Ann Lab Med.
2016 May;36(3):263-265. 10.3343/alm.2016.36.3.263.
Minor BCR-ABL1-Positive Acute Myeloid Leukemia Associated With the NPM1 Mutation and FLT3 Internal Tandem Duplication
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seonam University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. sungran@ajou.ac.kr
- 3SQ Laboratory, Yongin, Korea.
- 4Department of Hematology-Oncology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 5Green Cross Laboratories, Yongin, Korea.
- 6Department of Pathology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 7Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2373538
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2016.36.3.263
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Base Sequence
Bone Marrow/metabolism/pathology
DNA Mutational Analysis
Female
Fusion Proteins, bcr-abl/*genetics
Gene Duplication
Humans
In Situ Hybridization, Fluorescence
Leukemia, Myeloid, Acute/diagnosis/*genetics
Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction
Mutation
Nuclear Proteins/*genetics
Philadelphia Chromosome
fms-Like Tyrosine Kinase 3/*genetics
Fusion Proteins, bcr-abl
Nuclear Proteins
fms-Like Tyrosine Kinase 3
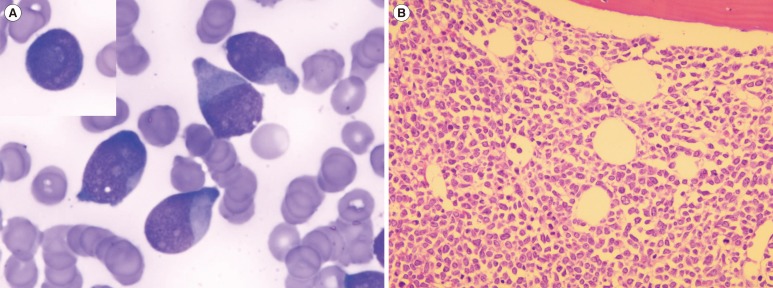
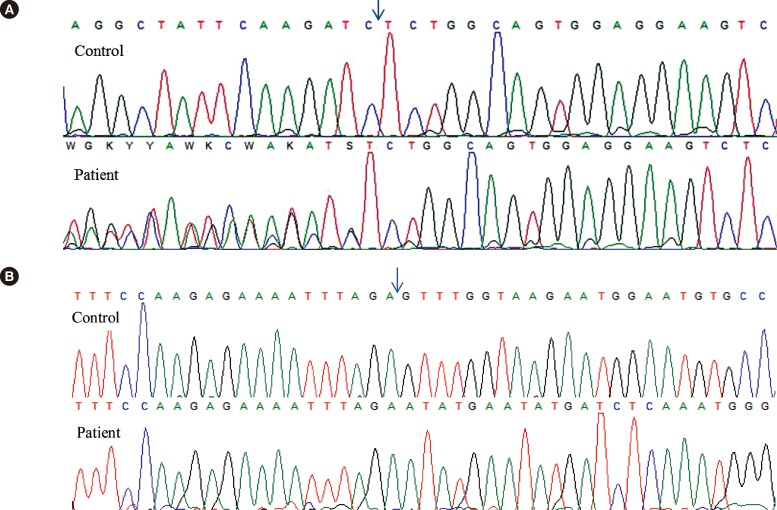
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nacheva EP, Grace CD, Brazma D, Gancheva K, Howard-Reeves J, Rai L, et al. Does BCR/ABL1 positive acute myeloid leukaemia exist? Br J Haematol. 2013; 161:541–550. PMID: 23521501.2. Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, Brunning RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A, et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood. 2009; 114:937–951. PMID: 19357394.
Article3. Konoplev S, Yin CC, Kornblau SM, Kantarjian HM, Konopleva M, Andreeff M, et al. Molecular characterization of de novo Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2013; 54:138–144. PMID: 22691121.4. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, editors. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC;2008. p. 130–139.5. Soupir CP, Vergilio JA, Dal Cin P, Muzikansky A, Kantarjian H, Jones D, et al. Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute myeloid leukemia: a rare aggressive leukemia with clinicopathologic features distinct from chronic myeloid leukemia in myeloid blast crisis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2007; 127:642–650. PMID: 17369142.6. Falini B, Mecucci C, Tiacci E, Alcalay M, Rosati R, Pasqualucci L, et al. Cytoplasmic nucleophosmin in acute myelogenous leukemia with a normal karyotype. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:254–266. PMID: 15659725.
Article7. Watkins DB, Hughes TP, White DL, D'Andrea RJ. NPM1 mutations occur rarely or not at all in chronic myeloid leukaemia patients in chronic phase or blast crisis. Leukemia. 2013; 27:489–490. PMID: 22791379.8. Bacher U, Haferlach T, Alpermann T, Zenger M, Hochhaus A, Beelen DW, et al. Subclones with the t(9;22)/BCR-ABL1 rearrangement occur in AML and seem to cooperate with distinct genetic alterations. Br J Haematol. 2011; 152:713–720. PMID: 21275954.9. Park BG, Chi HS, Jang S, Park CJ, Kim DY, Lee JH, et al. Association of cup-like nuclei in blasts with FLT3 and NPM1 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Ann Hematol. 2013; 92:451–457. PMID: 23238897.10. Jain P, Vega-Vazquez F, Faderl S. "Cup-like" blasts and NPM1 and FLT3 (ITD) mutations in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Int J Hematol. 2013; 98:3. PMID: 23690292.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prognostic significance of nucleophosmin mutations and FLT3 internal tandem duplication in adult patients with cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia
- Prognostic Significance of FLT3 Internal Tandem Duplication in Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Normal Karyotype
- A Case of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia with Co-existence of BCR-ABL1 and PML-RARA Rearrangements Detected by PCR
- Favorable long-term survival using consolidation chemotherapy without allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia with wild-type NPM1 without FLT3-ITD
- Prevalence of FLT3 Internal Tandem Duplication in Adult Acute Myelogenous Leukemia