Yonsei Med J.
2015 Jul;56(4):961-967. 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.4.961.
Low Serum Concentrations of Moxifloxacin, Prothionamide, and Cycloserine on Sputum Conversion in Multi-Drug Resistant TB
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary, Sleep, and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Ansan, Korea.
- 2Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacogenomics Research Center, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. dhkim@inje.ac.kr
- 3Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2366335
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.4.961
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Low serum concentrations of drugs used to treat multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) have occasionally been associated with treatment failure. We determined the frequencies of low serum concentrations of anti-MDR-TB drugs, and assessed the effects of these concentrations on 2-month sputum conversion.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The serum levels of moxifloxacin (MF), prothionamide (PTH), and cycloserine (CS) were determined for 89 serum samples by high-pressure liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
RESULTS
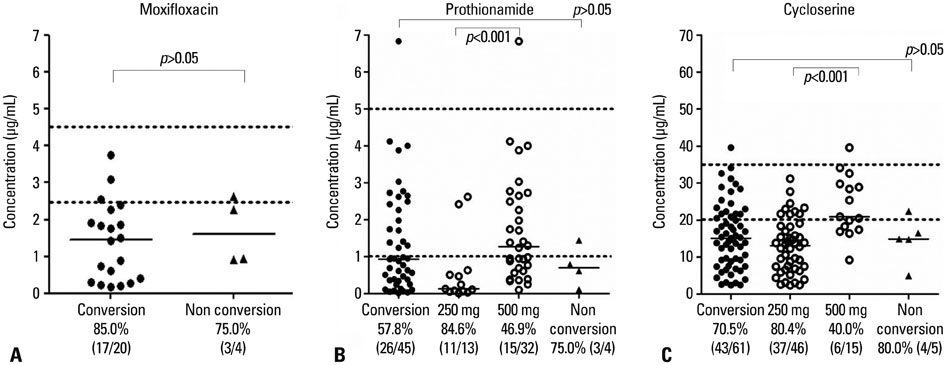
Low serum concentrations of MF, PTH, and CS below the minimal levels of the normal ranges were 83.3% (20/24), 59.2% (29/49), and 71.2% (47/66), respectively. There were no significant differences between the 2-month sputum conversion group (n=25) and the 2-month sputum non-conversion group (n=4) in median drug concentrations (microg/mL) of MF (1.46 vs. 1.60), PTH (0.91 vs. 0.70), and CS (14.90 vs. 14.90). However, a poor compliance rate was significantly greater in the 2-month sputum non-conversion group (75.0%, 3/4) than in the 2-month sputum conversion group (0%, 0/25) (p=0.001).
CONCLUSION
The frequency of low serum concentrations of anti-MDR-TB drugs was substantial and might not affect the 2-month sputum conversion rate. Larger prospective studies with timely sampling are needed to investigate the role of therapeutic drug monitoring in MDR-TB.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Antitubercular Agents/blood/*pharmacokinetics/therapeutic use
Chromatography, High Pressure Liquid
Cycloserine/blood/*pharmacokinetics/therapeutic use
Fluoroquinolones/blood/*pharmacokinetics/therapeutic use
Humans
Medication Adherence
Middle Aged
Prothionamide/blood/*pharmacokinetics/therapeutic use
Retrospective Studies
Sputum/*microbiology
Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Tuberculosis, Multidrug-Resistant/blood/*drug therapy
Young Adult
Antitubercular Agents
Cycloserine
Fluoroquinolones
Prothionamide
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Is Multi-Drug Resistant Tuberculosis More Prevalent in HIV-Infected Patients in Korea?
Shinwon Lee, Sun Hee Lee, Jeong Ha Mok, Su Jin Lee, Kye-Hyung Kim, Jeong Eun Lee, Seung Geun Lee, Joo Seop Chung, Ihm Soo Kwak
Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(6):1508-1510. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.6.1508.
Reference
-
1. World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis control: WHO report 2011. Geneva: World Health Organization;2011.2. Bai GH, Park YK, Choi YW, Bai JI, Kim HJ, Chang CL, et al. Trend of anti-tuberculosis drug resistance in Korea, 1994-2004. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2007; 11:571–576.3. Kim DH, Kim HJ, Park SK, Kong SJ, Kim YS, Kim TH, et al. Treatment outcomes and survival based on drug resistance patterns in multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010; 182:113–119.
Article4. Kim HR, Hwang SS, Kim HJ, Lee SM, Yoo CG, Kim YW, et al. Impact of extensive drug resistance on treatment outcomes in non-HIV-infected patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2007; 45:1290–1295.
