J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Jul;31(7):1082-1088. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.7.1082.
Early Changes in the Serotype Distribution of Invasive Pneumococcal Isolates from Children after the Introduction of Extended-valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines in Korea, 2011-2013
- Affiliations
-
- 1Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hoanlee@snu.ac.kr
- 2Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea.
- 3College of Medicine, the Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 4School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Eulji University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 8Hanyang University, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 9Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 10Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University, Incheon, Korea.
- 11Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 12Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 13Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 14Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 15Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 16CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seoul, Korea.
- 17Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- 18College of Medicine, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea.
- 19Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 20Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 21Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 22Changwon Fatima Hospital, Changwon, Korea.
- 23Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea.
- 24Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 25University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 26Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 2373727
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.7.1082
Abstract
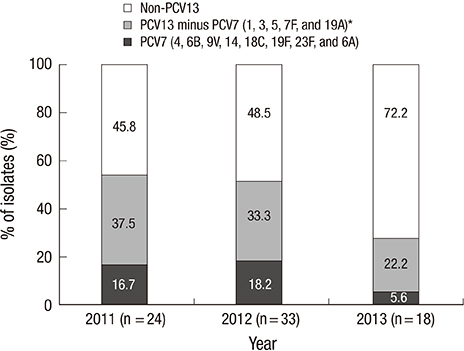
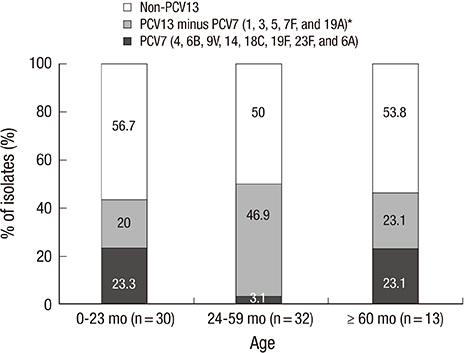
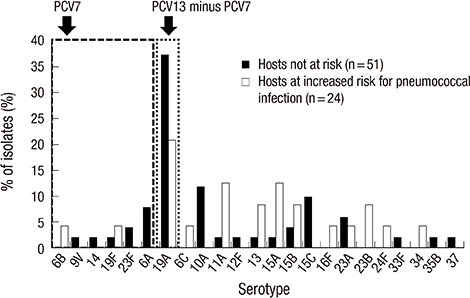
- This study was performed to measure early changes in the serotype distribution of pneumococci isolated from children with invasive disease during the 3-year period following the introduction of 10- and 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs) in Korea. From January 2011 to December 2013 at 25 hospitals located throughout Korea, pneumococci were isolated among children who had invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD). Serotypes were determined using the Quellung reaction, and the change in serotype distribution was analyzed. Seventy-five cases of IPD were included. Eighty percent of patients were aged 3-59 months, and 32% had a comorbidity that increased the risk of pneumococcal infection. The most common serotypes were 19A (32.0%), 10A (8.0%), and 15C (6.7%). The PCV7 serotypes (4, 6B, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F, 23F, and 6A) accounted for 14.7% of the total isolates and the PCV13 minus PCV7 types (1, 3, 5, 7F and 19A) accounted for 32.0% of the total isolates. Serotype 19A was the only serotype in the PCV13 minus PCV7 group. The proportion of serotype 19A showed decreasing tendency from 37.5% in 2011 to 22.2% in 2013 (P = 0.309), while the proportion of non-PCV13 types showed increasing tendency from 45.8% in 2011 to 72.2% in 2013 (P = 0.108). Shortly after the introduction of extended-valent PCVs in Korea, serotype 19A continued to be the most common serotype causing IPD in children. Subsequently, the proportion of 19A decreased, and non-vaccine serotypes emerged as an important cause of IPD. The impact of extended-valent vaccines must be continuously monitored.
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Bacteremia/complications/diagnosis
Child
Child, Preschool
Female
Hospitals
Humans
Infant
Male
Pneumococcal Infections/microbiology/*prevention & control
Pneumococcal Vaccines/*immunology
Republic of Korea
Serotyping
Streptococcus pneumoniae/*classification/isolation & purification
Vaccines, Conjugate/*immunology
Pneumococcal Vaccines
Vaccines, Conjugate
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
광범위 약제내성
Streptococcus pneumoniae 에 의한 급성 폐렴구균 파종성 감염 1례: 뇌수막염과 화농성 관절염 동반
Hye Jin Shi, Jin Yang Baek, Doo Ryeon Chung, Kihyun Kim, Kyong Ran Peck, Cheol-In Kang
Korean J Healthc Assoc Infect Control Prev. 2022;27(1):80-84. doi: 10.14192/kjicp.2022.27.1.80.
