World J Mens Health.
2016 Dec;34(3):217-223. 10.5534/wjmh.2016.34.3.217.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Premature Ejaculation by Urologists in South Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Changwon, Korea.
- 2Department of Urology, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea. hyunjs@gnu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Urology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Urology, Hallym University Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Urology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Urology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Urology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2364205
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.2016.34.3.217
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study discusses the treatment of premature ejaculation (PE) using various approaches with the goal of evaluating the methods of diagnosis and treatment of PE in clinical practice in 2014 in South Korea.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We surveyed 200 urologists and andrologists who treated patients with PE from July 1, 2014 to July 29, 2014 using an online questionnaire. The questionnaire was composed of 4 parts: disease, comorbidities, diagnosis, and treatment. Using the answers to this survey, current trends in the diagnosis and treatment of PE were investigated using weighted averages.
RESULTS
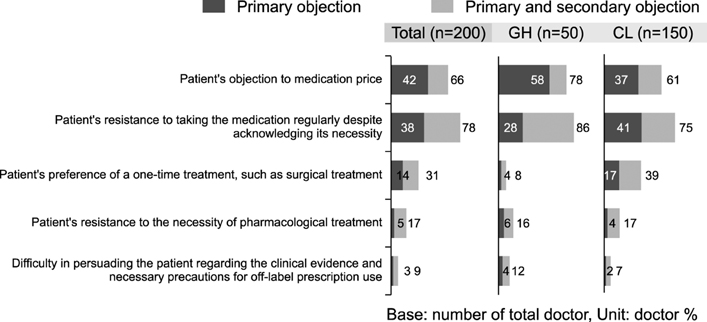
The median number per month of patients who were diagnosed with PE was 14 patients (interquartile range, 7~24). The time to ejaculation necessary for a diagnosis of PE was considered to be <1 minute by 12% of respondents, <2 minutes by 27%, <3 minutes by 28%, <5 minutes by 13%, and 20% stated that diagnosis was based on a patient's subjective complaint. The treatment methods preferred by PE patients were reported to be pharmacological treatment (87%), surgical treatment (9.5%), and behavioral management (3.5%). The treatment methods used by respondents were pharmacological treatment (77%), surgical treatment (15%), and behavioral management (14%). The most commonly used pharmacological treatment was the oral administration of dapoxetine (97%).
CONCLUSIONS
In 2014 in South Korea, various methods were used to diagnose and treat PE. The most commonly used treatment for PE was the oral administration of dapoxetine. It was also found that surgical treatment was applied in some cases.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. McMahon CG, Althof SE, Waldinger MD, Porst H, Dean J, Sharlip ID, et al. An evidence-based definition of lifelong premature ejaculation: report of the International Society for Sexual Medicine (ISSM) ad hoc committee for the definition of premature ejaculation. J Sex Med. 2008; 5:1590–1606.
Article2. Rowland DL, Patrick DL, Rothman M, Gagnon DD. The psychological burden of premature ejaculation. J Urol. 2007; 177:1065–1070.
Article3. Rowland DL, Kolba TN. Understanding the effects of establishing various cutoff criteria in the definition of men with premature ejaculation. J Sex Med. 2015; 12:1175–1183.
Article4. Rosen RC. Prevalence and risk factors of sexual dysfunction in men and women. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2000; 2:189–195.
Article5. Rowland D, Perelman M, Althof S, Barada J, McCullough A, Bull S, et al. Self-reported premature ejaculation and aspects of sexual functioning and satisfaction. J Sex Med. 2004; 1:225–232.
Article6. Laumann EO, Nicolosi A, Glasser DB, Paik A, Gingell C, Moreira E, et al. Sexual problems among women and men aged 40-80 y: prevalence and correlates identified in the global study of sexual attitudes and behaviors. Int J Impot Res. 2005; 17:39–57.
Article7. Buvat J. Pathophysiology of premature ejaculation. J Sex Med. 2011; 8:Suppl 4. 316–327.
Article8. Gökçe A, Halis F, Demirtas A, Ekmekcioglu O. The effects of three phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors on ejaculation latency time in lifelong premature ejaculators: a double-blind laboratory setting study. BJU Int. 2011; 107:1274–1277.
Article9. Kirby EW, Carson CC, Coward RM. Tramadol for the management of premature ejaculation: a timely systematic review. Int J Impot Res. 2015; 27:121–127.
