Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2016 Nov;20(6):649-655. 10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.6.649.
TonEBP suppresses adipocyte differentiation via modulation of early signaling in 3T3-L1 cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon 35015, Korea. sdlee@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2364269
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.6.649
Abstract
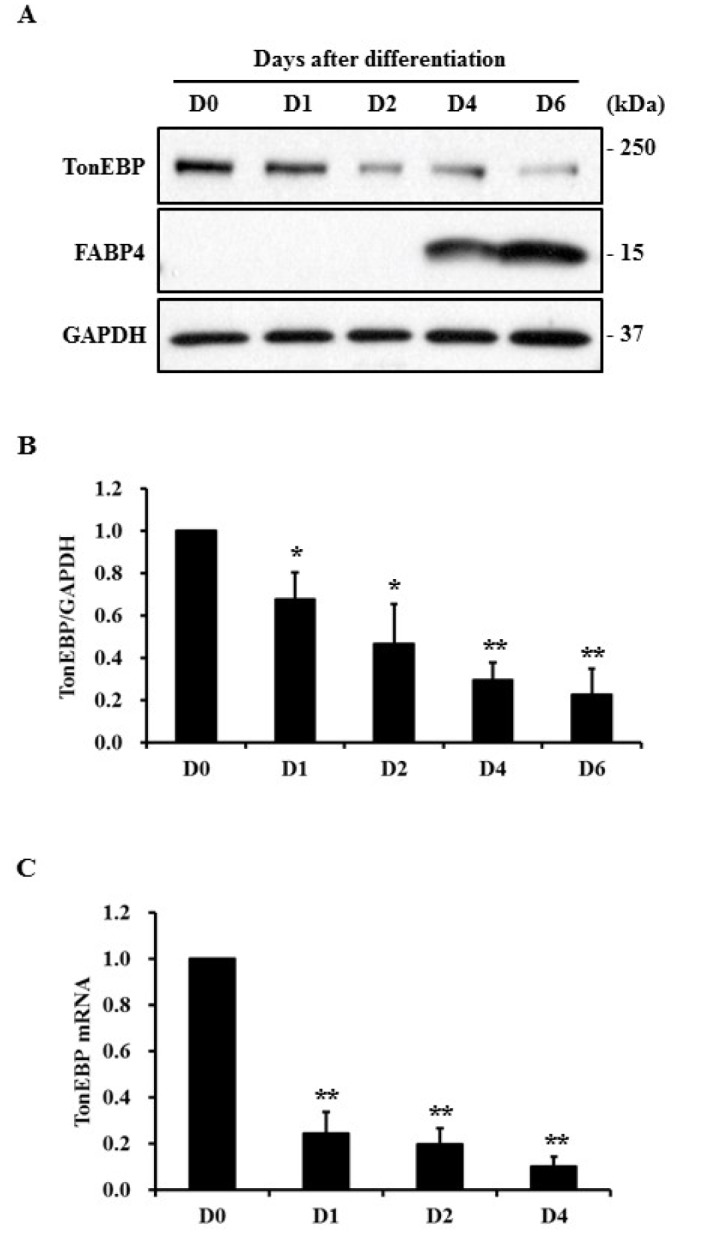
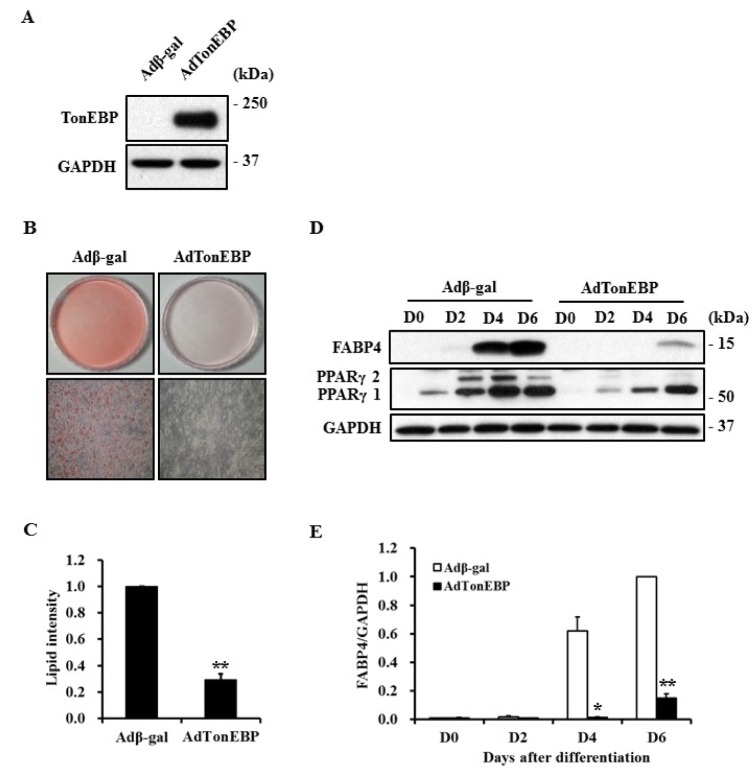
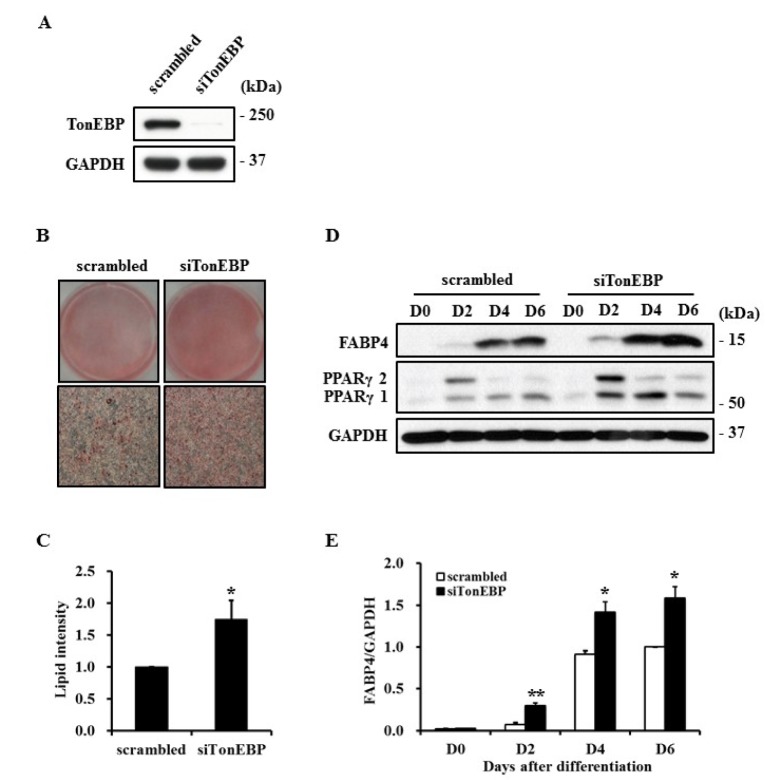
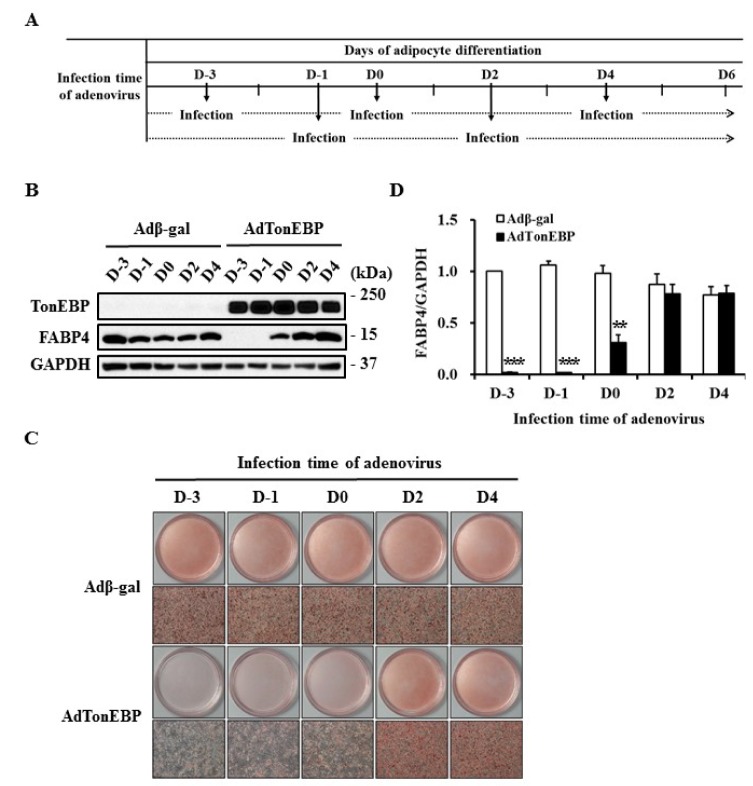
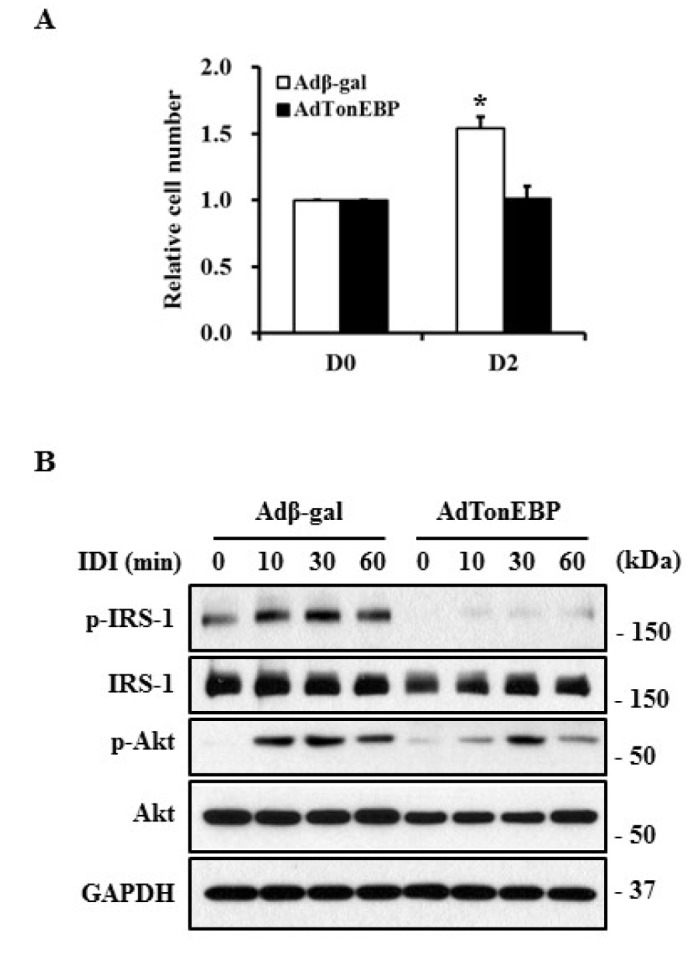
- TonEBP belongs to the Rel family of transcription factors and plays important roles in inflammation as well as kidney homeostasis. Recent studies suggest that TonEBP expression is also involved in differentiation of several cell types such as myocytes, chondrocytes, and osteocytes. In this study, we investigated the roles of TonEBP during adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells. TonEBP mRNA and protein expression was dramatically reduced during adipocyte differentiation. Sustained expression of TonEBP using an adenovirus suppressed the formation of lipid droplets as well as the expression of FABP4, a marker of differentiated adipocytes. TonEBP also inhibited the expression of PPARγ, a known master regulator of adipocytes. RNAi-mediated knock down of TonEBP promoted adipocyte differentiation. However, overexpression of TonEBP did not affect adipogenesis after the initiation of differentiation. Furthermore, TonEBP expression suppressed mitotic clonal expansion and insulin signaling, which are required early for adipocyte differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells. These results suggest that TonEBP may be an important regulatory factor in the early phase of adipocyte differentiation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stroud JC, Lopez-Rodriguez C, Rao A, Chen L. Structure of a TonEBP-DNA complex reveals DNA encircled by a transcription factor. Nat Struct Biol. 2002; 9:90–94. PMID: 11780147.
