Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2015 Mar;7(2):175-185. 10.4168/aair.2015.7.2.175.
The Association of GSDMB and ORMDL3 Gene Polymorphisms With Asthma: A Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Health Statistics, School of Public Health, Shanxi Medical University, China. wtstat@21n.com
- 2Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, School of Public Health, Shanxi Medical University, China.
- 3Department of Surgery, General Hospital of Datong Coal Mining Group, China.
- 4Department of Preventive Medicine, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL, USA.
- 5Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL, USA.
- KMID: 2365546
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2015.7.2.175
Abstract
- PURPOSE
ORM1-like 3 (ORMDL3) belongs to a highly conserved protein family which is anchored as transmembrane protein in the endoplasmic reticulum. Gasdermin B (GSDMB) is adjacent to ORMDL3 on chromosome 17q21.2 and belongs to the gasdermin-domain containing the protein family (GSDM family). Recent reports suggest that GSDMB and ORMDL3 are associated with asthma in several populations. However, genetic association studies that examined the association of GSDMB and ORMDL3 gene variants with asthma showed conflicting results. To assess whether combined evidence shows the association between GSDMB/ORMDL3 polymorphism and asthma.
METHODS
A bibliographic search from MEDLINE identified 13 original articles using the search keywords 'GSDMB', 'ORMDL3', and 'asthma'. An updated literature-based meta-analysis involving 6,691 subjects with asthma, 9,281 control individuals, and 1,360 families were conducted. Meta-odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) based on the fixed effects model or the random effects model depended on Cochran's Q-statistic and I2 values. Data from case-control and TDT studies were analyzed in an allelic model using the Catmap software.
RESULTS
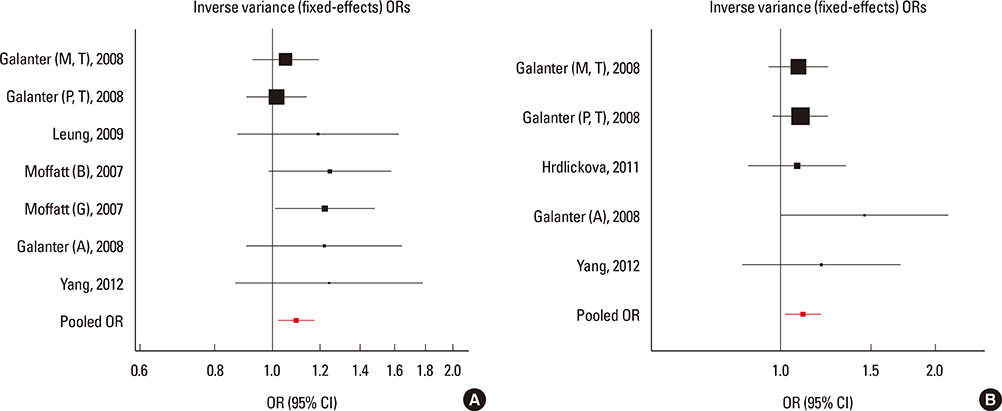
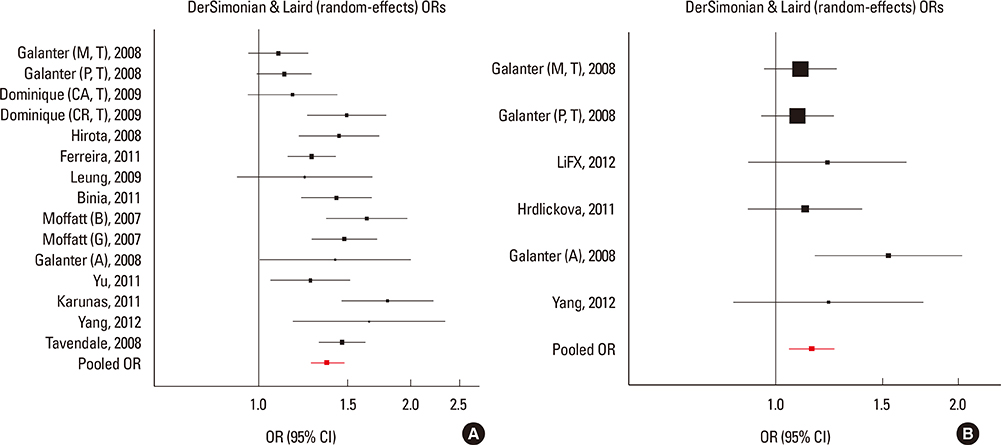
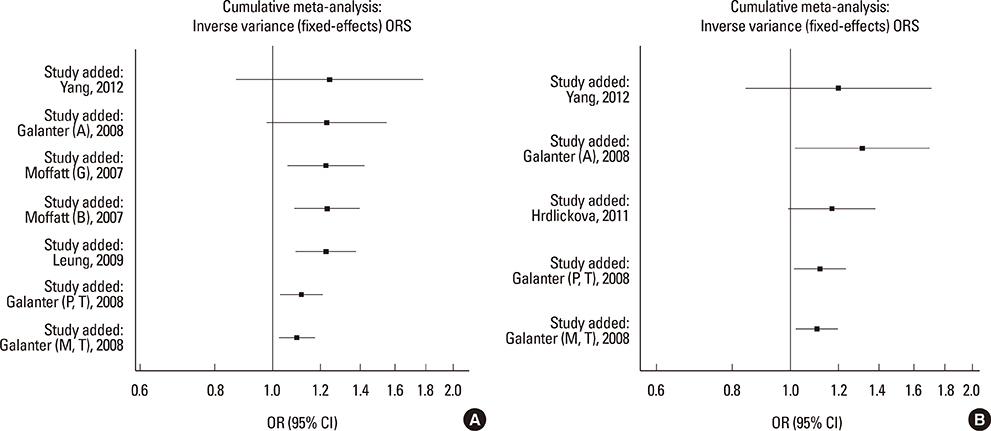
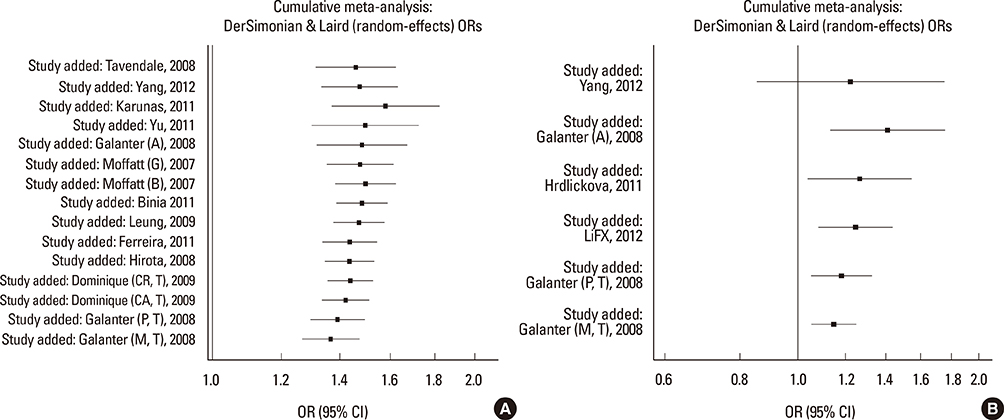
We selected and identified 3 SNPs of ORMDL3 associated with asthma (rs8076131: OR=1.10; 95% CI, 1.02-1.20; P=0.012. rs12603332: OR=1.15; 95% CI, 1.05-1.25; P=0.002. rs3744246: OR=1.10; 95% CI, 1.02-1.17; P=0.008) and 1 SNP of GSDMB associated with asthma (rs7216389: OR=1.37; 95% CI, 1.27-1.47; P<0.01). Publication bias was estimated using modified Egger's linear regression test proposed by Harbordetal and revealed no evidence of biases. Furthermore, cumulative meta-analysis in chronological order showed the inclination toward significant association for rs7216389 and rs12603332 with continually adding studies, and the inclination toward null-significant association for rs3744246 and rs8076131.