Article10. Kam SC, Han DH, Lee SW. The diagnostic value of the premature ejaculation diagnostic tool and its association with intravaginal ejaculatory latency time. J Sex Med. 2011; 8:865–871.
Article11. Shindel A, Nelson C, Brandes S. Urologist practice patterns in the management of premature ejaculation: a nationwide survey. J Sex Med. 2008; 5:199–205.
Article12. Symonds T, Perelman MA, Althof S, Giuliano F, Martin M, May K, et al. Development and validation of a premature ejaculation diagnostic tool. Eur Urol. 2007; 52:565–573.
Article13. Goodman RE. The management of premature ejaculation. J Int Med Res. 1977; 5:1 Suppl. 78–79.14. Cormio L, Massenio P, La Rocca R, Verze P, Mirone V, Carrieri G. The combination of dapoxetine and behavioral treatment provides better results than dapoxetine alone in the management of patients with lifelong premature ejaculation. J Sex Med. 2015; 12:1609–1615.
Article15. Waldinger MD, Hengeveld MW, Zwinderman AH. Paroxetine treatment of premature ejaculation: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Am J Psychiatry. 1994; 151:1377–1379.16. Wise TN. Sertraline as a treatment for premature ejaculation. J Clin Psychiatry. 1994; 55:417.17. Kara H, Aydin S, Yücel M, Agargün MY, Odabaş O, Yilmaz Y. The efficacy of fluoxetine in the treatment of premature ejaculation: a double-blind placebo controlled study. J Urol. 1996; 156:1631–1632.
Article18. Yue FG, Dong L, Hu TT, Qu XY. Efficacy of dapoxetine for the treatment of premature ejaculation: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials on intravaginal ejaculatory latency time, patient-reported outcomes, and adverse events. Urology. 2015; 85:856–861.
Article19. Mirone V, Arcaniolo D, Rivas D, Bull S, Aquilina JW, Verze P. PAUSE study team. Results from a prospective observational study of men with premature ejaculation treated with dapoxetine or alternative care: the PAUSE study. Eur Urol. 2014; 65:733–739.
Article20. Buvat J, Tesfaye F, Rothman M, Rivas DA, Giuliano F. Dapoxetine for the treatment of premature ejaculation: results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial in 22 countries. Eur Urol. 2009; 55:957–967.
Article21. Jiann BP, Huang YJ. Assessing satisfaction in men with premature ejaculation after dapoxetine treatment in real-world practice. Int J Clin Pract. 2015; 69:1326–1333.
Article22. Althof SE, Abdo CH, Dean J, Hackett G, McCabe M, McMahon CG, et al. International Society for Sexual Medicine's guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of premature ejaculation. J Sex Med. 2010; 7:2947–2969.
Article23. Morris BJ, Krieger JN. Does male circumcision affect sexual function, sensitivity, or satisfaction?: a systematic review. J Sex Med. 2013; 10:2644–2657.24. Zhang GX, Yu LP, Bai WJ, Wang XF. Selective resection of dorsal nerves of penis for premature ejaculation. Int J Androl. 2012; 35:873–879.
Article25. Kim JJ, Kwak TI, Jeon BG, Cheon J, Moon DG. Effects of glans penis augmentation using hyaluronic acid gel for premature ejaculation. Int J Impot Res. 2004; 16:547–551.
Article26. Yang DY, Ko K, Lee WK, Park HJ, Lee SW, Moon KH, et al. Urologist's practice patterns including surgical treatment in the management of premature ejaculation: a Korean nationwide survey. World J Mens Health. 2013; 31:226–231.
Article27. McMahon CG, Giuliano F, Dean J, Hellstrom WJ, Bull S, Tesfaye F, et al. Efficacy and safety of dapoxetine in men with premature ejaculation and concomitant erectile dysfunction treated with a phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor: randomized, placebo-controlled, phase III study. J Sex Med. 2013; 10:2312–2325.
Article28. Jannini EA, Isidori AM, Aversa A, Lenzi A, Althof SE. Which is first? The controversial issue of precedence in the treatment of male sexual dysfunctions. J Sex Med. 2013; 10:2359–2369.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clomipramine in the Treatment of Premature Ejaculation
- Sertraline Treatment in Premature Ejaculation: A Double Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study
- The Efficacy and Safety of Paroxetine on the Treatment of Premature Ejaculation
- Psychological Personality Test in Premature Ejaculation Patients
- Fluoxetine as a Treatment for Premature Ejaculation: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study