Anesth Pain Med.
2017 Jan;12(1):47-51. 10.17085/apm.2017.12.1.47.
Effects of thiopental sodium, ketamine, and propofol on the onset time of rocuronium in children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, School of Medicine, Chosun University, Busan, Korea. than@chosun.ac.kr
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Gwangju Daejung Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Chosun University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- 4Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 5Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2369666
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2017.12.1.47
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
In emergency condition, failure in securing airway is a common and serious reason of pediatric death. Rapid intubation is required to minimize physiologic complication in children due to airway failure. Rapid loss of consciousness and rapid onset of neuromuscular blocking agent are necessary for the rapid sequence intubation. In this study, we compared the effects of thiopental sodium, ketamine, and propofol (drugs commonly used to induce anesthesia in children) on the onset time of rocuronium. We also compared the effects of these anesthesia induction drugs on intubation condition and their duration of action.
METHODS
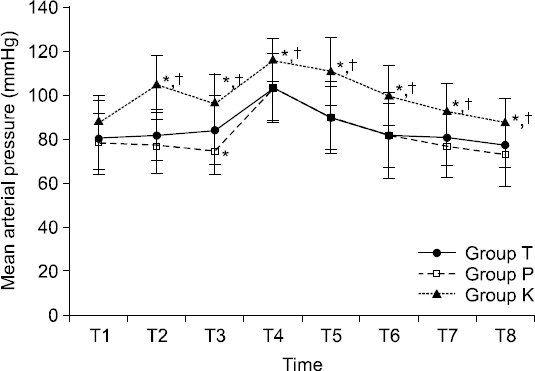
A total of 89 patients undergoing various elective surgeries were enrolled and allocated to the following three groups according to the anesthesia induction drug: 1) Group T, thiopental sodium; 2) Group P, propofol; and 3) Group K, ketamine. After loss of consciousness, neuromuscular monitoring was performed and rocurunium 0.6 mg/kg was administered. Onset time and duration of action of rocuronium were measured. Intubation condition was recorded with a tracheal intubation scoring system. Hemodynamic changes were observed before induction until 5 min after endotracheal intubation.
RESULTS
The onset time of rocuronium in group K (39.9 s) was significantly faster than that in group T (61.7 s) or group P (50.7 s). There was no significant difference in duration of action of rocuronium or intubation condition among the three groups.
CONCLUSIONS
Ketamine can decrease the onset time of rocuronium significantly compared to thiopental sodium or propofol.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. McAllister JD, Gnauck KA. Rapid sequence intubation of the pediatric patient. Fundamentals of practice. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1999; 46:1249–84. DOI: 10.1016/S0031-3955(05)70185-1.2. Ma OJ, Atchley RB, Hatley T, Green M, Young J, Brady W. Intubation success rates improve for an air medical program after implementing the use of neuromuscular blocking agents. Am J Emerg Med. 1998; 16:125–7. DOI: 10.1016/S0735-6757(98)90027-4.3. Zelicof-Paul A, Smith-Lockridge A, Schnadower D, Tyler S, Levin S, Roskind C, et al. Controversies in rapid sequence intubation in children. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2005; 17:355–62. DOI: 10.1097/01.mop.0000162365.64140.b7. PMID: 15891426.4. Ezri T, Szmuk P, Warters RD, Gebhard RE, Pivalizza EG, Katz J. Changes in onset time of rocuronium in patients pretreated with ephedrine and esmolol--the role of cardiac output. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2003; 47:1067–72. DOI: 10.1034/j.1399-6576.2003.00218.x. PMID: 12969097.5. Grounds RM, Twigley AJ, Carli F, Whitwam JG, Morgan M. The haemodynamic effects of intravenous induction. Comparison of the effects of thiopentone and propofol. Anaesthesia. 1985; 40:735–40. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1985.tb10996.x. PMID: 3876040.6. Leykin Y, Pellis T, Lucca M, Gullo A. Intubation conditions following rocuronium: influence of induction agent and priming. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2005; 33:462–8. PMID: 16119487.7. Cote CJ. Pediatric anesthesia. Miller’s Anesthesia. