J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Jul;31(7):1037-1041. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.7.1037.
The Poisoning Information Database Covers a Large Proportion of Real Poisoning Cases in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Emergency Medicine, Korea University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Emergency Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. emstar@yuhs.ac
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea.
- 4Department of Emergency Medicine, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 5Department of Emergency Medicine, Wonju College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Wonju, Korea.
- 6Department of Emergency Medicine, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- 7Department of Emergency Medicine, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 8Department of Emergency Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Cheongju, Korea.
- 9Department of Emergency Medicine, College of Medicine, Catholic University of Daegu, Daegu, Korea.
- 10Department of Emergency Medicine, Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea.
- 11Department of Emergency Medicine, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea.
- 12Department of Emergency Medicine, School of Medicine, CHA University, Gumi, Korea.
- 13Department of Emergency Medicine, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 14Department of Emergency Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 15Department of Emergency Medicine, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- 16Department of Emergency Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 17Department of Emergency Medicine, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea.
- 18Department of Emergency Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 19Department of Emergency Medicine, Jeju National University, Jeju, Korea.
- KMID: 2373720
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.7.1037
Abstract
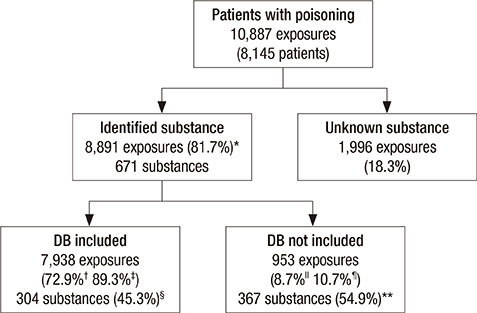
- The poisoning information database (PIDB) provides clinical toxicological information on commonly encountered toxic substances in Korea. The aim of this study was to estimate the coverage rate of the PIDB by comparing the database with the distribution of toxic substances that real poisoning patients presented to 20 emergency departments. Development of the PIDB started in 2007, and the number of toxic substances increased annually from 50 to 470 substances in 2014. We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of patients with toxic exposure who visited 20 emergency departments in Korea from January to December 2013. Identified toxic substances were classified as prescription drug, agricultural chemical, household product, animal or plant, herbal drug, or other. We calculated the coverage rate of the PIDB for both the number of poisoning cases and the kinds of toxic substances. A total of 10,887 cases of intoxication among 8,145 patients was collected. The 470 substances registered in the PIDB covered 89.3% of 8,891 identified cases related to poisoning, while the same substances only covered 45.3% of the 671 kinds of identified toxic substances. According to category, 211 prescription drugs, 58 agricultural chemicals, 28 household products, and 32 animals or plants were not covered by the PIDB. This study suggested that the PIDB covered a large proportion of real poisoning cases in Korea. However, the database should be continuously extended to provide information for even rare toxic substances.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Animals
Animals, Poisonous
Child
Child, Preschool
Databases, Factual
Drugs, Chinese Herbal/poisoning
Emergency Service, Hospital
Female
Humans
Infant
Male
Middle Aged
Pesticides/poisoning
Plants, Medicinal/poisoning
Poisoning/*epidemiology
Prescription Drugs/poisoning
Republic of Korea
Retrospective Studies
Young Adult
Drugs, Chinese Herbal
Pesticides
Prescription Drugs
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
The Characteristics of Elderly Individuals Who Attempted Suicide by Poisoning: a Nationwide Cross-sectional Study in Korea
Sun Jin Song, Gwan Jin Park, Ji Han Lee, Sang Chul Kim, Hoon Kim, Suk Woo Lee
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(35):e286. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e286.Characteristics of Drugs Ingested for Suicide Attempts in the Elderly
Ji Yeon Lim, Duk Hee Lee
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(11):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e86.
Reference
-
1. Rumack BH. POISINDEX: an emergency poison management system. Drug Inf J. 1975; 9:171–180.2. Bateman DN, Good AM, Laing WJ, Kelly CA. TOXBASE: poisons information on the internet. Emerg Med J. 2002; 19:31–34.3. Luke S, Fountain JS, Reith DM, Braitberg G, Cruickshank J. Use of poisons information resources and satisfaction with electronic products by Victorian emergency department staff. Emerg Med Australas. 2014; 26:494–499.4. National Institute of Food and Drug Safety Evaluation (KR). Tox-Info [Internet]. accessed on 3 January 2016. Available at http://www.nifds.go.kr/toxinfo/Index.5. So BH, Lee MJ, Kim H, Moon JM, Park KH, Sung AJ, Yeom SR, Oh SB, You JY, Lee KW, et al. 2008 Database of Korean toxic exposures: a preliminary study. J Korean Soc Clin Toxicol. 2010; 8:51–60.6. Oh BJ, Kim W, Cho GC, Kang HD, Shon YD, Lee JH, Lim KS. Research on poisoning data collection using toxic exposure surveillance system: retrospective preliminary survey. J Korean Soc Clin Toxicol. 2006; 4:32–43.7. Lee JW, Hwang IW, Kim JW, Moon HJ, Kim KH, Park S, Gil HW, Hong SY. Common pesticides used in suicide attempts following the 2012 paraquat ban in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2015; 30:1517–1521.8. Cho MK, Kim YW, Lee KR, Lee KW, Lee JY, Cho GC, Cho J, Kim HJ, Kim SH, Chung SP, et al. Clinical characteristics of intentional carbon monoxide poisoning. J Korean Soc Clin Toxicol. 2012; 10:73–79.9. Choi BH, Jeon J, Ryoo SM, Seo DW, Kim WY, Oh BJ, Lim KS, Sohn CH. Recent epidemiologic features of carbon monoxide poisoning in Korea: a single center retrospective cohort study. J Korean Soc Clin Toxicol. 2012; 10:80–85.10. Mowry JB, Spyker DA, Cantilena LR Jr, McMillan N, Ford M. 2013 annual report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers' National Poison Data System (NPDS): 31st annual report. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2014; 52:1032–1283.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Animal poisoning in Korea in 1974-June 2013
- Pulmonary edema in acute carbon monoxide poisoning
- Understanding the status of acute poisoning patients who visited the emergency room in 2018: using sample in-depth survey data
- Carbon Monoxide Poisoning in the Unusual Circumstance: Four Cases Report
- Acute Occupational Poisoning in Korea