Ann Lab Med.
2018 May;38(3):212-219. 10.3343/alm.2018.38.3.212.
Molecular Epidemiological Features and Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis Isolates from Korea and Japan
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chonbuk National University School of Medicine, Jeonju, Korea.
- 3Laboratory of Infectious Diseases, Kitasato Institute for Life Sciences, Kitasato University, Tokyo, Japan. taka2si@lisci.kitasato-u.ac.jp
- KMID: 2403454
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2018.38.3.212
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The molecular characterization of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis (SDSE) has not yet been performed in Korea. This study aimed to find the differences or similarities in the clinical features, molecular epidemiological findings, and antimicrobial resistance patterns of SDSE from two countries (Korea and Japan).
METHODS
SDSE isolates were collected from Korea (N=69) from 2012-2016 and Japan (N=71) from 2014-2016. Clinical characteristics, emm genotypes, and sequence types (STs) were compared. Microdilution tests were performed using different antimicrobials, and their resistance determinants were screened.
RESULTS
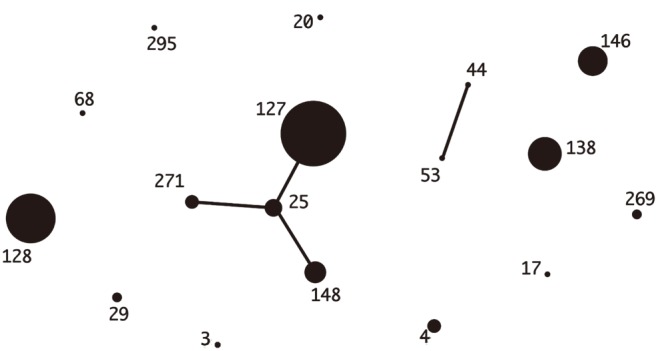
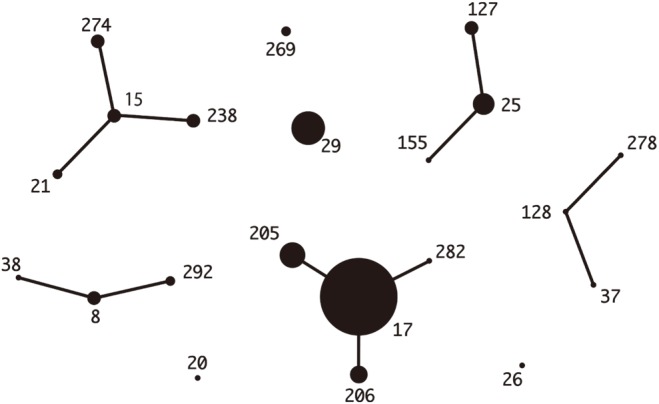
Median ages were 69 years in Korea and 76 years in Japan. The most common underlying diseases were diabetes and malignancy. Blood-derived isolates comprised 36.2% and 50.7% of Korean and Japanese isolates, respectively; mortality was not different between the two groups (5.8% vs 9.9%, P=0.53). Among Korean isolates with 20 different combined ST-emm types, ST127-stG245 (N=16), ST128-stG485 (N=10), and ST138-stG652 (N=8) were prevalent. Among Japanese isolates with 29 different combined types, ST17-stG6792 (N=11), ST29-stG485 (N=7), and ST205-stG6792 (N=6) were prevalent. Resistance rates to erythromycin, clindamycin, and minocycline were 34.8%, 17.4%, and 30.4% in Korea and 28.2%, 14.1%, and 21.4% in Japan, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
SDSE infections commonly occurred in elderly persons with underlying diseases. There was a significant difference in the distribution of ST-emm types between the two countries. Antimicrobial resistance rates were comparable with different frequencies of resistance determinants in each country.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Comparing Genomic Characteristics of
Streptococcus pyogenes Associated with Invasiveness over a 20-year Period in Korea
Hyoshim Shin, Takashi Takahashi, Seungjun Lee, Eun Hwa Choi, Takahiro Maeda, Yasuto Fukushima, Sunjoo Kim
Ann Lab Med. 2022;42(4):438-446. doi: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.4.438.
