J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Apr;31(4):489-496. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.4.489.
Environmental Exposure to Arsenic, Lead, and Cadmium in People Living near Janghang Copper Smelter in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive Medicine, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea. kimheon@cbu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, School of Medicine, Konyang University, Daejeon, Korea.
- 3Environmental Health Research Division, Environmental Health Research Department, National Institute of Environmental Research, Incheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Preventive Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2363685
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.4.489
Abstract
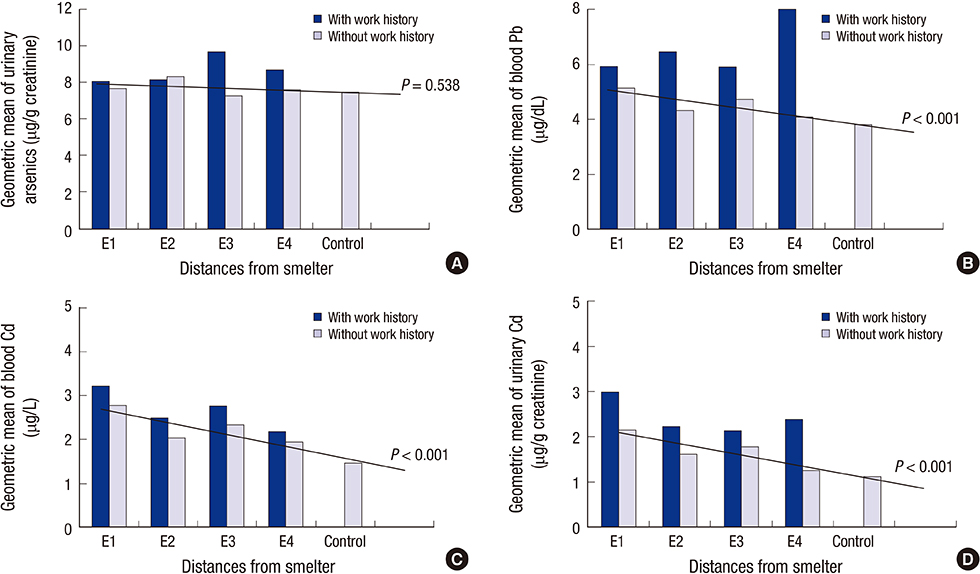
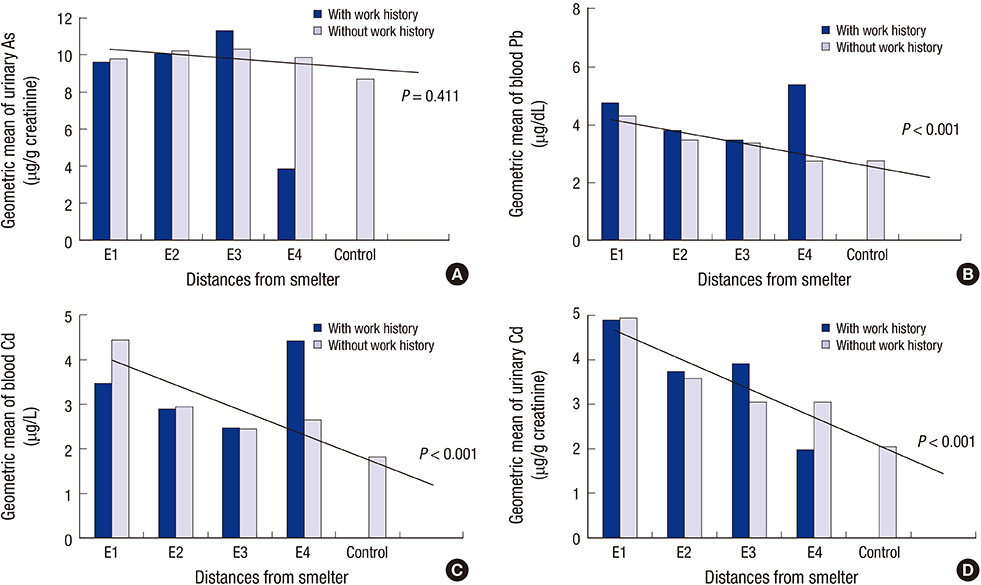
- Concentrations of heavy metals exceed safety thresholds in the soil near Janghang Copper Refinery, a smelter in Korea that operated from 1936 to 1989. This study was conducted to evaluate the level of exposure to toxic metals and the potential effect on health in people living near the smelter. The study included 572 adults living within 4 km of the smelter and compared them with 413 controls group of people living similar lifestyles in a rural area approximately 15 km from the smelter. Urinary arsenic (As) level did not decrease according to the distance from the smelter, regardless of gender and working history in smelters and mines. However, in subjects who had no occupational exposure to toxic metals, blood lead (Pb) and cadmium (Cd) and urinary Cd decreased according to the distance from the smelter, both in men and women. Additionally, the distance from the smelter was a determinant factor for a decrease of As, Pb, and Cd in multiple regression models, respectively. On the other hands, urinary Cd was a risk factor for renal tubular dysfunction in populations living near the smelter. These results suggest that Janghang copper smelter was a main contamination source of As, Pb, and Cd, and populations living near the smelter suffered some adverse health effects as a consequence. The local population should be advised to make efforts to reduce exposure to environmental contaminants, in order to minimize potential health effects, and to pay close attention to any health problems possibly related to toxic metal exposure.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acetylglucosaminidase/urine
Adult
Aged
Arsenic/*urine
Bone Density
Cadmium/*blood
Case-Control Studies
Chemical Industry
Creatinine/urine
*Environmental Exposure
Environmental Pollutants/*analysis/blood/urine
Female
Humans
Lead/*blood
Male
Middle Aged
Regression Analysis
Republic of Korea
Spectrophotometry, Atomic
Acetylglucosaminidase
Arsenic
Cadmium
Creatinine
Environmental Pollutants
Lead
