Yonsei Med J.
2015 Jul;56(4):1007-1014. 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.4.1007.
Outcomes of Hemodialysis in Children: A 35-Year Experience at Severance Hospital
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Severance Children's Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shinji@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Daewoo General Hospital, Ajou University School of Medicine, Geoje, Korea.
- KMID: 2366342
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.4.1007
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to analyze the results of children treated with hemodialysis (HD) at Severance Hospital over 35 years in terms of incidence, etiologies, characteristics, complications, and clinical outcomes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We analyzed 46 children admitted to Severance Hospital who had undergone HD between January 1979 and December 2013.
RESULTS
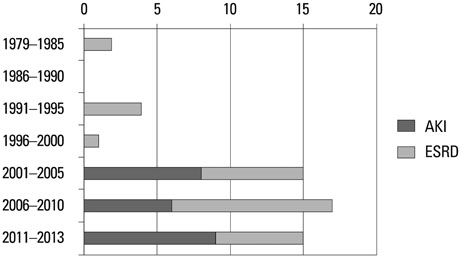
The main etiologies of the 23 end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients who had received HD were chronic glomerulonephritis (7 patients, 30.4%) and congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract (7 patients, 30.4%), whereas the etiology of the 23 acute kidney injury (AKI) patients was hemolytic uremic syndrome (6 patients, 26.1%). Compared with ESRD patients, hemocatheter placement in the femoral vein was preferred over the subclavian or internal jugular vein in the AKI patients (p=0.012). The most common complication was catheter related complication (10 patients, 21.7%). The site of hemocatheter insertion was not related to the frequency of oozing. Placing the hemocatheter in the femoral vein resulted in significantly more events of catheter obstruction than insertion in the internal jugular vein or the subclavian vein (p=0.001). Disequilibrium syndrome occurred more frequently in older patients (p=0.004), as well as patients with a greater body weight (p=0.008) and a higher systolic and diastolic blood pressure before HD (systolic: p=0.021; diastolic: p=0.040).
CONCLUSION
Based on the 35 years of experience in our center, HD can be sufficiently and safely carried out even in children without significant complications.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sethi SK, Bunchman T, Raina R, Kher V. Unique considerations in renal replacement therapy in children: core curriculum 2014. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014; 63:329–345.
Article2. Goldstein SL. Overview of pediatric renal replacement therapy in acute kidney injury. Semin Dial. 2009; 22:180–184.
Article3. Goldstein SL. Hemodialysis in the pediatric patient: state of the art. Adv Ren Replace Ther. 2001; 8:173–179.
Article4. Walters S, Porter C, Brophy PD. Dialysis and pediatric acute kidney injury: choice of renal support modality. Pediatr Nephrol. 2009; 24:37–48.
Article5. Harshman LA, Neuberger ML, Brophy PD. Chronic hemodialysis in pediatric patients: technical and practical aspects of use. Minerva Pediatr. 2012; 64:159–169.6. Paganini EP, Vidt DG. Renal replacement therapy utilizing hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Urol Clin North Am. 1983; 10:347–367.
Article7. Sutherland SM, Alexander SR. Continuous renal replacement therapy in children. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012; 27:2007–2016.
Article8. Mateer FM, Greenman L, Danowski TS. Hemodialysis of the uremic child. AMA Am J Dis Child. 1955; 89:645–655.
Article9. Warady BA, Neu AM, Schaefer F. Optimal care of the infant, child, and adolescent on dialysis: 2014 update. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014; 64:128–142.
Article10. Wedekin M, Ehrich JH, Offner G, Pape L. Renal replacement therapy in infants with chronic renal failure in the first year of life. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010; 5:18–23.
Article11. Kim PK, Lee C, Lee JS, Yun DJ, Park KL, Kwon TJ, et al. The first case of renal transplatation in childhood in Korea. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1980; 23:674–681.12. National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2004; 114:2 Suppl 4th Report. 555–576.13. Fischbach M, Edefonti A, Schröder C, Watson A. European Pediatric Dialysis Working Group. Hemodialysis in children: general practical guidelines. Pediatr Nephrol. 2005; 20:1054–1066.
