Ann Lab Med.
2017 Mar;37(2):162-165. 10.3343/alm.2017.37.2.162.
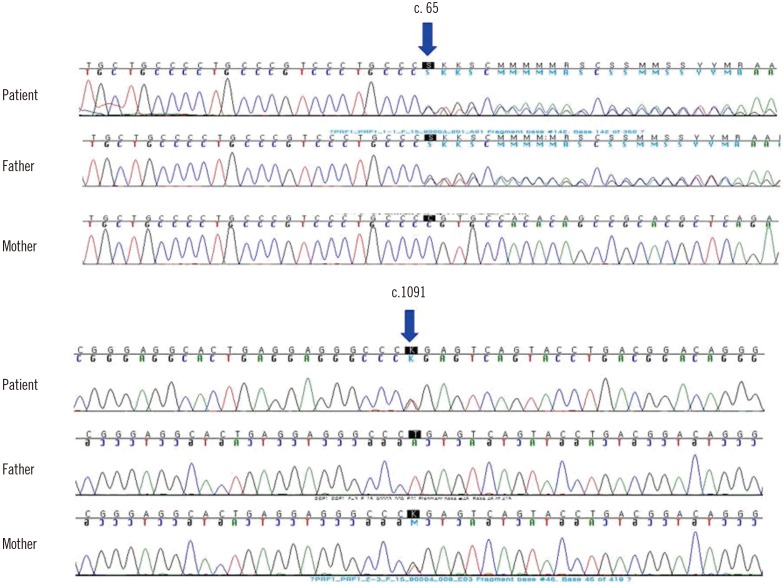
Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Type 2 in a Korean Infant With Compound Heterozygous PRF1 Defects Involving a PRF1 Mutation, c.1091T>G
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan, College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. yucho@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, University of Ulsan, College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2373636
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2017.37.2.162
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
-
Asian Continental Ancestry Group/*genetics
Base Sequence
Bone Marrow Cells/cytology/pathology
Cytomegalovirus Infections/diagnosis
Epstein-Barr Virus Infections/diagnosis
Female
Flow Cytometry
Heterozygote
Humans
Infant
Killer Cells, Natural/cytology/immunology
Lymphohistiocytosis, Hemophagocytic/*diagnosis/genetics
Perforin/*genetics
Phagocytosis
Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide
Republic of Korea
Sequence Analysis, DNA
Perforin
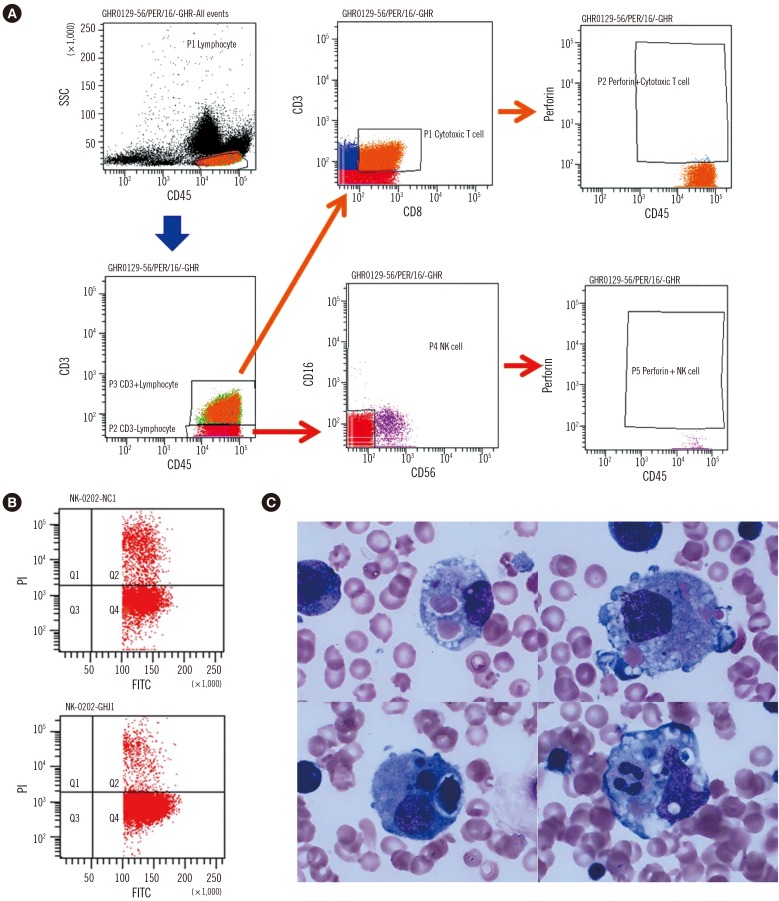
Figure
Reference
-
1. Usmani GN, Woda BA, Newburger PE. Advances in understanding the pathogenesis of HLH. Br J Haematol. 2013; 161:609–622. PMID: 23577835.2. Kogawa K, Lee SM, Villanueva J, Marmer D, Sumegi J, Filipovich AH. Perforin expression in cytotoxic lymphocytes from patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and their family members. Blood. 2002; 99:61–66. PMID: 11756153.3. Chung HJ, Park CJ, Lim JH, Jang S, Chi HS, Im HJ, et al. Establishment of a reference interval for natural killer cell activity through flow cytometry and its clinical application in the diagnosis of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Int J Lab Hematol. 2010; 32:239–247. PMID: 19614711.4. Henter JI, Horne A, Aricó M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Imashuku S, et al. HLH-2004: Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2007; 48:124–131. PMID: 16937360.5. Seo JY, Song JS, Lee KO, Won HH, Kim JW, Kim SH, et al. Founder effects in two predominant intronic mutations of UNC13D, c.118-308C>T and c.754-1G>C underlie the unusual predominance of type 3 familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL3) in Korea. Ann Hematol. 2013; 92:357–364. PMID: 23180437.6. Yoon HS, Kim HJ, Yoo KH, Sung KW, Koo HH, Kang HJ, et al. UNC13D is the predominant causative gene with recurrent splicing mutations in Korean patients with familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Haematologica. 2010; 95:622–626. PMID: 20015888.7. Kim JY, Shin JH, Sung SI, Kim JK, Jung JM, Ahn SY, et al. A novel PRF1 gene mutation in a fatal neonate case with type 2 familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Korean J Pediatr. 2014; 57:50–53. PMID: 24578718.8. Trizzino A, zur Stadt U, Ueda I, Risma K, Janka G, Ishii E, et al. Genotype-phenotype study of familial haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis due to perforin mutations. J Med Genet. 2008; 45:15–21. PMID: 17873118.9. Ishii E, Ohga S, Imashuku S, Kimura N, Ueda I, Morimoto A, et al. Review of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) in children with focus on Japanese experiences. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2005; 53:209–223. PMID: 15718147.10. Chiang GP, Li CK, Lee V, Cheng FW, Leung AW, Imashuku S, et al. Perforin gene mutation in familial haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: the first reported case from Hong Kong. Hong Kong Med J. 2014; 20:339–342. PMID: 25104007.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A novel PRF1 gene mutation in a fatal neonate case with type 2 familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
- Genetic and clinical characteristics of pediatric patients with familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
- Novel Mutations in the UNC13D Gene Carried by a Chinese Neonate with Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
- Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Adults: Overview, Diagnosis, and Treatment
- Griscelli syndrome type 2: a novel mutation in RAB27A gene with different clinical features in 2 siblings: a diagnostic conundrum