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Relationship between Heavy Metal Exposure and Bone Mineral Density in Korean Adult
Hee-Sook Lim, Hae-Hyeog Lee, Tae-Hee Kim, Bo-Ra Lee
J Bone Metab. 2016;23(4):223-231. doi: 10.11005/jbm.2016.23.4.223.A Case-Control Study of Skin Cancer and Exposure of Toxic Heavy Metals
Tae-Hoon Kim, Jeong-Wook Seo, Young-Seoub Hong, Ki-Hoon Song
Ann Dermatol. 2018;30(2):238-240. doi: 10.5021/ad.2018.30.2.238.Exposure to Hazardous Substances and Their Health Effects Among Residents Living Near Three Industrial Waste Incinerators in Korea
Sang-Yong Eom, Boeun Lee, Seonmi Hong, Young-Seoub Hong, Kyung-Hwa Choi, Ho-Jang Kwon, Mira Yoon, Youn-Seok Kang, Jun Hee Lee, Yong-Dae Kim, Heon Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2023;38(37):e289. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e289.
Reference
-
1. Genaidy AM, Sequeira R, Tolaymat T, Kohler J, Rinder M. Evidence-based integrated environmental solutions for secondary lead smelters: pollution prevention and waste minimization technologies and practices. Sci Total Environ. 2009; 407:3239–3268.2. Soto-Jiménez MF, Flegal AR. Childhood lead poisoning from the smelter in Torreón, México. Environ Res. 2011; 111:590–596.3. Rosado JL, Ronquillo D, Kordas K, Rojas O, Alatorre J, Lopez P, Garcia-Vargas G, Del Carmen Caamaño M, Cebrián ME, Stoltzfus RJ. Arsenic exposure and cognitive performance in Mexican schoolchildren. Environ Health Perspect. 2007; 115:1371–1375.4. Hwang YH, Bornschein RL, Grote J, Menrath W, Roda S. Environmental arsenic exposure of children around a former copper smelter site. Environ Res. 1997; 72:72–81.5. Escobar J, Varela-Nallar L, Coddou C, Nelson P, Maisey K, Valdés D, Aspee A, Espinosa V, Rozas C, Montoya M, et al. Oxidative damage in lymphocytes of copper smelter workers correlated to higher levels of excreted arsenic. Mediators Inflamm. 2010; 403830.6. Chrastný V, Vaněk A, Teper L, Cabala J, Procházka J, Pechar L, Drahota P, Penížek V, Komárek M, Novák M. Geochemical position of Pb, Zn and Cd in soils near the Olkusz mine/smelter, South Poland: effects of land use, type of contamination and distance from pollution source. Environ Monit Assess. 2012; 184:2517–2536.7. Jeong SK, An J, Kim YJ, Kim GH, Choi SI, Nam KP. Study on heavy metal contamination characteristics and plant bioavailability for soils in the Janghang smelter area. J Soil Groundw Environ. 2011; 16:42–50.8. Cao Y, Chen A, Radcliffe J, Dietrich KN, Jones RL, Caldwell K, Rogan WJ. Postnatal cadmium exposure, neurodevelopment, and blood pressure in children at 2, 5, and 7 years of age. Environ Health Perspect. 2009; 117:1580–1586.9. Chowdhury UK, Rahman MM, Sengupta MK, Lodh D, Chanda CR, Roy S, Quamruzzaman Q, Tokunaga H, Ando M, Chakraborti D. Pattern of excretion of arsenic compounds [arsenite, arsenate, MMA(V), DMA(V)] in urine of children compared to adults from an arsenic exposed area in Bangladesh. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst. Environ Eng. 2003; 38:87–113.10. Wen W, Wen J, Lu L, Liu H, Yang J, Cheng H, Che W, Li L, Zhang G. Metabolites of arsenic and increased DNA damage of p53 gene in arsenic plant workers. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011; 254:41–47.11. Hsueh YM, Chung CJ, Shiue HS, Chen JB, Chiang SS, Yang MH, Tai CW, Su CT. Urinary arsenic species and CKD in a Taiwanese population: a case-control study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009; 54:859–870.12. Bae HS, Ryu DY, Choi BS, Park JD. Urinary arsenic concentrations and their associated factors in Korean adults. Toxicol Res. 2013; 29:137–142.13. Järup L. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br Med Bull. 2003; 68:167–182.14. Carrizales L, Razo I, Téllez-Hernández JI, Torres-Nerio R, Torres A, Batres LE, Cubillas AC, Díaz-Barriga F. Exposure to arsenic and lead of children living near a copper-smelter in San Luis Potosi, Mexico: Importance of soil contamination for exposure of children. Environ Res. 2006; 101:1–10.15. Kim NS, Lee BK. National estimates of blood lead, cadmium, and mercury levels in the Korean general adult population. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2011; 84:53–63.16. Lilis R, Valciukas JA, Weber JP, Fischbein A, Nicholson WJ, Campbell C, Malkin J, Selikoff IJ. Distribution of blood lead, blood cadmium, urinary cadmium, and urinary arsenic levels in employees of a copper smelter. Environ Res. 1984; 33:76–95.17. Rubin CH, Esteban E, Reissman DB, Daley WR, Noonan GP, Karpati A, Gurvitch E, Kuzmin SV, Privalova LI, Zukov A, et al. Lead poisoning among young children in Russia: concurrent evaluation of childhood lead exposure in Ekaterinburg, Krasnouralsk, and Volgograd. Environ Health Perspect. 2002; 110:559–562.18. Kim YD, Yim DH, Eom SY, Moon SI, Park CH, Kim GB, Yu SD, Choi BS, Park JD, Kim H. Differences in the susceptibility to cadmium-induced renal tubular damage and osteoporosis according to sex. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2014; 38:272–278.19. Kim YD, Yim DH, Eom SY, Moon SI, Park CH, Kim GB, Yu SD, Choi BS, Park JD, Kim H. Temporal changes in urinary levels of cadmium, N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase and β2-microglobulin in individuals in a cadmium-contaminated area. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2015; 39:35–41.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Association of Blood Concentrations of Healvy Metals and Blood Pressure in Residents Living Near Janghang Copper Smelter in Korea
- Trend of the Changes in the Level of Blood Lead, Urinary Arsenic and Urinary Cadmium of Children in Ulsan: 3-year Follow-up Study
- Association Between Multiple Heavy Metal Exposures and Cholesterol Levels in Residents Living Near a Smelter Plant in Korea
- Trace Metal Contents in Human Hair of Korean
- The association between cadmium and lead exposure and blood pressure among workers of a smelting industry: a cross-sectional study