J Korean Med Sci.
2016 May;31(5):817-821. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.5.817.
The First Successful Heart-Lung Transplant in a Korean Child with Humidifier Disinfectant-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Asan Medical Center Children's Hospital, College of Medicine, University of Ulsan, Seoul, Korea. jyu3922@gmail.com
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Korea Cancer Center Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- 4Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2373684
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.5.817
Abstract
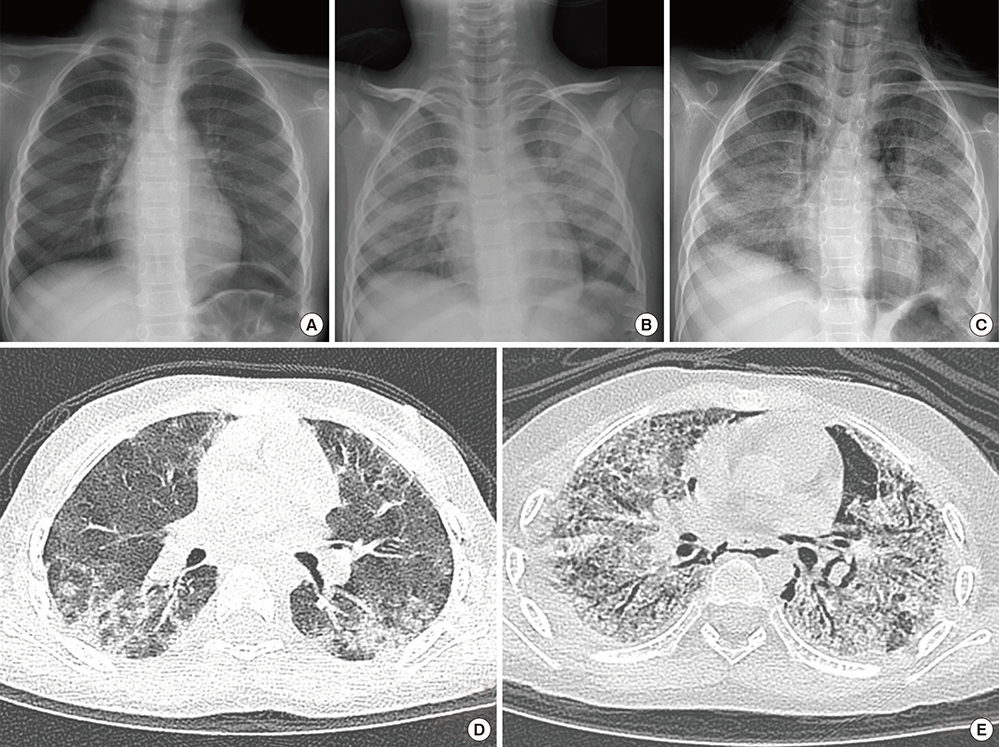
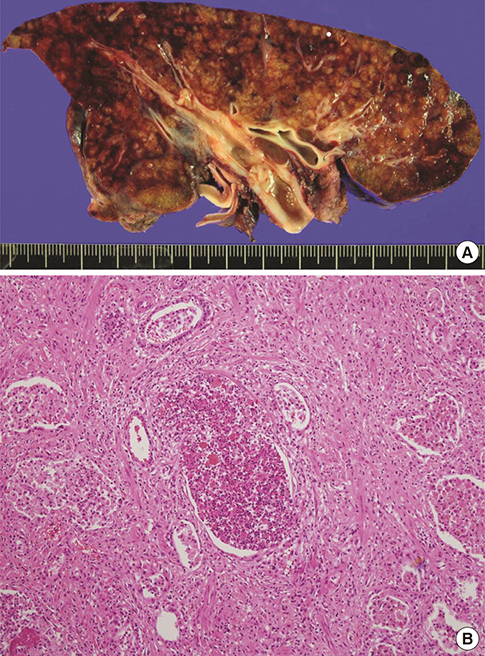
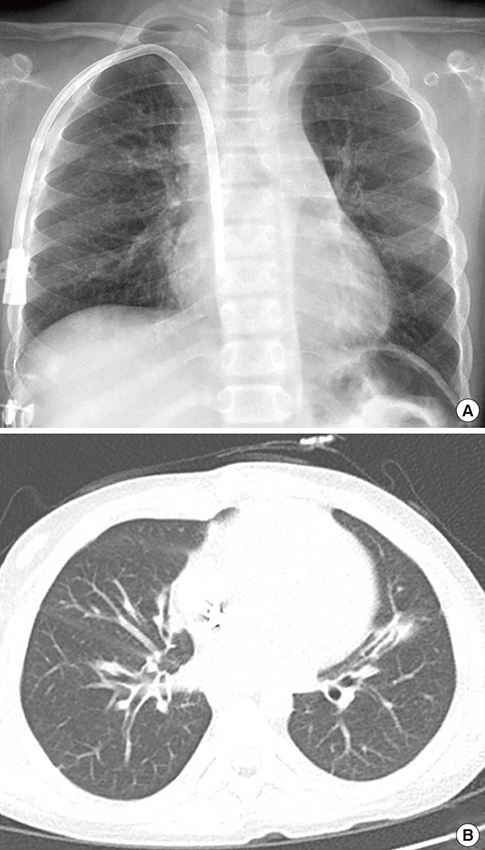
- From 2006 to 2011, an outbreak of a particular type of childhood interstitial lung disease occurred in Korea. The condition was intractable and progressed to severe respiratory failure, with a high mortality rate. Moreover, in several familial cases, the disease affected young women and children simultaneously. Epidemiologic, animal, and post-interventional studies identified the cause as inhalation of humidifier disinfectants. Here, we report a 4-year-old girl who suffered from severe progressive respiratory failure. She could survive by 100 days of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support and finally, underwent heart-lung transplantation. This is the first successful pediatric heart-lung transplantation carried out in Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Child, Preschool
Disinfectants/toxicity
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation
Female
Humans
*Humidifiers
Lung/drug effects/pathology
Lung Diseases, Interstitial/*chemically induced/pathology/*therapy
*Lung Transplantation
Republic of Korea
Respiratory Rate
Retrospective Studies
Thorax/diagnostic imaging
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Disinfectants
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Pediatric Case Report on an Interstitial Lung Disease with a Novel Mutation of SFTPC Successfully Treated with Lung Transplantation
Ji Soo Park, Yun Jung Choi, Young Tae Kim, Samina Park, Jong-Hee Chae, June Dong Park, Yeon Jin Cho, Woo-Sun Kim, Moon-Woo Seong, Sung-Hye Park, Dohee Kwon, Doo Hyun Chung, Dong In Suh
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(22):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e159.Literature review and future strategies of childhood respiratory diseases in Korea
Man Yong Han, Hai Lee Chung, Young Min Ahn, Jung Yeon Shim
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(Suppl 1):S66-S76. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.S1.S66.
