Korean J Crit Care Med.
2016 Nov;31(4):324-333. 10.4266/kjccm.2016.00024.
Changes in Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Level in Patients with Sepsis and Septic Shock
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Institute of Chest Diseases, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. pms70@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2371188
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/kjccm.2016.00024
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Despite many ongoing, prospective studies on the topic, sepsis still remains one of the main causes of death in hospital. The hormone insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) has a similar molecular structure to that of insulin. IGF-1 exerts anabolic effects and plays important roles in both normal physiology and pathologic processes. Previous studies have observed low serum IGF-1 level in patients with critical illnesses. Here, we evaluated changes in IGF-1 level based on survival of septic patients.
METHODS
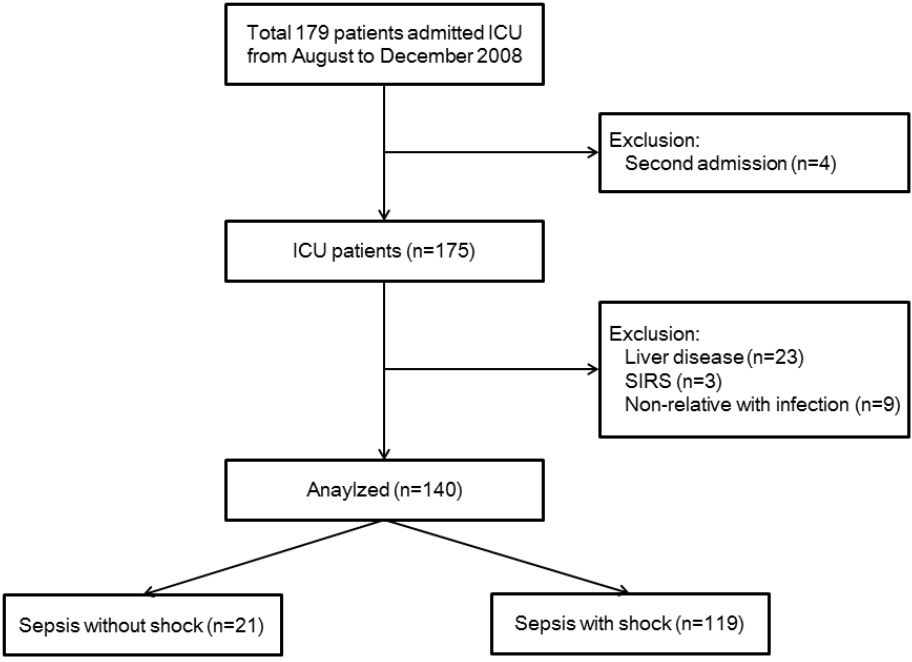
We evaluated 140 patients with sepsis and septic shock (21 with sepsis and 119 with septic shock) admitted to the intensive care unit of a university-affiliated hospital in Korea. Serum IGF-1 level was measured on days 0, 1, 3, and 7. Patients with liver disease were excluded from this study. All data were analyzed using SPSS version 20 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
RESULTS
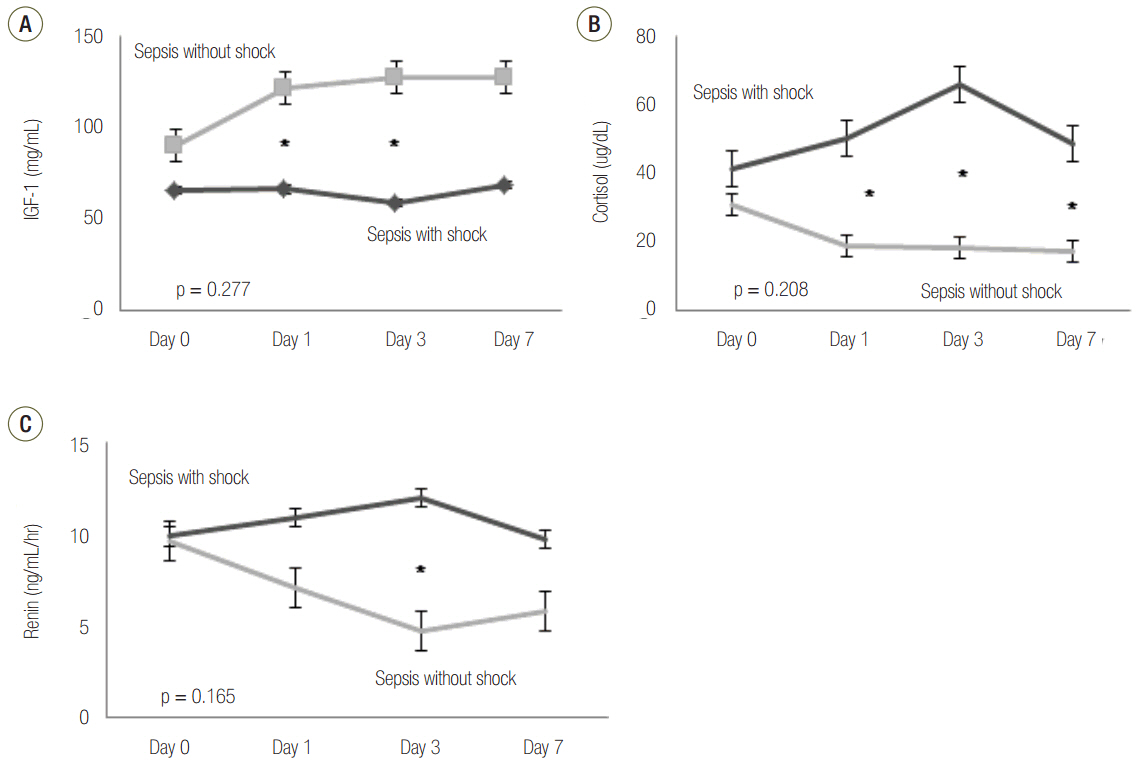
Patients with septic shock had significantly lower serum IGF-1 level on days 1 and 3 than patients without septic shock (p = 0.002 and p = 0.007, respectively). Generally, there was a negative relationship between IGF-1 and serum cortisol levels; however, this relationship was only significant on day 3 (p = 0.029). Furthermore, renin showed significantly negative correlation with IGF-1 on day 3 (p = 0.038). IGF-1 level did not show significant difference between survivors and non-survivors.
CONCLUSIONS
Our results showed that IGF-1 was associated with septic shock, and that the IGF-1 axis is severely disrupted in septic patients. Additionally, serum cortisol and renin levels were associated with IGF-1 level.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Anabolic Agents
Cause of Death
Critical Illness
Humans
Hydrocortisone
Insulin
Insulin-Like Growth Factor I
Intensive Care Units
Korea
Liver Diseases
