Yonsei Med J.
2015 Jul;56(4):928-934. 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.4.928.
In Vivo Selection of Pan-Drug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii during Antibiotic Treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- 2Department of Dental Hygiene, Silla University, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine and Research Institute of Bacterial Resistance, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kscpjsh@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2366331
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.4.928
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Colistin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii (A. baumannii) is mediated by a complete loss of lipopolysaccharide production via mutations in lpxA, lpxC, and lpxD gene or lipid A modifications via mutations in the pmrA and pmrB genes. However, the exact mechanism of therapy-induced colistin resistance in A. baumannii is not well understood.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
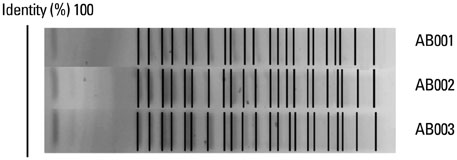
We investigated the genotypic and phenotypic changes that underlie pan-drug resistance mechanisms by determining differences between the alterations in extensively drug-resistant (XDR) A. baumannii (AB001 and AB002) isolates and a pan-drug resistant (PDR) counterpart (AB003) recovered from one patient before and after antibiotic treatment, respectively.
RESULTS
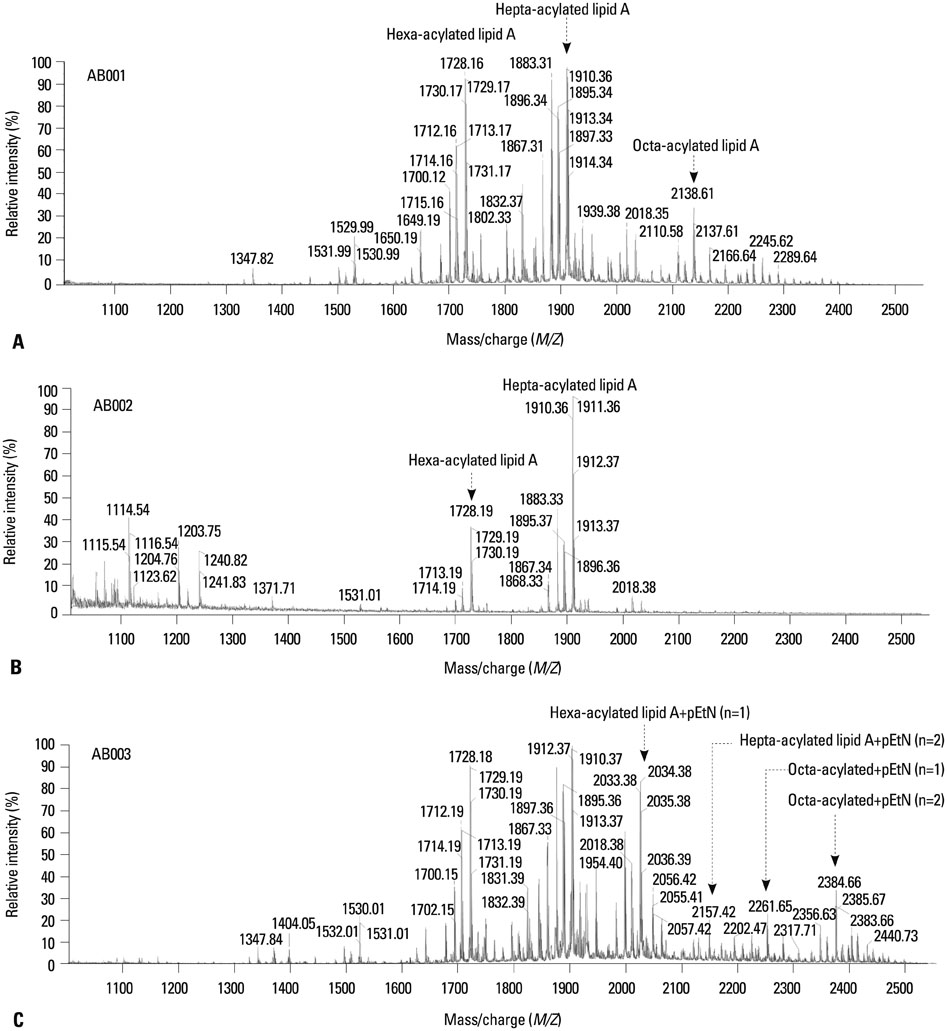
All three clinical isolates shared an identical sequence type (ST138), belonging to the global epidemic clone, clonal complex 92, and all produced OXA-23 carbapenemase. The PDR AB003 showed two genetic differences, acquisition of armA gene and an amino acid substitution (Glu229Asp) in pmrB gene, relative to XDR isolates. No mutations were detected in the pmrA, pmrC, lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD genes in all three isolates. In matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight analysis, the three isolates commonly showed two major peaks at 1728 m/z and 1912 m/z, but peaks at 2034 m/z, 2157 m/z, 2261 m/z, and 2384 m/z were detected only in the PDR A. baumannii AB003 isolate.
