J Pathol Transl Med.
2017 Jan;51(1):17-23. 10.4132/jptm.2016.09.23.
Clinicopathologic Significance of Survivin Expression in Relation to CD133 Expression in Surgically Resected Stage II or III Colorectal Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea. meeyon@yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Lifestyle Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- 3Institute of Genomic Cohort, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2367676
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.09.23
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Cancer stem cells have been investigated as new targets for colorectal cancer (CRC) treatment. We recently reported that CD133+ colon cancer cells showed chemoresistance to 5-fluorouracil through increased survivin expression and proposed the survivin inhibitor YM155 as an effective therapy for colon cancer in an in vitro study. Here, we investigate the relationship between survivin and CD133 expression in surgically resected CRC to identify whether the results obtained in our in vitro study are applicable to clinical samples.
METHODS
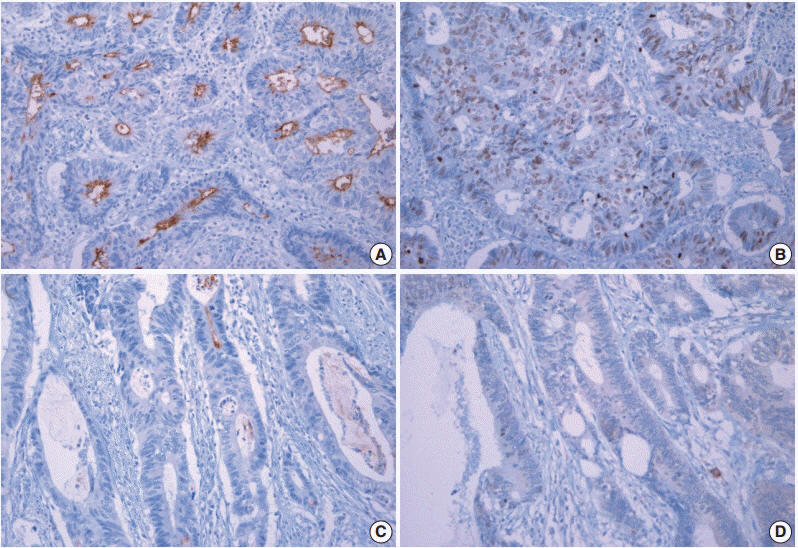
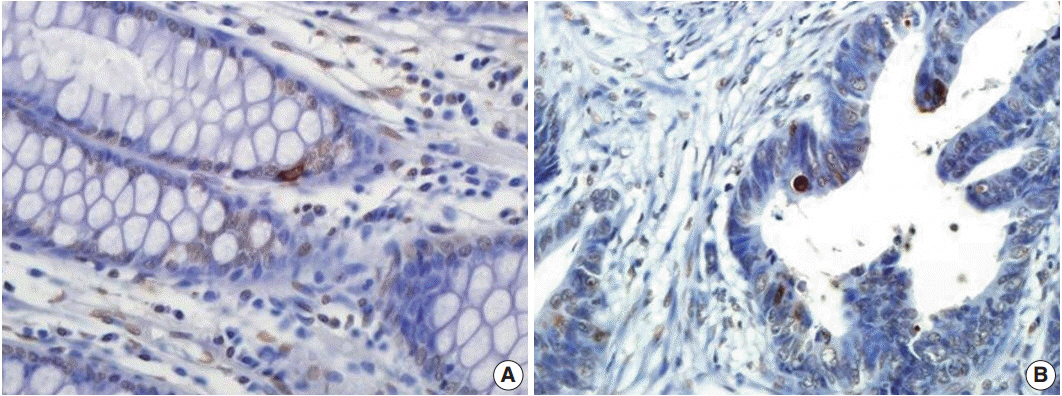
We performed immunohistochemical staining for survivin and CD133 in surgically resected tissue from 187 stage II or III CRC patients. We also comparatively analyzed apoptosis according to survivin and CD133 expression using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate nick-end labeling.