Molecular Structure
Pathologic Processes
Physiology
Prospective Studies
Renin
Sepsis*
Shock, Septic*
Survivors
Anabolic Agents
Hydrocortisone
Insulin
Insulin-Like Growth Factor I
Renin
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Assuncao MS, Teich V, Shiramizo SC, Araújo DV, Carrera RM, Serpa Neto A, et al. The cost-effectiveness ratio of a managed protocol for severe sepsis. J Crit Care. 2014; 29:692. e1-6.
Article2. Mouncey PR, Osborn TM, Power GS, Harrison DA, Sadique MZ, Grieve RD, et al. Trial of early, goal-directed resuscitation for septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2015; 372:1301–11.
Article3. ARISE Investigators; ANZICS Clinical Trials Group, Peake SL, Delaney A, Bailey M, Bellomo R, et al. Goal-directed resuscitation for patients with early septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2014; 371:1496–506.
Article4. ProCESS Investigators, Yealy DM, Kellum JA, Huang DT, Barnato AE, Weissfeld LA, et al. A randomized trial of protocol-based care for early septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2014; 370:1683–93.
Article5. Russell JA. Management of sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:1699–713.
Article6. Vincent JL, Marshall JC, Namendys-Silva SA, François B, Martin-Loeches I, Lipman J, et al. Assessment of the worldwide burden of critical illness: the intensive care over nations (ICON) audit. Lancet Respir Med. 2014; 2:380–6.
Article7. Zhang Q, Dong G, Zhao X, Wang M, Li CS. Prognostic significance of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis hormones in early sepsis: a study performed in the emergency department. Intensive Care Med. 2014; 40:1499–508.
Article8. Bondanelli M, Zatelli MC, Ambrosio MR, degli Uberti EC. Systemic illness. Pituitary. 2008; 11:187–207.
Article9. Papastathi C, Mavrommatis A, Mentzelopoulos S, Konstandelou E, Alevizaki M, Zakynthinos S. Insulin-like growth factor I and its binding protein 3 in sepsis. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2013; 23:98–104.
Article10. Takala J, Ruokonen E, Webster NR, Nielsen MS, Zandstra DF, Vundelinckx G, et al. Increased mortality associated with growth hormone treatment in critically ill adults. N Engl J Med. 1999; 341:785–92.
Article11. Donmez R, Oren D, Ozturk G, Kisaoglu A, Ozogul B, Atamanalp SS. The combined effects of glutamine and growth hormone on intestinal anastomosis in the rat intra-abdominal sepsis model. J Surg Res. 2013; 182:142–5.