Article14. Youssef DM, Neemat-Allah MA. Hemodialysis in children: eleven years in a single center in Egypt. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2013; 7:468–474.15. Abdelraheem M, Ali el-T, Osman R, Ellidir R, Bushara A, Hussein R, et al. Outcome of acute kidney injury in Sudanese children - an experience from a sub-Saharan African unit. Perit Dial Int. 2014; 34:526–533.
Article16. Jiang Y, Shen Y, Lau KK. Survey of chronic haemodialysis in children between 2007 and 2012 in China. Nephrology (Carlton). 2014; 19:375–378.
Article17. Chavers BM, Li S, Collins AJ, Herzog CA. Cardiovascular disease in pediatric chronic dialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2002; 62:648–653.
Article18. Orr NI, McDonald SP, McTaggart S, Henning P, Craig JC. Frequency, etiology and treatment of childhood end-stage kidney disease in Australia and New Zealand. Pediatr Nephrol. 2009; 24:1719–1726.
Article19. Lewis MA, Shaw J, Sinha MD, Adalat S, Hussain F, Castledine C, et al. UK Renal Registry 12th Annual Report (December 2009): chapter 14: demography of the UK paediatric renal replacement therapy population in 2008. Nephron Clin Pract. 2010; 115:Suppl 1. c279–c288.20. Hattori S, Yosioka K, Honda M, Ito H. Japanese Society for Pediatric Nephrology. The 1998 report of the Japanese National Registry data on pediatric end-stage renal disease patients. Pediatr Nephrol. 2002; 17:456–461.
Article21. Gulati S, Mittal S, Sharma RK, Gupta A. Etiology and outcome of chronic renal failure in Indian children. Pediatr Nephrol. 1999; 13:594–596.
Article22. Mong Hiep TT, Janssen F, Ismaili K, Khai Minh D, Vuong Kiet D, Robert A. Etiology and outcome of chronic renal failure in hospitalized children in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Pediatr Nephrol. 2008; 23:965–970.
Article23. Orta-Sibu N, Lopez M, Moriyon JC, Chavez JB. Renal diseases in children in Venezuela, South America. Pediatr Nephrol. 2002; 17:566–569.
Article24. Harambat J, van Stralen KJ, Kim JJ, Tizard EJ. Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease in children. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012; 27:363–373.
Article25. Hui-Stickle S, Brewer ED, Goldstein SL. Pediatric ARF epidemiology at a tertiary care center from 1999 to 2001. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005; 45:96–101.
Article26. Wartman SM, Rosen D, Woo K, Gradman WS, Weaver FA, Rowe V. Outcomes with arteriovenous fistulas in a pediatric population. J Vasc Surg. 2014; 60:170–174.
Article27. Chand DH, Valentini RP. International pediatric fistula first initiative: a call to action. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008; 51:1016–1024.
Article28. Zepeda-Orozco D, Quigley R. Dialysis disequilibrium syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012; 27:2205–2211.
Article29. Patel N, Dalal P, Panesar M. Dialysis disequilibrium syndrome: a narrative review. Semin Dial. 2008; 21:493–498.30. Arieff AI. Dialysis disequilibrium syndrome: current concepts on pathogenesis and prevention. Kidney Int. 1994; 45:629–635.
Article31. Bagshaw SM, Peets AD, Hameed M, Boiteau PJ, Laupland KB, Doig CJ. Dialysis Disequilibrium Syndrome: brain death following hemodialysis for metabolic acidosis and acute renal failure--a case report. BMC Nephrol. 2004; 5:9.32. Arieff AI, Lazarowitz VC, Guisado R. Experimental dialysis dis equilibrium syndrome: prevention with glycerol. Kidney Int. 1978; 14:270–278.33. Flannery T, Shoakazemi A, McLaughlin B, Woodman A, Cooke S. Dialysis disequilibrium syndrome: a consideration in patients with hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2008; 2:143–145.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pediatric Hemodialysis
- Outcomes of Peritonitis in Children on Peritoneal Dialysis: A 25-Year Experience at Severance Hospital
- Long-Term Surgical Outcomes of TOF-Severance Hospital Experience
- Experience of Hemodialysis in the Chronic Renal Failure Clients
- The Experience of Fluid Management in Hemodialysis Patients