RESULTS
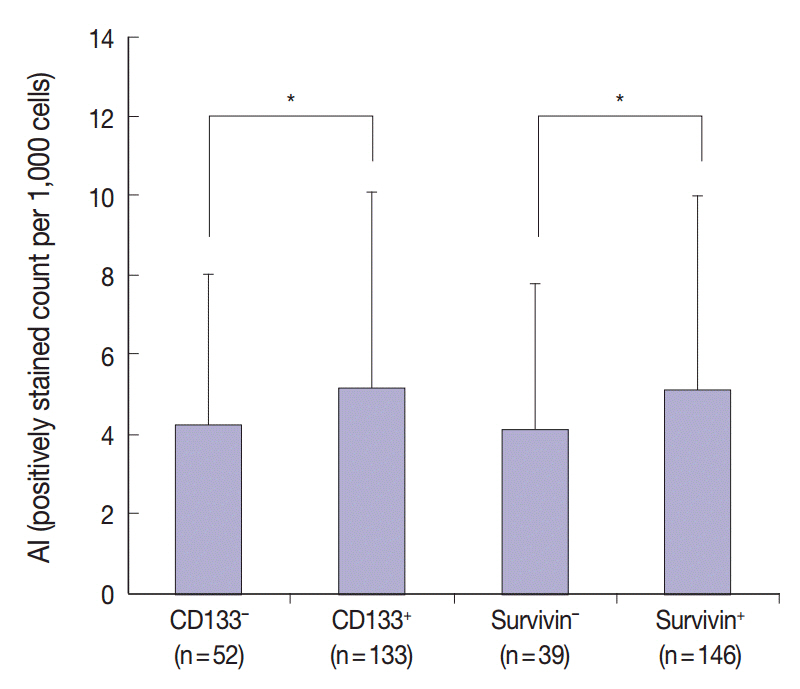
The results of the Mantel-Haenszel test established a linear association between nuclear survivin and CD133 expression (p = .018), although neither had prognostic significance, according to immunohistochemical expression level. No correlation was found between survivin expression and the following pathological parameters: invasion depth, lymph node metastasis, or histologic differentiation (p > .05). The mean apoptotic index in survivin+ and CD133+ tumors was higher than that in negative tumors: 5.116 ± 4.894 in survivin+ versus 4.103 ± 3.691 in survivin- (p = .044); 5.165 ± 4.961 in CD133+ versus 4.231 ± 3.812 in CD133- (p = .034).
CONCLUSIONS
As observed in our in vitro study, survivin expression is significantly related to CD133 expression. Survivin may be considered as a new therapeutic target for chemoresistant CRC.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015; 136:E359–86.
Article2. Ren F, Sheng WQ, Du X. CD133: a cancer stem cells marker, is used in colorectal cancers. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:2603–11.
Article3. Lee MR, Ji SY, Mia-Jan K, Cho MY. Chemoresistance of CD133(+) colon cancer may be related with increased survivin expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015; 463:229–34.4. Li WL, Lee MR, Cho MY. The small molecule survivin inhibitor YM155 may be an effective treatment modality for colon cancer through increasing apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016; 471:309–14.
Article5. Sung JJ, Noh SJ, Bae JS, et al. Immunohistochemical expression and clinical significance of suggested stem cell markers in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Pathol Transl Med. 2016; 50:52–7.
Article6. Dalerba P, Dylla SJ, Park IK, et al. Phenotypic characterization of human colorectal cancer stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007; 104:10158–63.
Article7. Deng YH, Pu XX, Huang MJ, et al. 5-Fluorouracil upregulates the activity of Wnt signaling pathway in CD133-positive colon cancer stem-like cells. Chin J Cancer. 2010; 29:810–5.
Article8. Corbo C, Orrù S, Gemei M, et al. Protein cross-talk in CD133+ colon cancer cells indicates activation of the Wnt pathway and upregulation of SRp20 that is potentially involved in tumorigenicity. Proteomics. 2012; 12:2045–59.
Article9. Sikandar SS, Pate KT, Anderson S, et al. NOTCH signaling is required for formation and self-renewal of tumor-initiating cells and for repression of secretory cell differentiation in colon cancer. Cancer Res. 2010; 70:1469–78.