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Inc;2015. p. 2857–98.8. Fuchs-Buder T, Claudius C, Skovgaard LT, Eriksson LI, Mirakhur RK, Viby-Mogensen J. Good clinical research practice in pharmacodynamic studies of neuromuscular blocking agents II: the Stockholm revision. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2007; 51:789–808. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2007.01352.x. PMID: 17635389.9. Viby-Mogensen J, Engbaek J, Eriksson LI, Gramstad L, Jensen E, Jensen FS, et al. Good clinical research practice (GCRP) in pharmacodynamic studies of neuromuscular blocking agents. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1996; 40:59–74. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1996.tb04389.x. PMID: 8904261.10. Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, Buchner A. G*Power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav Res Methods. 2007; 39:175–91. DOI: 10.3758/BF03193146. PMID: 17695343.11. Howes MC. Ketamine for paediatric sedation/analgesia in the emergency department. Emerg Med J. 2004; 21:275–80. DOI: 10.1136/emj.2003.005769. PMID: 15107362. PMCID: PMC1726352.12. Donati F. Onset of action of relaxants. Can J Anaesth. 1988; 35:S52–8. DOI: 10.1007/BF03026928. PMID: 3289780.13. Harrison GA, Junius F. The effect of circulation time on the neuromuscular action of suxamethonium. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1972; 1:33–40. PMID: 4569966.14. Muñoz HR, González AG, Dagnino JA, González JA, Pérez AE. The effect of ephedrine on the onset time of rocuronium. Anesth Analg. 1997; 85:437–40. DOI: 10.1213/00000539-199708000-00034.15. Gill RS, Scott RP. Etomidate shortens the onset time of neuromuscular block. Br J Anaesth. 1992; 69:444–6. DOI: 10.1093/bja/69.5.444.16. Aun CS, Sung RY, O’Meara ME, Short TG, Oh TE. Cardiovascular effects of i.v. induction in children: comparison between propofol and thiopentone. Br J Anaesth. 1993; 70:647–53. DOI: 10.1093/bja/70.6.647. PMID: 8329259.17. Lebovic S, Reich DL, Steinberg LG, Vela FP, Silvay G. Comparison of propofol versus ketamine for anesthesia in pediatric patients undergoing cardiac catheterization. Anesth Analg. 1992; 74:490–4. DOI: 10.1213/00000539-199204000-00003. PMID: 1554114.18. Reich DL, Silvay G. Ketamine: an update on the first twenty-five years of clinical experience. Can J Anaesth. 1989; 36:186–97. DOI: 10.1007/BF03011442. PMID: 2650898.19. Berman W Jr, Fripp RR, Rubler M, Alderete L. Hemodynamic effects of ketamine in children undergoing cardiac catheterization. Pediatr Cardiol. 1990; 11:72–6. DOI: 10.1007/BF02239565. PMID: 2349145.20. Souza DD, McDaniel GM, Baum VC. Cardiovascular physiology. Smith’s Anesthesia for Infants and Children. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Inc;2011. p. 80–115. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-323-06612-9.00004-3.21. Kim MH, Oh AY, Han SH, Kim JH, Hwang JW, Jeon YT. The effect of magnesium sulphate on intubating condition for rapid-sequence intubation: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Anesth. 2015; 27:595–601. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2015.07.002. PMID: 26315876.22. White PF, Way WL, Trevor AJ. Ketamine--its pharmacology and therapeutic uses. Anesthesiology. 1982; 56:119–36. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-198202000-00007. PMID: 6892475.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of intravenous induction agents on emergence delirium after sevoflurane anesthesia in pre-school aged children undergoing adenotonsillectomy
- Effect of Intravenous Anesthetics on Systemic Vascular Resistance during Cardiopulmanary Bypass
- Intubating Conditions and Hemodynamic Changes according to Induction Agent and Tracheal Intubation Time after Rocuronium
- The Onset of Neuromuscular Blockade and Hemodynamic Effects after Atracurium, Vecuronium, or Rocuronium in Children
- Comparison of Thiopental Sodium and Propofol as Anesthetic Induction Agents for Hypnotic Time