CONCLUSION
Our results show that changes in lipid A structure via a mutation in the pmrB gene and acquisition of armA gene might confer resistance to colistin and aminoglycosides to XDR A. baumannii strains, resulting in appearance of a PDR A. baumannii strain of ST138.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acinetobacter Infections/*drug therapy/microbiology
Acinetobacter baumannii/*drug effects/*genetics/isolation & purification
Aged
Anti-Bacterial Agents/*pharmacology/therapeutic use
Bacterial Proteins/*genetics
Colistin/*pharmacology/therapeutic use
*Drug Resistance, Bacterial
Electrophoresis, Gel, Pulsed-Field
Genotype
Humans
Male
Microbial Sensitivity Tests
Molecular Typing
Mutation
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Transcription Factors
beta-Lactamases
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Bacterial Proteins
Colistin
Transcription Factors
beta-Lactamases
Figure
Reference
-
1. Magiorakos AP, Srinivasan A, Carey RB, Carmeli Y, Falagas ME, Giske CG, et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012; 18:268–281.
Article2. Chang HL, Tang CH, Hsu YM, Wan L, Chang YF, Lin CT, et al. Nosocomial outbreak of infection with multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a medical center in Taiwan. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2009; 30:34–38.
Article3. Maragakis LL, Perl TM. Acinetobacter baumannii: epidemiology, antimicrobial resistance, and treatment options. Clin Infect Dis. 2008; 46:1254–1263.
Article4. Cho HH, Kwon KC, Sung JY, Koo SH. Spread and genetic characterization of ST137 and ST138 multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from a tertiary hospital in Korea. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2013; 43:145–150.5. Endo S, Yano H, Hirakata Y, Arai K, Kanamori H, Ogawa M, et al. Molecular epidemiology of carbapenem-non-susceptible Acinetobacter baumannii in Japan. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012; 67:1623–1626.
Article6. Lee Y, Lee J, Jeong SH, Lee J, Bae IK, Lee K. Carbapenem-non-susceptible Acinetobacter baumannii of sequence type 92 or its single-locus variants with a G428T substitution in zone 2 of the rpoB gene. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011; 66:66–72.
Article7. Wang X, Qiao F, Yu R, Gao Y, Zong Z. Clonal diversity of Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates revealed by a snapshot study. BMC Microbiol. 2013; 13:234.
Article8. Cai Y, Chai D, Wang R, Liang B, Bai N. Colistin resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii: clinical reports, mechanisms and antimicrobial strategies. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012; 67:1607–1615.
Article9. Lee K, Yong D, Jeong SH, Chong Y. Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter spp.: increasingly problematic nosocomial pathogens. Yonsei Med J. 2011; 52:879–891.
Article10. O'Hara JA, Ambe LA, Casella LG, Townsend BM, Pelletier MR, Ernst RK, et al. Activities of vancomycin-containing regimens against colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013; 57:2103–2108.11. Valencia R, Arroyo LA, Conde M, Aldana JM, Torres MJ, Fernández-Cuenca F, et al. Nosocomial outbreak of infection with pan-drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a tertiary care university hospital. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2009; 30:257–263.
Article12. Adams MD, Nickel GC, Bajaksouzian S, Lavender H, Murthy AR, Jacobs MR, et al. Resistance to colistin in Acinetobacter baumannii associated with mutations in the PmrAB two-component system. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009; 53:3628–3634.
Article13. Moffatt JH, Harper M, Harrison P, Hale JD, Vinogradov E, Seemann T, et al. Colistin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii is mediated by complete loss of lipopolysaccharide production. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010; 54:4971–4977.
Article14. La Scola B, Gundi VA, Khamis A, Raoult D. Sequencing of the rpoB gene and flanking spacers for molecular identification of Acinetobacter species. J Clin Microbiol. 2006; 44:827–832.
Article15. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: twenty-second informational supplement, M100-S22. Wayne (PA): Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2012.16. Bartual SG, Seifert H, Hippler C, Luzon MA, Wisplinghoff H, Rodríguez-Valera F. Development of a multilocus sequence typing scheme for characterization of clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 43:4382–4390.