Article10. Lin L, Fuchs J, Li C, Olson V, Bekaii-Saab T, Lin J. STAT3 signaling pathway is necessary for cell survival and tumorsphere forming capacity in ALDH(+)/CD133(+) stem cell-like human colon cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011; 416:246–51.
Article11. Roy S, Majumdar AP. Signaling in colon cancer stem cells. J Mol Signal. 2012; 7:11.
Article12. Dick JE. Looking ahead in cancer stem cell research. Nat Biotechnol. 2009; 27:44–6.
Article13. Alcaide J, Funez R, Rueda A, et al. The role and prognostic value of apoptosis in colorectal carcinoma. BMC Clin Pathol. 2013; 13:24.
Article14. Mobahat M, Narendran A, Riabowol K. Survivin as a preferential target for cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2014; 15:2494–516.
Article15. Huang YJ, Qi WX, He AN, Sun YJ, Shen Z, Yao Y. The prognostic value of survivin expression in patients with colorectal carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2013; 43:988–95.
Article16. Krieg A, Werner TA, Verde PE, Stoecklein NH, Knoefel WT. Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of survivin in colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e65338.
Article17. Qi G, Tuncel H, Aoki E, et al. Intracellular localization of survivin determines biological behavior in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 2009; 22:557–62.
Article18. De Oliveira Lima F, De Oliveira Costa H, Barrezueta LF, et al. Immunoexpression of inhibitors of apoptosis proteins and their antagonist SMAC/DIABLO in colorectal carcinoma: correlation with apoptotic index, cellular proliferation and prognosis. Oncol Rep. 2009; 22:295–303.
Article19. Rauch A, Hennig D, Schäfer C, et al. Survivin and YM155: how faithful is the liaison? Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014; 1845:202–20.
Article20. Miura K, Fujibuchi W, Ishida K, et al. Inhibitor of apoptosis protein family as diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets of colorectal cancer. Surg Today. 2011; 41:175–82.
Article21. Gyurászová K, Mikeš J, Halaburková A, Jendželovský R, Fedorocˇko P. YM155, a small molecule inhibitor of survivin expression, sensitizes cancer cells to hypericin-mediated photodynamic therapy. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2016; 15:812–21.
Article22. Kim ST, Sohn I, Do IG, et al. Transcriptome analysis of CD133-positive stem cells and prognostic value of survivin in colorectal cancer. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2014; 11:259–66.23. Li Y, Ma X, Wu X, Liu X, Liu L. Prognostic significance of survivin in breast cancer: meta-analysis. Breast J. 2014; 20:514–24.
Article24. Shintani M, Sangawa A, Yamao N, Kamoshida S. Immunohistochemical expression of nuclear and cytoplasmic survivin in gastrointestinal carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013; 6:2919–27.25. Bedi A, Pasricha PJ, Akhtar AJ, et al. Inhibition of apoptosis during development of colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 1995; 55:1811–6.26. Zhao X, Ogunwobi OO, Liu C. Survivin inhibition is critical for Bcl-2 inhibitor-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e21980.
Article27. Kemper K, Rodermond H, Colak S, Grandela C, Medema JP. Targeting colorectal cancer stem cells with inducible caspase-9. Apoptosis. 2012; 17:528–37.
Article28. Sam S, Sam MR, Esmaeillou M, Safaralizadeh R. Effective targeting survivin, caspase-3 and microRNA-16-1 expression by methyl-3-pentyl-6-methoxyprodigiosene triggers apoptosis in colorectal cancer stem-like cells. Pathol Oncol Res. 2016; 22:715–23.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of Survivin and HSP90 in Colorectal Cancer and its Relationship with Clinicopathologic Factors
- Expression of Survivin and KAI-1 in Gastric Adenocarcinomas
- Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and survivin in endometrioid and nonendometrioid endometrial cancers and clinicopathologic significance
- Expression of Survivin and Its Correlation with Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer
- Clinicopathologic Implications of PIWIL2 Expression in Colorectal Cancer