CONCLUSIONS
Moderate evidence exists for associations of the ORMDL3 rs8076131, rs12603332, and rs3744246 and GSDMB rs7216389 variants with asthma. Large sample size and representative population-based studies and TDT studies with homogeneous asthmatic patients and well-matched controls are warranted to confirm this finding.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lemanske RF Jr, Busse WW. Asthma: clinical expression and molecular mechanisms. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:S95–S102.2. Laitinen LA, Heino M, Laitinen A, Kava T, Haahtela T. Damage of the airway epithelium and bronchial reactivity in patients with asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985; 131:599–606.3. Koppelman GH, Los H, Postma DS. Genetic and environment in asthma: the answer of twin studies. Eur Respir J. 1999; 13:2–4.4. Zhang G, Goldblatt J, LeSouëf P. The era of genome-wide association studies: opportunities and challenges for asthma genetics. J Hum Genet. 2009; 54:624–628.5. Breslow DK, Collins SR, Bodenmiller B, Aebersold R, Simons K, Shevchenko A, et al. Orm family proteins mediate sphingolipid homeostasis. Nature. 2010; 463:1048–1053.6. Cantero-Recasens G, Fandos C, Rubio-Moscardo F, Valverde MA, Vicente R. The asthma-associated ORMDL3 gene product regulates endoplasmic reticulum-mediated calcium signaling and cellular stress. Hum Mol Genet. 2010; 19:111–121.7. Yang FF, Huang Y, Li QB, Dai JH, Fu Z. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the ORM1-like 3 gene associated with childhood asthma in a Chinese population. Genet Mol Res. 2012; 11:4646–4653.8. Galanter J, Choudhry S, Eng C, Nazario S, Rodríguez-Santana JR, Casal J, et al. ORMDL3 gene is associated with asthma in three ethnically diverse populations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008; 177:1194–1200.9. Hrdlickova B, Holla LI. Relationship between the 17q21 locus and adult asthma in a Czech population. Hum Immunol. 2011; 72:921–925.10. Li FX, Tan JY, Yang XX, Wu YS, Wu D, Li M. Genetic variants on 17q21 are associated with asthma in a Han Chinese population. Genet Mol Res. 2012; 11:340–347.11. Leung TF, Sy HY, Ng MC, Chan IH, Wong GW, Tang NL, et al. Asthma and atopy are associated with chromosome 17q21 markers in Chinese children. Allergy. 2009; 64:621–628.12. Moffatt MF, Kabesch M, Liang L, Dixon AL, Strachan D, Heath S, et al. Genetic variants regulating ORMDL3 expression contribute to the risk of childhood asthma. Nature. 2007; 448:470–473.13. Tamura M, Tanaka S, Fujii T, Aoki A, Komiyama H, Ezawa K, et al. Members of a novel gene family, Gsdm, are expressed exclusively in the epithelium of the skin and gastrointestinal tract in a highly tissue-specific manner. Genomics. 2007; 89:618–629.14. Carl-McGrath S, Schneider-Stock R, Ebert M, Röcken C. Differential expression and localisation of gasdermin-like (GSDML), a novel member of the cancer-associated GSDMDC protein family, in neoplastic and non-neoplastic gastric, hepatic, and colon tissues. Pathology. 2008; 40:13–24.15. Zhang Y, Moffatt MF, Cookson WO. Genetic and genomic approaches to asthma: new insights for the origins. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2012; 18:6–13.16. Tavendale R, Macgregor DF, Mukhopadhyay S, Palmer CN. A polymorphism controlling ORMDL3 expression is associated with asthma that is poorly controlled by current medications. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 121:860–863.17. Karunas AS, Iunusbaev BB, Fedorova I, Gimalova GF, Ramazanova NN, Gur'eva LL, et al. Genome-wide association study of bronchial asthma in the Volga-Ural region of Russia. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2011; 45:992–1003.18. Yu J, Kang MJ, Kim BJ, Kwon JW, Song YH, Choi WA, et al. Polymorphisms in GSDMA and GSDMB are associated with asthma susceptibility, atopy and BHR. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2011; 46:701–708.19. Binia A, Khorasani N, Bhavsar PK, Adcock I, Brightling CE, Chung KF, et al. Chromosome 17q21 SNP and severe asthma. J Hum Genet. 2011; 56:97–98.20. Ferreira MA, McRae AF, Medland SE, Nyholt DR, Gordon SD, Wright MJ, et al. Association between ORMDL3, IL1RL1 and a deletion on chromosome 17q21 with asthma risk in Australia. Eur J Hum Genet. 2011; 19:458–464.21. Hirota T, Harada M, Sakashita M, Doi S, Miyatake A, Fujita K, et al. Genetic polymorphism regulating ORM1-like 3 (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) expression is associated with childhood atopic asthma in a Japanese population. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 121:769–770.22. Verlaan DJ, Berlivet S, Hunninghake GM, Madore AM, Larivière M, Moussette S, et al. Allele-specific chromatin remodeling in the ZPBP2/GSDMB/ORMDL3 locus associated with the risk of asthma and autoimmune disease. Am J Hum Genet. 2009; 85:377–393.23. Lander ES, Schork NJ. Genetic dissection of complex traits. Science. 1994; 265:2037–2048.24. Mantel N, Haenszel W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959; 22:719–748.25. DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986; 7:177–188.26. Deeks JJ, Altman DG, Bradburn MJ. Chapter 15. Statistical methods for examining heterogeneity and combining results from several studies in meta-analysis. In : Egger M, Smith GD, Altman DG, editors. Systematic reviews in health care: meta-analysis in context. 2nd ed. London: BMJ;2001. p. 285–312.27. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997; 315:629–634.28. Kazeem GR, Farrall M. Integrating case-control and TDT studies. Ann Hum Genet. 2005; 69:329–335.29. Nicodemus KK. Catmap: case-control and TDT meta-analysis package. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008; 9:130.30. Rogers AJ, Raby BA, Lasky-Su JA, Murphy A, Lazarus R, Klanderman BJ, et al. Assessing the reproducibility of asthma candidate gene associations, using genome-wide data. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009; 179:1084–1090.31. Wu H, Romieu I, Sienra-Monge JJ, Li H, del Rio-Navarro BE, London SJ. Genetic variation in ORM1-like 3 (ORMDL3) and gasdermin-like (GSDML) and childhood asthma. Allergy. 2009; 64:629–635.32. Madore AM, Tremblay K, Hudson TJ, Laprise C. Replication of an association between 17q21 SNPs and asthma in a French-Canadian familial collection. Hum Genet. 2008; 123:93–95.33. Marinho S, Custovic A, Marsden P, Smith JA, Simpson A. 17q12-21 variants are associated with asthma and interact with active smoking in an adult population from the United Kingdom. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2012; 108:402–411.e9.34. Flory JH, Sleiman PM, Christie JD, Annaiah K, Bradfield J, Kim CE, et al. 17q12-21 variants interact with smoke exposure as a risk factor for pediatric asthma but are equally associated with early-onset versus late-onset asthma in North Americans of European ancestry. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124:605–607.35. Smit LA, Bouzigon E, Pin I, Siroux V, Monier F, Aschard H, et al. 17q21 variants modify the association between early respiratory infections and asthma. Eur Respir J. 2010; 36:57–64.36. Moffatt MF, Gut IG, Demenais F, Strachan DP, Bouzigon E, Heath S, et al. A large-scale, consortium-based genomewide association study of asthma. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:1211–1221.37. Halapi E, Gudbjartsson DF, Jonsdottir GM, Bjornsdottir US, Thorleifsson G, Helgadottir H, et al. A sequence variant on 17q21 is associated with age at onset and severity of asthma. Eur J Hum Genet. 2010; 18:902–908.38. Wan YI, Shrine NR, Soler Artigas M, Wain LV, Blakey JD, Moffatt MF, et al. Genome-wide association study to identify genetic determinants of severe asthma. Thorax. 2012; 67:762–768.39. Kang MJ, Yu HS, Seo JH, Kim HY, Jung YH, Kim YJ, et al. GSDMB/ORMDL3 variants contribute to asthma susceptibility and eosinophil-mediated bronchial hyperresponsiveness. Hum Immunol. 