Article2. Halterman JA, Kwon HM, Wamhoff BR. Tonicity-independent regulation of the osmosensitive transcription factor TonEBP (NFAT5). Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012; 302:C1–C8. PMID: 21998140.
Article3. Adachi A, Takahashi T, Ogata T, Imoto-Tsubakimoto H, Nakanishi N, Ueyama T, Matsubara H. NFAT5 regulates the canonical Wnt pathway and is required for cardiomyogenic differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012; 426:317–323. PMID: 22935419.
Article4. O'Connor RS, Mills ST, Jones KA, Ho SN, Pavlath GK. A combinatorial role for NFAT5 in both myoblast migration and differentiation during skeletal muscle myogenesis. J Cell Sci. 2007; 120:149–159. PMID: 17164296.5. Caron MM, van der Windt AE, Emans PJ, van Rhijn LW, Jahr H, Welting TJ. Osmolarity determines the in vitro chondrogenic differentiation capacity of progenitor cells via nuclear factor of activated T-cells 5. Bone. 2013; 53:94–102. PMID: 23219947.
Article6. Kaur J. A comprehensive review on metabolic syndrome. Cardiol Res Pract. 2014; 2014:943162. PMID: 24711954.
Article7. Aballay LR, Eynard AR, Díaz Mdel P, Navarro A, Muñoz SE. Overweight and obesity: a review of their relationship to metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, and cancer in South America. Nutr Rev. 2013; 71:168–179. PMID: 23452284.
Article8. MacLean PS, Higgins JA, Giles ED, Sherk VD, Jackman MR. The role for adipose tissue in weight regain after weight loss. Obes Rev. 2015; 16(Suppl 1):45–54. PMID: 25614203.
Article9. Jo J, Gavrilova O, Pack S, Jou W, Mullen S, Sumner AE, Cushman SW, Periwal V. Hypertrophy and/or Hyperplasia: dynamics of adipose tissue growth. PLoS Comput Biol. 2009; 5:e1000324. PMID: 19325873.
Article10. Giordano A, Smorlesi A, Frontini A, Barbatelli G, Cinti S. White, brown and pink adipocytes: the extraordinary plasticity of the adipose organ. Eur J Endocrinol. 2014; 170:R159–R171. PMID: 24468979.11. Hirsch J, Han PW. Cellularity of rat adipose tissue: effects of growth, starvation, and obesity. J Lipid Res. 1969; 10:77–82. PMID: 5764119.
Article12. Faust IM, Johnson PR, Stern JS, Hirsch J. Diet-induced adipocyte number increase in adult rats: a new model of obesity. Am J Physiol. 1978; 235:E279–E286. PMID: 696822.
Article13. Farmer SR. Transcriptional control of adipocyte formation. Cell Metab. 2006; 4:263–273. PMID: 17011499.
Article14. Gregoire FM, Smas CM, Sul HS. Understanding adipocyte differentiation. Physiol Rev. 1998; 78:783–809. PMID: 9674695.
Article15. Ntambi JM, Young-Cheul K. Adipocyte differentiation and gene expression. J Nutr. 2000; 130:3122S–33126. PMID: 11110885.
Article16. Green H, Kehinde O. An established preadipose cell line and its differentiation in culture. II. Factors affecting the adipose conversion. Cell. 1975; 5:19–27. PMID: 165899.
