J Bacteriol Virol.
2016 Dec;46(4):295-302. 10.4167/jbv.2016.46.4.295.
Eosinophils Regulate Type 2 Immune Responses Following Infection with the Nematode Trichinella spiralis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, School of Medicine, Gachon University, Incheon, Korea. yjjung@gachon.ac.kr
- KMID: 2366876
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2016.46.4.295
Abstract
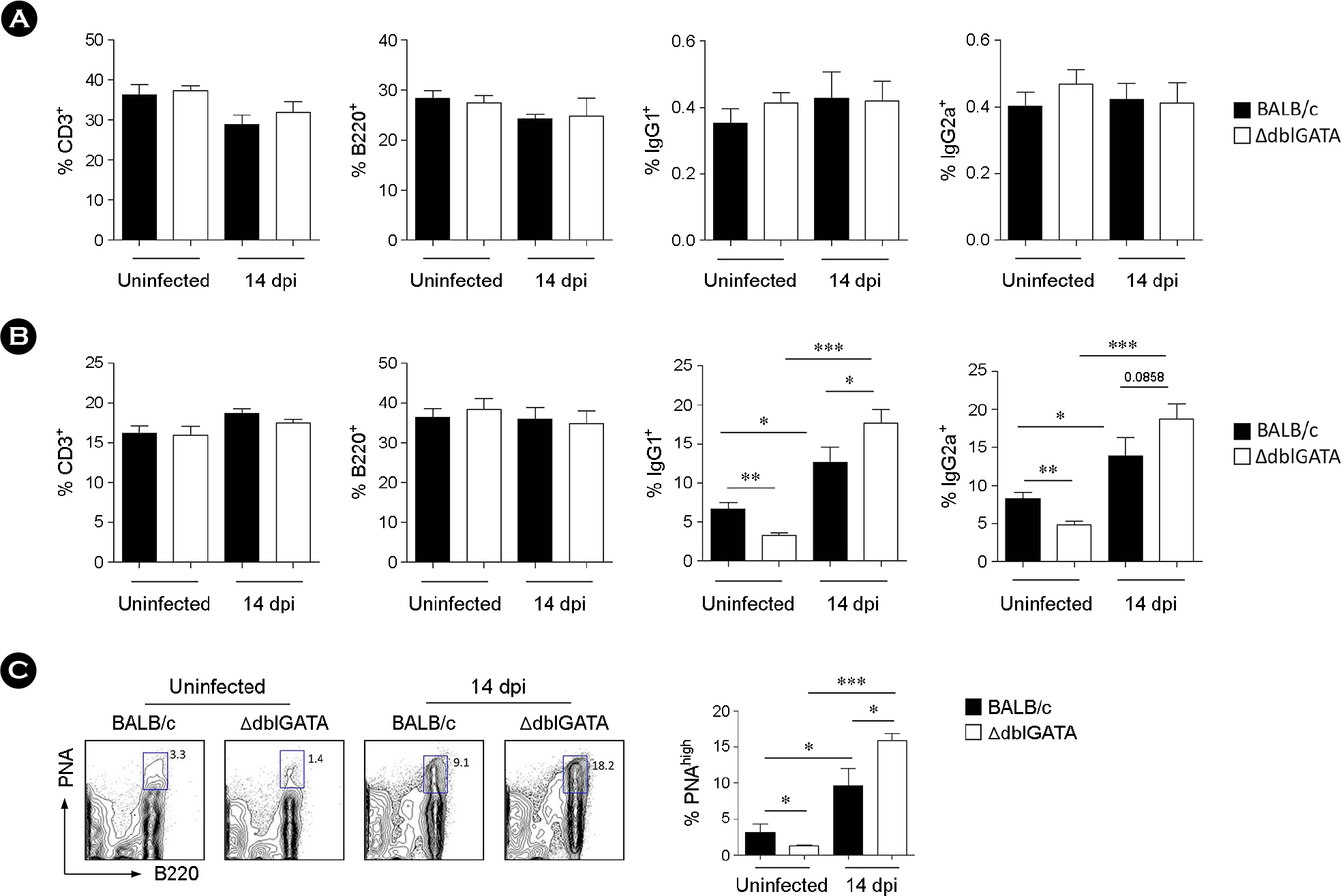
- Eosinophils are multifunctional leukocytes implicated in protection against helminth infections. Although eosinophils comprise between 1~5% of peripheral blood leukocytes, they primarily reside in the gastrointestinal tract under homeostatic conditions, and rapidly proliferate upon parasitic infection. Intestinal infection with Trichinella spiralis (T. spiralis) induces eosinophilia when the parasite enters the larval stages and larvae finally migrate to the skeletal muscle. Eosinophils are known to mediate parasite death through antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. In this study, we aimed to address the functional significance of eosinophils in the intestinal phase of T. spiralis infection by analysis of immune responses in the Peyer's patch (PP) of infected BALB/c and eosinophil-ablated ΔdblGATA mice. Trafficking of eosinophils to the PP was significantly increased, with upregulation of interleukin-5 at 14 days post infection. Eosinophil deficiency led to a significant augmentation of serum immunoglobulin (Ig) M and IgG1 antibody levels. In accordance with this, IgG1+ B cells in the PP were substantially increased in ΔdblGATA mice compared to that in BALB/c mice. Transforming growth factor-β expression in the PP of infected ΔdblGATA mice was significantly decreased compared to that in BALB/c mice, whereas the number of T. spiralis larvae in the diaphragm was increased. Taken together, these findings indicate that eosinophils contribute to the regulation of Th2 immune responses, and protect the host from T. spiralis attempting to establish larvae in the skeletal muscle.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Jung Y. Eosinophils are required for immune responses induced by oral immunization. J Bacteriol Virol. 2015; 45:354–63.
Article2). Rothenberg ME, Hogan SP. The eosinophil. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006; 24:147–74.
Article3). Yu C, Cantor AB, Yang H, Browne C, Wells RA, Fujiwara Y, et al. Targeted deletion of a high-affinity GATA-binding site in the GATA-1 promoter leads to selective loss of the eosinophil lineage in vivo. J Exp Med. 2002; 195:1387–95.4). Jung Y, Rothenberg ME. Roles and regulation of gastrointestinal eosinophils in immunity and disease. J Immunol. 2014; 193:999–1005.
Article5). Rosenberg HF, Phipps S, Foster PS. Eosinophil trafficking in allergy and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 119:1303–10.
Article6). Lee TD. Helminthotoxic responses of intestinal eosinophils to Trichinella spiralis newborn larvae. Infect Immun. 1991; 59:4405–11.7). Kazura JW, Aikawa M. Host defense mechanisms against Trichinella spiralis infection in the mouse: eosinophil-mediated destruction of newborn larvae in vitro. J Immunol. 1980; 124:355–61.8). Specht S, Saeftel M, Arndt M, Endl E, Dubben B, Lee NA, et al. Lack of eosinophil peroxidase or major basic protein impairs defense against murine filarial infection. Infect Immun. 2006; 74:5236–43.
Article9). Kita H. The eosinophil: a cytokine-producing cell? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996; 97:889–92.
Article10). Jacobsen EA, Helmers RA, Lee JJ, Lee NA. The expanding role(s) of eosinophils in health and disease. Blood. 2012; 120:3882–90.
Article11). Goh YP, Henderson NC, Heredia JE, Red Eagle A, Odegaard JI, Lehwald N, et al. Eosinophils secrete IL-4 to facilitate liver regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013; 110:9914–9.
Article12). Heredia JE, Mukundan L, Chen FM, Mueller AA, Deo RC, Locksley RM, et al. Type 2 innate signals stimulate fibro/adipogenic progenitors to facilitate muscle regeneration. Cell. 2013; 153:376–88.