2012; 73:954–959.40. Sleiman PM, Annaiah K, Imielinski M, Bradfield JP, Kim CE, Frackelton EC, et al. ORMDL3 variants associated with asthma susceptibility in North Americans of European ancestry. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 122:1225–1227.41. Sterne JA, Gavaghan D, Egger M. Publication and related bias in meta-analysis: power of statistical tests and prevalence in the literature. J Clin Epidemiol. 2000; 53:1119–1129.42. Willemsen G, van Beijsterveldt TC, van Baal CG, Postma D, Boomsma DI. Heritability of self-reported asthma and allergy: a study in adult Dutch twins, siblings and parents. Twin Res Hum Genet. 2008; 11:132–142.43. Fagnani C, Annesi-Maesano I, Brescianini S, D'Ippolito C, Medda E, Nisticò L, et al. Heritability and shared genetic effects of asthma and hay fever: an Italian study of young twins. Twin Res Hum Genet. 2008; 11:121–131.44. Bouzigon E, Corda E, Aschard H, Dizier MH, Boland A, Bousquet J, et al. Effect of 17q21 variants and smoking exposure in early-onset asthma. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:1985–1994.45. Saeki N, Kuwahara Y, Sasaki H, Satoh H, Shiroishi T. Gasdermin (Gsdm) localizing to mouse Chromosome 11 is predominantly expressed in upper gastrointestinal tract but significantly suppressed in human gastric cancer cells. Mamm Genome. 2000; 11:718–724.46. Saeki N, Usui T, Aoyagi K, Kim DH, Sato M, Mabuchi T, et al. Distinctive expression and function of four GSDM family genes (GSDMA-D) in normal and malignant upper gastrointestinal epithelium. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2009; 48:261–271.47. Hjelmqvist L, Tuson M, Marfany G, Herrero E, Balcells S, Gonzàlez-Duarte R. ORMDL proteins are a conserved new family of endoplasmic reticulum membrane proteins. Genome Biol. 2002; 3:RESEARCH0027.48. Heinemeyer T, Wingender E, Reuter I, Hermjakob H, Kel AE, Kel OV, et al. Databases on transcriptional regulation: TRANSFAC, TRRD and COMPEL. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998; 26:362–367.49. Ellenberger T, Fass D, Arnaud M, Harrison SC. Crystal structure of transcription factor E47: e-box recognition by a basic region helix-loop-helix dimer. Genes Dev. 1994; 8:970–980.50. Quong MW, Romanow WJ, Murre C. E protein function in lymphocyte development. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002; 20:301–322.51. Murre C. Helix-loop-helix proteins and lymphocyte development. Nat Immunol. 2005; 6:1079–1086.52. Tomita K, Sakashita M, Hirota T, Tanaka S, Masuyama K, Yamada T, et al. Variants in the 17q21 asthma susceptibility locus are associated with allergic rhinitis in the Japanese population. Allergy. 2013; 68:92–100.53. Miller M, Tam AB, Cho JY, Doherty TA, Pham A, Khorram N, et al. ORMDL3 is an inducible lung epithelial gene regulating metalloproteases, chemokines, OAS, and ATF6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012; 109:16648–16653.54. Ha SG, Ge XN, Bahaie NS, Kang BN, Rao A, Rao SP, et al. ORMDL3 promotes eosinophil trafficking and activation via regulation of integrins and CD48. Nat Commun. 2013; 4:2479.55. Miller M, Rosenthal P, Beppu A, Mueller JL, Hoffman HM, Tam AB, et al. ORMDL3 transgenic mice have increased airway remodeling and airway responsiveness characteristic of asthma. J Immunol. 2014; 192:3475–3487.56. CalXMLLink_XYZkan M, Bochkov YA, Kreiner-Møller E, Bønnelykke K, Stein MM, Du G, et al. Rhinovirus wheezing illness and genetic risk of childhood-onset asthma. N Engl J Med. 2013; 368:1398–1407.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gene - Gene Interactions Among MCP Genes Polymorphisms in Asthma
- Association of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Toll-like Receptor Genes With Asthma Risk: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Severe Refractory Asthma and Genetics
- NJK14047 Suppression of the p38 MAPK Ameliorates OVA-Induced Allergic Asthma during Sensitization and Challenge Periods
- Association of beta2-adrenoceptor Polymorphisms with Baseline FEV1 in Asthmatics