Ann Lab Med.
2016 Jan;36(1):9-14. 10.3343/alm.2016.36.1.9.
Epidemiological Study of Erythromycin-Resistant Streptococcus pyogenes From Korea and Japan by emm Genotyping and Multilocus Sequence Typing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Laboratory of Infectious Diseases, Kitasato Institute for Life Sciences & Graduate School of Infection Control Sciences, Kitasato University, Tokyo, Japan.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. sjkim8239@hanmail.net
- 3Department of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Nara Medical University, Nara, Japan.
- 4Department of Infection Control and Laboratory Diagnostics, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine, Miyagi, Japan.
- KMID: 2373491
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2016.36.1.9
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
We determined the epidemiological characteristics of erythromycin (EM)-resistant Streptococcus pyogenes (group A streptococci, GAS) strains isolated from Korea and Japan, using emm genotyping and multilocus sequence typing (MLST).
METHODS
Clinical isolates of GAS had been collected from 1992 to 2012 in Korea and from 2004 to 2009 in Japan. EM resistance was determined by the microdilution method, and resistance genotypes were assessed by PCR. The emm genotyping and MLST were performed by DNA sequencing.
RESULTS
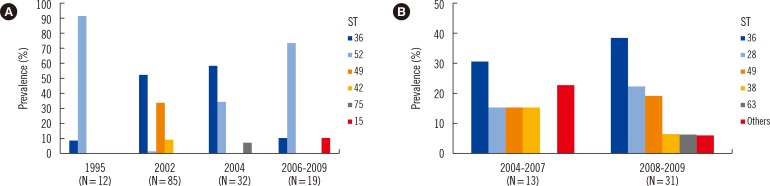
The emm genotypes and sequence types (STs) were concordant in 143 (85.1%) of 168 EM-resistant GAS strains from Korea. ST36/emm12 (35.1%), ST52/emm28 (22.6%), and ST49/emm75 (16.1%) were the most common types. Most of the ST36 (93.9%) and ST52 (95.8%) strains harbored erm(B), whereas strains ST49, ST42, and ST15 contained mef(A). The concordance between emm genotypes and STs was 41 (93.2%) among 44 EM-resistant GAS strains from Japan. ST36/emm12 (34.1%), ST49/emm75 (18.2%), and ST28/emm1 (15.9%) were the major types. ST36 isolates harbored either erm(B) (56.3%) or mef(A) (37.5%), whereas isolates ST28, ST49, and ST38 carried only mef(A). The proportion of erm(B) and mef(A) was 66.1% and 33.3% in Korea and 22.7% and 68.2% in Japan, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
The common STs in Korea and Japan were ST36 and ST49, whereas ST52 was present only in Korea and ST28 only in Japan. Genotype erm(B) was predominant in Korea, whereas mef(A) was frequent in Japan. There were differences between Korea and Japan regarding the frequencies of emm genotypes, STs, and EM resistance genes among the EM-resistant GAS.
MeSH Terms
-
Anti-Bacterial Agents/*pharmacology/therapeutic use
Bacterial Proteins/*genetics
Bacterial Typing Techniques
*Drug Resistance, Bacterial
Epidemiologic Studies
Erythromycin/*pharmacology/therapeutic use
Genotype
Humans
Japan/epidemiology
Microbial Sensitivity Tests
Multilocus Sequence Typing
Republic of Korea/epidemiology
Streptococcal Infections/drug therapy/*microbiology
Streptococcus pyogenes/drug effects/*genetics/isolation & purification
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Bacterial Proteins
Erythromycin
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Comparing Genomic Characteristics of
Streptococcus pyogenes Associated with Invasiveness over a 20-year Period in Korea
Hyoshim Shin, Takashi Takahashi, Seungjun Lee, Eun Hwa Choi, Takahiro Maeda, Yasuto Fukushima, Sunjoo Kim
Ann Lab Med. 2022;42(4):438-446. doi: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.4.438.
