J Korean Med Sci.
2017 Mar;32(3):534-541. 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.3.534.
Playground Equipment Related Injuries in Preschool-Aged Children: Emergency Department-based Injury In-depth Surveillance
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Emergency Medicine, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea. woowoochan@gmail.com
- 2Department of Emergency medicine, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2366653
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.3.534
Abstract
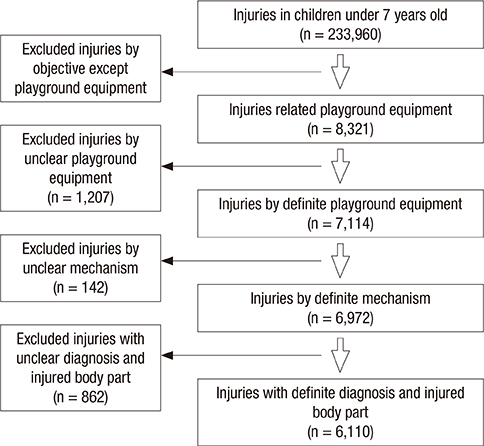
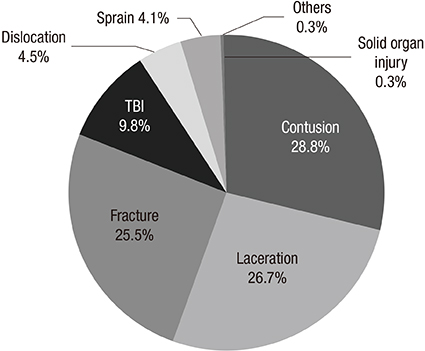
- In this study, we investigated playground equipment related injuries in preschool-aged children. This was a retrospective observational study using Emergency Department based Injury In-depth Surveillance, (2011-2014). We included the preschool-aged children with playground equipment related injuries. We surveyed the mechanism and incidence of injuries, and estimated the odds ratio (OR) of traumatic brain injury (TBI) and upper/lower extremities fracture. There were 6,110 patients, mean age was 4.14 ± 1.95 years old. Slide and swing related injuries were 2,475 (40.5%) and 1,102 (18.0%). Fall down (48.5%) was the most common mechanism. The OR of TBI in children 0-2 years old was 1.88 times higher than children 3-7 years old, and in swing was 4.72 (OR, 4.72; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.37-9.40) times higher than seesaw. The OR of upper extremity fracture in children 3-7 years old was 3.07 times higher than children 0-2 years old, and in climbing was 2.03 (OR, 2.03; 95% CI, 1.63-2.52) times higher than swing. The OR of lower extremity fractures in horizontal bars, tightropes, and trampolines was 2.95 (OR, 2.95; 95% CI, 1.55-5.61) times higher than swing. The most common mechanism and playground equipment were fall down and slide. TBI was associated to younger children (0-2 years old) and swing. Fracture of upper extremities was associated to older children (3-7 years old) and climbing. Fracture of lower extremities was associated to others such as horizontal bars, tightropes, and trampolines.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mack MG, Hudson S, Thompson D. A descriptive analysis of children’s playground injuries in the United States 1990-4. Inj Prev. 1997; 3:100–103.2. Tinsworth DK, McDonald JE. Special Study: Injuries and Deaths Associated with Children’s Playground Equipment. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission;2001.3. Vollman D, Witsaman R, Comstock RD, Smith GA. Epidemiology of playground equipment-related injuries to children in the United States, 1996-2005. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2009; 48:66–71.4. Schwebel DC, Brezausek CM. Child development and pediatric sport and recreational injuries by age. J Athl Train. 2014; 49:780–785.5. Song HD, Kim KH, Kim AJ, Park JS, Shin DW, Roh JY, Lee KM. A preliminary study of an emergency department-based in-depth injury surveillance system of preschool children injury. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 2009; 20:649–657.6. Mott A, Evans R, Rolfe K, Potter D, Kemp KW, Sibert JR. Patterns of injuries to children on public playgrounds. Arch Dis Child. 1994; 71:328–330.7. Loder RT. The demographics of playground equipment injuries in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2008; 43:691–699.8. Lam KY, Sumanth Kumar G, Mahadev A. Severity of playground-related fractures: more than just playground factors? J Pediatr Orthop. 2013; 33:221–226.9. Schwebel DC, Summerlin AL, Bounds ML, Morrongiello BA. The Stamp-in-Safety program: a behavioral intervention to reduce behaviors that can lead to unintentional playground injury in a preschool setting. J Pediatr Psychol. 2006; 31:152–162.10. Brussoni M, Gibbons R, Gray C, Ishikawa T, Sandseter EB, Bienenstock A, Chabot G, Fuselli P, Herrington S, Janssen I, et al. What is the relationship between risky outdoor play and health in children? A systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015; 12:6423–6454.11. Burrows P, Trefan L, Houston R, Hughes J, Pearson G, Edwards RJ, Hyde P, Maconochie I, Parslow RC, Kemp AM. Head injury from falls in children younger than 6 years of age. Arch Dis Child. 2015; 100:1032–1037.12. Thomas AG, Hegde SV, Dineen RA, Jaspan T. Patterns of accidental craniocerebral injury occurring in early childhood. Arch Dis Child. 2013; 98:787–792.13. Joeris A, Lutz N, Wicki B, Slongo T, Audigé L. An epidemiological evaluation of pediatric long bone fractures - a retrospective cohort study of 2716 patients from two Swiss tertiary pediatric hospitals. BMC Pediatr. 2014; 14:314.14. Chan V, Thurairajah P, Colantonio A. Defining pediatric traumatic brain injury using International Classification of Diseases Version 10 Codes: a systematic review. BMC Neurol. 2015; 15:7.15. Ghajar J. Traumatic brain injury. Lancet. 2000; 356:923–929.16. Ministry of Public Safety and Security (KR). The facility and technical standards of play equipment for children [Internet]. accessed on 15 March 2016. Available at http://www.cpf.go.kr/front/index.do.17. Sherker S, Ozanne-Smith J. Are current playground safety standards adequate for preventing arm fractures? Med J Aust. 2004; 180:562–565.18. Sherker S, Ozanne-Smith J, Rechnitzer G, Grzebieta R. Out on a limb: risk factors for arm fracture in playground equipment falls. Inj Prev. 2005; 11:120–124.19. Mathison DJ, Agrawal D. An update on the epidemiology of pediatric fractures. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2010; 26:594–603.20. Macarthur C, Hu X, Wesson DE, Parkin PC. Risk factors for severe injuries associated with falls from playground equipment. Accid Anal Prev. 2000; 32:377–382.21. Howard AW, Macarthur C, Rothman L, Willan A, Macpherson AK. School playground surfacing and arm fractures in children: a cluster randomized trial comparing sand to wood chip surfaces. PLoS Med. 2009; 6:e1000195.22. Sosin DM, Keller P, Sacks JJ, Kresnow M, van Dyck PC. Surface-specific fall injury rates on Utah school playgrounds. Am J Public Health. 1993; 83:733–735.23. Laforest S, Robitaille Y, Lesage D, Dorval D. Surface characteristics, equipment height, and the occurrence and severity of playground injuries. Inj Prev. 2001; 7:35–40.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pediatric Injuries in Kids Cafés and Risk Factors for Significant Injuries: a 6-Year Cross-Sectional Study Using a Multicenter Injury Registry in Korea
- A Preliminary Study of an Emergency Department-based In-depth Injury Surveillance System of Preschool Children Injury
- ICECI Based External Causes Analysis of Severe Pediatric Injury
- The effect of medically-attended injury experience on the use of home safety equipment
- A Preliminary Application of an Emergency Department-based Indepth Injury Surveillance System