Reference
-
1. Rantala S. Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis bacteremia: an emerging infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014; 33:1303–1310. PMID: 24682845.2. Brandt CM, Spellerberg B. Human infections due to Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis. Clin Infect Dis. 2009; 49:766–772. PMID: 19635028.3. Son JA, Shin JH. Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis possessing Lancefield's group A antigen. Lab Med Online. 2013; 3:60–61. https://labmedonline.org/Synapse/Data/PDFData/9997LMO/lmo-3-60.pdf (Accessed on 20th December 2017, in Korean language).4. Wajima T, Morozumi M, Hanada S, Sunaoshi K, Chiba N, Iwata S, et al. Molecular characterization of invasive Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis, Japan. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016; 22:247–254. PMID: 26760778.5. Bruun T, Kittang BR, de Hoog BJ, Aardal S, Flaatten HK, Langeland N, et al. Necrotizing soft tissue infections caused by Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis of groups C and G in western Norway. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013; 19:E545–E550. PMID: 23795951.6. Lu B, Fang Y, Huang L, Diao B, Du X, Kan B, et al. Molecular characterization and antibiotic resistance of clinical Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis in Beijing, China. Infect Genet Evol. 2016; 40:119–125. PMID: 26925701.7. Leitner E, Zollner-Schwetz I, Zarfel G, Masoud-Landgraf L, Gehrer M, Wagner-Eibel U, et al. Prevalence of emm types and antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis in Austria. Int J Med Microbiol. 2015; 305:918–924. PMID: 26507866.8. Ahmad Y, Gertz RE Jr, Li Z, Sakota V, Broyles LN, Van Beneden C, et al. Genetic relationships deduced from emm and multilocus sequence typing of invasive Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis and S. canis recovered from isolates collected in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 2009; 47:2046–2054. PMID: 19386831.9. Jensen A, Kilian M. Delineation of Streptococcus dysgalactiae, its subspecies, and its clinical and phylogenetic relationship to Streptococcus pyogenes. J Clin Microbiol. 2012; 50:113–126. PMID: 22075580.10. Broyles LN, Van Beneden C, Beall B, Facklam R, Shewmaker PL, Malpiedi P, et al. Population-based study of invasive disease due to beta-hemolytic streptococci of groups other than A and B. Clin Infect Dis. 2009; 48:706–712. PMID: 19187026.11. Takahashi T, Sunaoshi K, Sunakawa K, Fujishima S, Watanabe H, Ubukata K, et al. Clinical aspects of invasive infections with Streptococcus dysgalactiae ssp. equisimilis in Japan: differences with respect to Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus agalactiae infections. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010; 16:1097–1103. PMID: 19732082.12. Vandamme P, Pot B, Falsen E, Kersters K, Devriese LA. Taxonomic study of Lancefield streptococcal groups C, G, and L (Streptococcus dysgalactiae) and proposal of S. dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis subsp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1996; 46:774–781. PMID: 8782689.13. Fujita T, Horiuchi A, Ogawa M, Yoshida H, Hirose Y, Nagano N, et al. Genetic diversity in Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis isolates from patients with invasive and noninvasive infections in a Japanese university hospital (2014-2015). Jpn J Infect Dis. 2017; 70:100–104. PMID: 27000456.14. Takahashi T, Arai K, Lee DH, Koh EH, Yoshida H, Yano H, et al. Epidemiological study of erythromycin-resistant Streptococcus pyogenes from Korea and Japan by emm genotyping and multilocus sequence typing. Ann Lab Med. 2016; 36:9–14. PMID: 26522753.15. Takahashi T, Fujita T, Shibayama A, Tsuyuki Y, Yoshida H. Prevalence of complement-mediated cell lysis-like gene (sicG) in Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis isolates from Japan (2014-2016). Ann Lab Med. 2017; 37:297–304. PMID: 28445008.16. McMillan DJ, Bessen DE, Pinho M, Ford C, Hall GS, Melo-Cristino J, et al. Population genetics of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis reveals widely dispersed clones and extensive recombination. PLoS One. 2010; 5:e11741. PMID: 20668530.17. CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. 18th ed. CLSI supplement M100. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2008.18. CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. 22nd ed. CLSI supplement M100. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2012.19. Haenni M, Saras E, Bertin S, Leblond P, Madec JY, Payot S. Diversity and mobility of integrative and conjugative elements in bovine isolates of Streptococcus agalactiae, S. dysgalactiae subsp. dysgalactiae, and S. uberis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010; 76:7957–7965. PMID: 20952646.20. Malhotra-Kumar S, Lammens C, Piessens J, Goossens H. Multiplex PCR for simultaneous detection of macrolide and tetracycline resistance determinants in streptococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005; 49:4798–4800. PMID: 16251336.21. Hu JY, Kim EH, Lee HW, Cha SA, Choi JY, Kim YJ, et al. Emm typing of invasive infections caused by Streptococcus dysgalactiae. Korean J Med. 2014; 87:630–635.22. Tseng SP, Lin YY, Tsai JC, Hsueh PR, Chen HJ, Hung WC, et al. Distribution of emm types and genetic characterization of the mgc locus in group G Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis from a hospital in northern Taiwan. J Clin Microbiol. 2010; 48:2975–2977. PMID: 20573871.23. Loubinoux J, Plainvert C, Collobert G, Touak G, Bouvet A, Poyart C, et al. Adult invasive and noninvasive infections due to Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis in France from 2006 to 2010. J Clin Microbiol. 2013; 51:2724–2727. PMID: 23698531.24. Uh Y, Hwang GY, Jang IH, Cho HM, Noh SM, Kim HY, et al. Macrolide resistance trends in beta-hemolytic streptococci in a tertiary Korean hospital. Yonsei Med J. 2007; 48:773–778. PMID: 17963333.25. Lo HH, Nien HH, Cheng YY, Su FY. Antibiotic susceptibility pattern and erythromycin resistance mechanisms in beta-hemolytic group G Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis isolates from central Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2015; 48:613–617. PMID: 24856419.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Characteristics of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis Isolates Causing Repetitive vs Single Infections
- A Case of Neonatal Meningitis Caused by Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies dysgalactiae and Herpes Simplex Virus
- Pathologic and molecular characterization of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis infection in neonatal piglets
- Prevalence of Complement-Mediated Cell Lysis-like Gene (sicG) in Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis Isolates From Japan (2014–2016)
- Molecular subtyping and antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis isolates from clinically diseased pigs