Reference
-
1. Cunningham MW. Pathogenesis of group A streptococcal infections and their sequelae. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008; 609:29–42. PMID: 18193655.2. Takahashi T, Sunaoshi K, Sunakawa K, Fujishima S, Watanabe H, Ubukata K. Clinical aspects of invasive infections with Streptococcus dysgalactiae ssp. equisimilis in Japan: differences with respect to Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus agalactiae infections. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010; 16:1097–1103. PMID: 19732082.3. Cha S, Lee H, Lee K, Hwang K, Bae S, Lee Y. The emergence of erythromycin-resistant Streptococcus pyogenes in Seoul, Korea. J Infect Chemother. 2001; 7:81–86. PMID: 11455497.4. Kim S, Lee NY. Antibiotic resistance and genotypic characteristics of group A streptococci associated with acute pharyngitis in Korea. Microb Drug Resist. 2004; 10:300–305. PMID: 15650374.5. Koh E, Kim S. Decline in erythromycin resistance in group A Streptococci from acute pharyngitis due to changes in the emm genotypes rather than restriction of antibiotic use. Korean J Lab Med. 2010; 30:485–490. PMID: 20890080.6. Enright MC, Spratt BG, Kalia A, Cross JH, Bessen DE. Multilocus sequence typing of Streptococcus pyogenes and the relationships between emm type and clone. Infect Immun. 2001; 69:2416–2427. PMID: 11254602.7. Wajima T, Chiba N, Morozumi M, Shouji M, Sunaoshi K, Sugita K, et al. Prevalence of macrolide resistance among group A streptococci isolated from pharyngotonsillitis. Microb Drug Resist. 2014; 20:431–435. PMID: 24571416.8. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Twenty-second Informational supplement, M100-S23. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2013.9. Arai K, Hirakata Y, Yano H, Kanamori H, Endo S, Hirotani A, et al. Emergence of fluoroquinolone-resistant Streptococcus pyogenes in Japan by a point mutation leading to a new amino acid substitution. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011; 66:494–498. PMID: 21172783.10. Reinert RR, Lütticken R, Bryskier A, Al-Lahham A. Macrolide-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pyogenes in the pediatric population in Germany during 2000-2001. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003; 47:489–493. PMID: 12543648.11. Li Z, Sakota V, Jackson D, Franklin AR, Beall B. Array of M protein gene subtypes in 1064 recent invasive group A streptococcus isolates recovered from the active bacterial core surveillance. J Infect Dis. 2003; 188:1587–1592. PMID: 14624386.12. Robinson DA, Sutcliffe JA, Tewodros W, Manoharan A, Bessen DE. Evolution and global dissemination of macrolide-resistant group A streptococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006; 50:2903–2911. PMID: 16940080.13. Huang CY, Lai JF, Huang IW, Chen PC, Wang HY, Shiau YR, et al. Epidemiology and molecular characterization of macrolide-resistant Streptococcus pyogenes in Taiwan. J Clin Microbiol. 2014; 52:508–516. PMID: 24478481.14. Wajima T, Murayama SY, Sunaoshi K, Nakayama E, Sunakawa K, Ubukata K. Distribution of emm type and antibiotic susceptibility of group A streptococci causing invasive and noninvasive disease. J Med Microbiol. 2008; 57:1383–1388. PMID: 18927416.15. Chang H, Shen X, Huang G, Fu Z, Zheng Y, Wang L, et al. Molecular analysis of Streptococcus pyogenes strains isolated from Chinese children with pharyngitis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011; 69:117–122. PMID: 21251553.16. Wajima T, Morozumi M, Chiba N, Shouji M, Iwata S, Sakata H, et al. Associations of macrolide and fluoroquinolone resistance with molecular typing in Streptococcus pyogenes from invasive infections, 2010-2012. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013; 42:447–449. PMID: 23988719.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Epidemiology and Erythromycin Resistance of Streptococcus pyogenes in the Last 20 Years
- T Types, emm Genotypes and Antibiotic Resistance of Streptococcus pyogenes Isolated fromSchool Children in Jinju, 2006
- Molecular Genetic Characterization of Clinical Isolates of Streptococcus pyogenes
- emm Types and Clusters of Group A Streptococcus Causing Acute Pharyngitis in Changwon Korea, 2018–2019
- Molecular Epidemiological Features and Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis Isolates from Korea and Japan