Article13). Wu D, Molofsky AB, Liang HE, Ricardo-Gonzalez RR, Jouihan HA, Bando JK, et al. Eosinophils sustain adipose alternatively activated macrophages associated with glucose homeostasis. Science. 2011; 332:243–7.
Article14). Shin MH. Eosinophil and tissue-invasive parasitic helminth. Hanyang Med Rev. 2010; 30:238–45.
Article15). Harley JP, Gallicchio V. Trichinella spiralis: migration of larvae in the rat. Exp Parasitol. 1971; 30:11–21.16). Despommier D. Adaptive changes in muscle fibers infected with Trichinella spiralis. Am J Pathol. 1975; 78:477–96.17). Bruschi F, Korenaga M, Watanabe N. Eosinophils and Trichinella infection: toxic for the parasite and the host? Trends Parasitol. 2008; 24:462–7.18). Venturiello SM, Giambartolomei GH, Costantino SN. Immune cytotoxic activity of human eosinophils against Trichinella spiralis newborn larvae. Parasite Immunol. 1995; 17:555–9.19). Kazura JW, Grove DI. Stage-specific antibody-dependent eosinophil-mediated destruction of Trichinella spiralis. Nature. 1978; 274:588–9.20). Gebreselassie NG, Moorhead AR, Fabre V, Gagliardo LF, Lee NA, Lee JJ, et al. Eosinophils preserve parasitic nematode larvae by regulating local immunity. J Immunol. 2012; 188:417–25.
Article21). Fabre V, Beiting DP, Bliss SK, Gebreselassie NG, Gagliardo LF, Lee NA, et al. Eosinophil deficiency compromises parasite survival in chronic nematode infection. J Immunol. 2009; 182:1577–83.
Article22). Huang L, Appleton JA. Eosinophils in Helminth Infection: Defenders and Dupes. Trends Parasitol. 2016; 32:798–807.
Article23). Grove DI, Mahmoud AA, Warren KS. Eosinophils and resistance to Trichinella spiralis. J Exp Med. 1977; 145:755–9.24). Mowat AM. Anatomical basis of tolerance and immunity to intestinal antigens. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003; 3:331–41.
Article25). Mishra A, Hogan SP, Brandt EB, Rothenberg ME. Peyer's patch eosinophils: identification, characterization, and regulation by mucosal allergen exposure, interleukin-5, and eotaxin. Blood. 2000; 96:1538–44.
Article26). Franssen FF, Fonville M, Takumi K, Vallée I, Grasset A, Koedam MA, et al. Antibody response against Trichinella spiralis in experimentally infected rats is dose dependent. Vet Res. 2011; 42:113.27). Coico RF, Bhogal BS, Thorbecke GJ. Relationship of germinal centers in lymphoid tissue to immunologic memory. VI. Transfer of B cell memory with lymph node cells fractionated according to their receptors for peanut agglutinin. J Immunol. 1983; 131:2254–7.28). Masterson JC, McNamee EN, Fillon SA, Hosford L, Harris R, Fernando SD, et al. Eosinophil-mediated signalling attenuates inflammatory responses in experimental colitis. Gut. 2015; 64:1236–47.
Article29). Chen Z, Andreev D, Oeser K, Krljanac B, Hueber A, Kleyer A, et al. Th2 and eosinophil responses suppress inflammatory arthritis. Nat Commun. 2016; 7:11596.
Article30). Beiting DP, Gagliardo LF, Hesse M, Bliss SK, Meskill D, Appleton JA. Coordinated control of immunity to muscle stage Trichinella spiralis by IL-10, regulatory T cells, and TGF-beta. J Immunol. 2007; 178:1039–47.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Immune Correlates of Resistance to Trichinella spiralis Reinfection in Mice
- Mucosal immunity against parasitic gastrointestinal nematodes
- Toll-Like Receptor Gene Expression during Trichinella spiralis Infection
- Family Outbreak of Trichinosis After Eating a Raw Meat of Wild Swine
- Protease-Activated Receptor 2 Is Involved in Th2 Responses against Trichinella spiralis Infection