Reference
-
1. Fan LL, Deterding RR, Langston C. Pediatric interstitial lung disease revisited. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2004; 38:369–378.2. Dinwiddie R, Wallis C. Paediatric interstitial lung disease (PILD)—an update. Curr Paediatr. 2006; 16:230–236.3. Clement A, Eber E. Interstitial lung diseases in infants and children. Eur Respir J. 2008; 31:658–666.4. Lee E, Seo JH, Kim HY, Yu J, Jhang WK, Park SJ, Kwon JW, Kim BJ, Do KH, Cho YA, et al. Toxic inhalational injury-associated interstitial lung disease in children. J Korean Med Sci. 2013; 28:915–923.5. Lee E, Seo JH, Kim HY, Yu J, Song JW, Park YS, Jang SJ, Do KH, Kwon J, Park SW, et al. Two series of familial cases with unclassified interstitial pneumonia with fibrosis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:240–244.6. Kim KW, Ahn K, Yang HJ, Lee S, Park JD, Kim WK, Kim JT, Kim HH, Rha YH, Park YM, et al. Humidifier disinfectant-associated children’s interstitial lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014; 189:48–56.7. Yang HJ, Kim HJ, Yu J, Lee E, Jung YH, Kim HY, Seo JH, Kwon GY, Park JH, Gwack J, et al. Inhalation toxicity of humidifier disinfectants as a risk factor of children’s interstitial lung disease in Korea: a case-control study. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e64430.8. Ohnuma A, Yoshida T, Tajima H, Fukuyama T, Hayashi K, Yamaguchi S, Ohtsuka R, Sasaki J, Fukumori J, Tomita M, et al. Didecyldimethylammonium chloride induces pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in mice. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2010; 62:643–651.9. Lee JH, Kim YH, Kwon JH. Fatal misuse of humidifier disinfectants in Korea: importance of screening risk assessment and implications for management of chemicals in consumer products. Environ Sci Technol. 2012; 46:2498–2500.10. Kim BJ, Kim HA, Song YH, Yu J, Kim S, Park SJ, Kim KW, Kim KE, Kim DS, Park JD, et al. Nationwide surveillance of acute interstitial pneumonia in Korea. Korean J Pediatr. 2009; 52:324–329.11. Huddleston CB. Pediatric lung transplantation. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2006; 15:199–207.12. Kirkby S, Hayes D Jr. Pediatric lung transplantation: indications and outcomes. J Thorac Dis. 2014; 6:1024–1031.13. Huddleston CB. Pediatric lung transplantation. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2011; 13:68–78.14. Benden C, Edwards LB, Kucheryavaya AY, Christie JD, Dipchand AI, Dobbels F, Kirk R, Lund LH, Rahmel AO, Yusen RD, et al. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Sixteenth Official Pediatric Lung and Heart-Lung Transplantation Report--2013; focus theme: age. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2013; 32:989–997.15. Yusen RD, Christie JD, Edwards LB, Kucheryavaya AY, Benden C, Dipchand AI, Dobbels F, Kirk R, Lund LH, Rahmel AO, et al. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirtieth Adult Lung and Heart-Lung Transplant Report--2013; focus theme: age. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2013; 32:965–978.16. Marshall SE, Kramer MR, Lewiston NJ, Starnes VA, Theodore J. Selection and evaluation of recipients for heart-lung and lung transplantation. Chest. 1990; 98:1488–1494.17. Alvarez A, Algar FJ, Santos F, Lama R, Baamonde C, Cerezo F, Salvatierra A. Pediatric lung transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2005; 37:1519–1522.18. Couetil JP, Tolan MJ, Loulmet DF, Guinvarch A, Chevalier PG, Achkar A, Birmbaum P, Carpentier AF. Pulmonary bipartitioning and lobar transplantation: a new approach to donor organ shortage. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1997; 113:529–537.19. Aigner C, Mazhar S, Jaksch P, Seebacher G, Taghavi S, Marta G, Wisser W, Klepetko W. Lobar transplantation, split lung transplantation and peripheral segmental resection--reliable procedures for downsizing donor lungs. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004; 25:179–183.20. Santos F, Lama R, Alvarez A, Algar FJ, Quero F, Cerezo F, Salvatierra A, Baamonde C. Pulmonary tailoring and lobar transplantation to overcome size disparities in lung transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2005; 37:1526–1529.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Major concerns regarding lung injury and related health conditions caused by the use of humidifier disinfectant
- Frequency of Humidifier and Humidifier Disinfectant Usage in Gyeonggi Provine
- Problems with diagnostic criteria for humidifier disinfectant lung injury (HDLI): two cases of radiologically improved HDLI
- Health Effects Associated With Humidifier Disinfectant Use: A Systematic Review for Exploration
- Mental health impact on a humidifier disinfectant disaster victim: a case report