. Reimers J. The stability of the hip in children. A radiological study of the results of muscle surgery in cerebral palsy. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 1980; 184:1–100.30. Parrott J, Boyd RN, Dobson F, Lancaster A, Love S, Oates J, Wolfe R, Nattrass GR, Graham HK. Hip displacement in spastic cerebral palsy: repeatability of radiologic measurement. J Pediatr Orthop. 2002; 22:660–667.31. Scrutton D, Baird G, Smeeton N. Hip dysplasia in bilateral cerebral palsy: incidence and natural history in children aged 18 months to 5 years. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2001; 43:586–600.32. Terjesen T. The natural history of hip development in cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2012; 54:951–957.33. Davids JR, Marshall AD, Blocker ER, Frick SL, Blackhurst DW, Skewes E. Femoral anteversion in children with cerebral palsy. Assessment with two and three-dimensional computed tomography scans. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85-A:481–488.34. Sauser DD, Hewes RC, Root L. Hip changes in spastic cerebral palsy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1986; 146:1219–1222.35. Settecerri JJ, Karol LA. Effectiveness of femoral varus osteotomy in patients with cerebral palsy. J Pediatr Orthop. 2000; 20:776–780.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Obturator Nerve Block on Hip Lateralization in Low Functioning Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy
- Hip Migration after Selective Posterior Rhizotomy in Cerebral Palsy
- Surgical treatment for adduction contracture of hip in spastic cerebral palsy
- Early Subluxation of Hip in Children with Cerebral Palsy
- Plain Radiography of the Hip: A Review of Radiographic Techniques and Image Features