Article12. Voerman HJ, van Schijndel RJ, Groeneveld AB, de Boer H, Nauta JP, van der Veen EA, et al. Effects of recombinant human growth-hormone in patients with severe sepsis. Ann Surg. 1992; 216:648–55.13. Bjarnason R, Wickelgren R, Hermansson M, Hammarqvist F, Carlsson B, Carlsson LM. Growth hormone treatment prevents the decrease in insulin-like growth factor I gene expression in patients undergoing abdominal surgery. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998; 83:1566–72.
Article14. Yue C, Wang W, Tian WL, Huang Q, Zhao RS, Zhao YZ, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-induced failure of the gut barrier is site-specific and inhibitable by growth hormone. Inflamm Res. 2013; 62:407–15.
Article15. Jaffa AA, Vio C, Velarde V, LeRoith D, Mayfield RK. Induction of renal kallikrein and renin gene expression by insulin and IGF-I in the diabetic rat. Diabetes. 1997; 46:2049–56.
Article16. Haddad GE, Blackwell K, Bikhazi A. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor-1 by the renin-angiotensin system during regression of cardiac eccentric hypertrophy through angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor and AT1 antagonist. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2003; 81:142–9.
Article17. Spicer LJ, Chamberlain CS. Influence of cortisol on insulin- and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1)-induced steroid production and on IGF-1 receptors in cultured bovine granulosa cells and thecal cells. Endocrine. 1998; 9:153–61.
Article18. Weber MM, Simmler P, Fottner C, Engelhardt D. Insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) is more potent than IGF-I in stimulating cortisol secretion from cultured bovine adrenocortical cells: interaction with the IGF-I receptor and IGF-binding proteins. Endocrinology. 1995; 136:3714–20.
Article19. American-College of Chest Physicians Society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus Conference: definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Crit Care Med. 1992; 20:864–74.20. Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Carlet JM, Bion J, Parker MM, Jaeschke R, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2008. Crit Care Med. 2008; 36:296–327.
Article21. Lin MC, Leung SY, Fang WF, Chin CH, Chung KF. Down-regulation of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) in the mouse diaphragm during sepsis. Chang Gung Med J. 2010; 33:501–8.22. Heemskerk VH, Daemen MA, Buurman WA. Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and growth hormone (GH) in immunity and inflammation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1999; 10:5–14.
Article23. Dahn MS, Lange MP, Jacobs LA. Insulinlike growth factor-I production is inhibited in human sepsis. Arch Surg. 1988; 123:1409–14.24. Van den Berghe G. Endocrine changes in critically ill patients. Growth Horm IGF Res. 1999; 9 Suppl A:77–81.25. Ashare A, Nymon AB, Doerschug KC, Morrison JM, Monick MM, Hunninghake GW. Insulin-like growth factor-1 improves survival in sepsis via enhanced hepatic bacterial clearance. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008; 178:149–57.
Article26. Gianotti L, Broglio F, Aimaretti G, Arvat E, Colombo S, Di Summa M, et al. Low IGF-I levels are often uncoupled with elevated GH levels in catabolic conditions. J Endocrinol Invest. 1998; 21:115–21.
Article27. Frayn KN, Price DA, Maycock PF, Carroll SM. Plasma somatomedin activity after injury in man and its relationship to other hormonal and metabolic changes. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1984; 20:179–87.
Article28. Schuetz P, Müller B, Nusbaumer C, Wieland M, Christ-Crain M. Circulating levels of GH predict mortality and complement prognostic scores in critically ill medical patients. Eur J Endocrinol. 2009; 160:157–63.
Article29. de Groof F, Joosten KF, Janssen JA, de Kleijn ED, Hazelzet JA, Hop WC, et al. Acute stress response in children with meningococcal sepsis: important differences in the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor I axis between nonsurvivors and survivors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002; 87:3118–24.
Article30. Doerschug KC, Delsing AS, Schmidt GA, Ashare A. Renin-angiotensin system activation correlates with microvascular dysfunction in a prospective cohort study of clinical sepsis. Crit Care. 2010; 14:R24.
Article31. Salgado DR, Rocco JR, Silva E, Vincent JL. Modulation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in sepsis: a new therapeutic approach? Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2010; 14:11–20.
Article32. Volbeda M, Wetterslev J, Gluud C, Zijlstra JG, van der Horst ICC, Keus F. Glucocorticosteroids for sepsis: systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2015; 41:1220–34.
Article33. Kajstura J, Fiordaliso F, Andreoli AM, Li B, Chimenti S, Medow MS, et al. IGF-1 overexpression inhibits the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy and angiotensin II-mediated oxidative stress. Diabetes. 2001; 50:1414–24.
Article