Reference
-
1. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. Preventing pneumococcal disease among infants and young children. Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2000; 49:1–35.2. Nuorti JP, Whitney CG; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Prevention of pneumococcal disease among infants and children - use of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine and 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine - recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2010; 59:1–18.3. Moore MR, Link-Gelles R, Schaffner W, Lynfield R, Lexau C, Bennett NM, Petit S, Zansky SM, Harrison LH, Reingold A, et al. Effect of use of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in children on invasive pneumococcal disease in children and adults in the USA: analysis of multisite, population-based surveillance. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015; 15:301–309.4. Lee JH, Cho HK, Kim KH, Kim CH, Kim DS, Kim KN, Cha SH, Oh SH, Hur JK, Kang JH, et al. Etiology of invasive bacterial infections in immunocompetent children in Korea (1996-2005): a retrospective multicenter study. J Korean Med Sci. 2011; 26:174–183.5. Choe YJ, Yang JJ, Park SK, Choi EH, Lee HJ. Comparative estimation of coverage between national immunization program vaccines and non-NIP vaccines in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2013; 28:1283–1288.6. Cho EY, Lee H, Choi EH, Kim YJ, Eun BW, Cho YK, Kim YK, Jo DS, Lee HS, Lee J, et al. Serotype distribution and antibiotic resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolated from invasive infections after optional use of the 7-valent conjugate vaccine in Korea, 2006-2010. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014; 78:481–486.7. Pai R, Gertz RE, Beall B. Sequential multiplex PCR approach for determining capsular serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 2006; 44:124–131.8. Yun KW, Cho EY, Hong KB, Choi EH, Lee HJ. Streptococcus pneumoniae type determination by multiplex polymerase chain reaction. J Korean Med Sci. 2011; 26:971–978.9. Choi EH, Lee HJ, Cho EY, Oh CE, Eun BW, Lee J, Kim MJ. Prevalence and genetic structures of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 6D, South Korea. Emerg Infect Dis. 2010; 16:1751–1753.10. Ben-Shimol S, Greenberg D, Givon-Lavi N, Schlesinger Y, Somekh E, Aviner S, Miron D, Dagan R. Early impact of sequential introduction of 7-valent and 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on IPD in Israeli children <5 years: an active prospective nationwide surveillance. Vaccine. 2014; 32:3452–3459.11. Choi EH, Kim SH, Eun BW, Kim SJ, Kim NH, Lee J, Lee HJ. Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 19A in children, South Korea. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008; 14:275–281.12. Waight PA, Andrews NJ, Ladhani SN, Sheppard CL, Slack MP, Miller E. Effect of the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on invasive pneumococcal disease in England and Wales 4 years after its introduction: an observational cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015; 15:535–543.13. Olarte L, Barson WJ, Barson RM, Lin PL, Romero JR, Tan TQ, Givner LB, Bradley JS, Hoffman JA, Hultén KG, et al. Impact of the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on pneumococcal meningitis in US children. Clin Infect Dis. 2015; 61:767–775.14. Guevara M, Ezpeleta C, Gil-Setas A, Torroba L, Beristain X, Aguinaga A, García-Irure JJ, Navascués A, García-Cenoz M, Castilla J. Reduced incidence of invasive pneumococcal disease after introduction of the 13-valent conjugate vaccine in Navarre, Spain, 2001-2013. Vaccine. 2014; 32:2553–2562.15. Iroh Tam PY, Madoff LC, Coombes B, Pelton SI. Invasive pneumococcal disease after implementation of 13-valent conjugate vaccine. Pediatrics. 2014; 134:210–217.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy and effectiveness of extended-valency pneumococcal conjugate vaccines
- A case of fatal pneumococcal 19A meningoencephalitis despite administration of seven-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines
- Recommendation for use of the newly introduced pneumococcal protein conjugate vaccines in Korea
- Direct and Indirect Effects of Pneumococcal Protein Conjugate Vaccine
- Pneumococcal vaccine