Article17. Tenover FC, Arbeit RD, Goering RV, Mickelsen PA, Murray BE, Persing DH, et al. Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: criteria for bacterial strain typing. J Clin Microbiol. 1995; 33:2233–2239.
Article18. Cho YJ, Moon DC, Jin JS, Choi CH, Lee YC, Lee JC. Genetic basis of resistance to aminoglycosides in Acinetobacter spp. and spread of armA in Acinetobacter baumannii sequence group 1 in Korean hospitals. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009; 64:185–190.
Article19. Vila J, Ruiz J, Goñi P, Jimenez de Anta T. Quinolone-resistance mutations in the topoisomerase IV parC gene of Acinetobacter baumannii. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1997; 39:757–762.
Article20. Vila J, Ruiz J, Goñi P, Marcos A, Jimenez de Anta T. Mutation in the gyrA gene of quinolone-resistant clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995; 39:1201–1203.
Article21. Woodford N, Ellington MJ, Coelho JM, Turton JF, Ward ME, Brown S, et al. Multiplex PCR for genes encoding prevalent OXA carbapenemases in Acinetobacter spp. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2006; 27:351–353.
Article22. Lin YC, Hsia KC, Chen YC, Sheng WH, Chang SC, Liao MH, et al. Genetic basis of multidrug resistance in Acinetobacter clinical isolates in Taiwan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010; 54:2078–2084.
Article23. Beceiro A, Llobet E, Aranda J, Bengoechea JA, Doumith M, Hornsey M, et al. Phosphoethanolamine modification of lipid A in colistin-resistant variants of Acinetobacter baumannii mediated by the pmrAB two-component regulatory system. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011; 55:3370–3379.
Article24. Yi EC, Hackett M. Rapid isolation method for lipopolysaccharide and lipid A from gram-negative bacteria. Analyst. 2000; 125:651–656.
Article25. Petrosillo N, Ioannidou E, Falagas ME. Colistin monotherapy vs. combination therapy: evidence from microbiological, animal and clinical studies. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2008; 14:816–827.
Article26. López-Rojas R, Jiménez-Mejías ME, Lepe JA, Pachón J. Acinetobacter baumannii resistant to colistin alters its antibiotic resistance profile: a case report from Spain. J Infect Dis. 2011; 204:1147–1148.
Article27. López-Rojas R, McConnell MJ, Jiménez-Mejías ME, Domínguez-Herrera J, Fernández-Cuenca F, Pachón J. Colistin resistance in a clinical Acinetobacter baumannii strain appearing after colistin treatment: effect on virulence and bacterial fitness. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013; 57:4587–4589.
Article28. Arroyo LA, Herrera CM, Fernandez L, Hankins JV, Trent MS, Hancock RE. The pmrCAB operon mediates polymyxin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 17978 and clinical isolates through phosphoethanolamine modification of lipid A. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011; 55:3743–3751.
Article29. Gunn JS. The Salmonella PmrAB regulon: lipopolysaccharide modifications, antimicrobial peptide resistance and more. Trends Microbiol. 2008; 16:284–290.
Article30. Gunn JS, Lim KB, Krueger J, Kim K, Guo L, Hackett M, et al. PmrA-PmrB-regulated genes necessary for 4-aminoarabinose lipid A modification and polymyxin resistance. Mol Microbiol. 1998; 27:1171–1182.
Article31. Zhou Z, Ribeiro AA, Lin S, Cotter RJ, Miller SI, Raetz CR. Lipid A modifications in polymyxin-resistant Salmonella typhimurium: PMRA-dependent 4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinose, and phosphoethanolamine incorporation. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:43111–43121.32. Kim Y, Bae IK, Lee H, Jeong SH, Yong D, Lee K. In vivo emergence of colistin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates of sequence type 357 during colistin treatment. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014; 79:362–366.
Article33. Gordon NC, Wareham DW. Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: mechanisms of virulence and resistance. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2010; 35:219–226.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erratum to “In Vivo Selection of Pan-Drug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii during Antibiotic Treatment†by Kim Y, et al. (Yonsei Med J 2015;56:928-934.)
- Successful Management of Pan-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Meningitis without Intrathecal or Intraventricular Antibiotic Therapy in a Neonate
- Current Analysis of Acintobacter baumannii Infection among Pediatric Patients in a Single-centered Study
- Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
- The Changing Patterns of Antibiotic Susceptibility for Acinetobacter baumannii in Pediatric Burn Patients