Article5. World Health Organization. Guidelines for the programmatic management of drug-resistant tuberculosis-2011 update. Geneva: World Health Organization;2011.6. Cremades R, Rodríguez JC, García-Pachón E, Galiana A, Ruiz-García M, López P, et al. Comparison of the bactericidal activity of various fluoroquinolones against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in an in vitro experimental model. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011; 66:2281–2283.
Article7. Blumberg HM, Burman WJ, Chaisson RE, Daley CL, Etkind SC, Friedman LN, et al. American Thoracic Society/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/Infectious Diseases Society of America: treatment of tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003; 167:603–662.
Article8. Gler MT, Skripconoka V, Sanchez-Garavito E, Xiao H, Cabrera-Rivero JL, Vargas-Vasquez DE, et al. Delamanid for multidrug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:2151–2160.
Article9. Peloquin CA. Therapeutic drug monitoring in the treatment of tuberculosis. Drugs. 2002; 62:2169–2183.
Article10. McIlleron H, Wash P, Burger A, Norman J, Folb PI, Smith P. Determinants of rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol pharmacokinetics in a cohort of tuberculosis patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006; 50:1170–1177.
Article11. Tappero JW, Bradford WZ, Agerton TB, Hopewell P, Reingold AL, Lockman S, et al. Serum concentrations of antimycobacterial drugs in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis in Botswana. Clin Infect Dis. 2005; 41:461–469.
Article12. van Crevel R, Alisjahbana B, de Lange WC, Borst F, Danusantoso H, van der Meer JW, et al. Low plasma concentrations of rifampicin in tuberculosis patients in Indonesia. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2002; 6:497–502.
Article13. Li J, Burzynski JN, Lee YA, Berg D, Driver CR, Ridzon R, et al. Use of therapeutic drug monitoring for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis patients. Chest. 2004; 126:1770–1776.
Article14. Weiner M, Benator D, Burman W, Peloquin CA, Khan A, Vernon A, et al. Association between acquired rifamycin resistance and the pharmacokinetics of rifabutin and isoniazid among patients with HIV and tuberculosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2005; 40:1481–1491.
Article15. Kimerling ME, Phillips P, Patterson P, Hall M, Robinson CA, Dunlap NE. Low serum antimycobacterial drug levels in non-HIV-infected tuberculosis patients. Chest. 1998; 113:1178–1183.
Article16. U.S. National Tuberculosis Association. Diagnostic standards and classification of tuberculosis. New York: National Tuberculosis Association;1961.17. Alffenaar JW, van Altena R, Bökkerink HJ, Luijckx GJ, van Soolingen D, Aarnoutse RE, et al. Pharmacokinetics of moxifloxacin in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma in patients with tuberculous meningitis. Clin Infect Dis. 2009; 49:1080–1082.
Article18. Schumacher GE, Barr JT. Economic and outcome issues for therapeutic drug monitoring in medicine. Ther Drug Monit. 1998; 20:539–542.
Article19. Heysell SK, Moore JL, Staley D, Dodge D, Houpt ER. Early Therapeutic Drug Monitoring for Isoniazid and Rifampin among Diabetics with Newly Diagnosed Tuberculosis in Virginia, USA. Tuberc Res Treat. 2013; 2013:129723.
Article20. Pasipanodya JG, Srivastava S, Gumbo T. Meta-analysis of clinical studies supports the pharmacokinetic variability hypothesis for acquired drug resistance and failure of antituberculosis therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2012; 55:169–177.
Article21. Weis SE, Slocum PC, Blais FX, King B, Nunn M, Matney GB, et al. The effect of directly observed therapy on the rates of drug resistance and relapse in tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 1994; 330:1179–1184.
Article22. Wallis RS, Wang C, Meyer D, Thomas N. Month 2 culture status and treatment duration as predictors of tuberculosis relapse risk in a meta-regression model. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e71116.
Article23. Koh WJ, Lee SH, Kang YA, Lee CH, Choi JC, Lee JH, et al. Comparison of levofloxacin versus moxifloxacin for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013; 188:858–864.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Medical Treatment of Pulmonary Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis
- The Criteria of Drug Resistance to Secondary Antituberculosis Drugs
- A clinical effect of retreatment by prothionamide, cycloserine, para-aminosalicylic acid, streptomycin(kanamycin or tuberactinomyc-in) on pulmonary tuberculosis
- Outcomes and Use of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring in Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis Patients Treated in Virginia, 2009-2014