Article17. Orlicky DJ, Schaack J. Adenovirus transduction of 3T3-L1 cells. J Lipid Res. 2001; 42:460–466. PMID: 11254759.
Article18. Zebisch K, Voigt V, Wabitsch M, Brandsch M. Protocol for effective differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells to adipocytes. Anal Biochem. 2012; 425:88–90. PMID: 22425542.
Article19. Rosen ED, Walkey CJ, Puigserver P, Spiegelman BM. Transcriptional regulation of adipogenesis. Genes Dev. 2000; 14:1293–1307. PMID: 10837022.
Article20. Miyakawa H, Woo SK, Dahl SC, Handler JS, Kwon HM. Tonicity-responsive enhancer binding protein, a rel-like protein that stimulates transcription in response to hypertonicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999; 96:2538–2542. PMID: 10051678.
Article21. Jeon US, Kim JA, Sheen MR, Kwon HM. How tonicity regulates genes: story of TonEBP transcriptional activator. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2006; 187:241–247. PMID: 16734761.
Article22. Tang QQ, Otto TC, Lane MD. Mitotic clonal expansion: a synchronous process required for adipogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003; 100:44–49. PMID: 12502791.
Article23. Fajas L. Adipogenesis: a cross-talk between cell proliferation and cell differentiation. Ann Med. 2003; 35:79–85. PMID: 12795337.
Article24. Xu J, Liao K. Protein kinase B/AKT 1 plays a pivotal role in insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor signaling induced 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279:35914–35922. PMID: 15192111.
Article25. Zhang HH, Huang J, Düvel K, Boback B, Wu S, Squillace RM, Wu CL, Manning BD. Insulin stimulates adipogenesis through the Akt-TSC2-mTORC1 pathway. PLoS One. 2009; 4:e6189. PMID: 19593385.
Article26. Blüher M, Michael MD, Peroni OD, Ueki K, Carter N, Kahn BB, Kahn CR. Adipose tissue selective insulin receptor knockout protects against obesity and obesity-related glucose intolerance. Dev Cell. 2002; 3:25–38. PMID: 12110165.
Article27. Blüher M, Patti ME, Gesta S, Kahn BB, Kahn CR. Intrinsic heterogeneity in adipose tissue of fat-specific insulin receptor knock-out mice is associated with differences in patterns of gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279:31891–31901. PMID: 15131119.
Article28. Lee JH, Lee HH, Ye BJ, Lee-Kwon W, Choi SY, Kwon HM. TonEBP suppresses adipogenesis and insulin sensitivity by blocking epigenetic transition of PPARγ2. Sci Rep. 2015; 5:10937. PMID: 26042523.
Article29. Ullah I, Subbarao RB, Rho GJ. Human mesenchymal stem cells - current trends and future prospective. Biosci Rep. 2015; 35(2):pii: e00191.
Article30. Takada I, Kouzmenko AP, Kato S. Wnt and PPARgamma signaling in osteoblastogenesis and adipogenesis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009; 5:442–447. PMID: 19581903.31. Kirton JP, Crofts NJ, George SJ, Brennan K, Canfield AE. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling stimulates chondrogenic and inhibits adipogenic differentiation of pericytes: potential relevance to vascular disease? Circ Res. 2007; 101:581–589. PMID: 17673669.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of (6)-gingerol, ginger component on adipocyte development and differentiation in 3T3-L1
- Cryptotanshinone Inhibits Lipid Accumulation in Differentiating 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes by Down-regulating C/EBP-α, PPAR-γ, FAS, Perilipin A, and STAT-3
- Cryptotanshinone Inhibits Lipid Accumulation in Differentiating 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes by Down-regulating C/EBP-α, PPAR-γ, FAS, Perilipin A, and STAT-3
- Cryptotanshinone Inhibits Lipid Accumulation in Differentiating 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes by Down-regulating C/EBP-α, PPAR-γ, FAS, Perilipin A, and STAT-3
- Effects of quercetin on cell differentiation and adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes