Ann Lab Med.
2015 Jan;35(1):181-184. 10.3343/alm.2015.35.1.181.
Identification of Compound Heterozygous Mutations in the BBS7 Gene in a Korean Family with Bardet-Biedl Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Catholic Genetic Laboratory Center, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. lsok@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2363175
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.1.181
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Alleles
Asian Continental Ancestry Group/*genetics
Bardet-Biedl Syndrome/diagnosis/*genetics
Base Sequence
Blindness/pathology
DNA/chemistry/metabolism
Exons
*Heterozygote
Humans
Macular Degeneration/diagnosis
Male
*Mutation
Pedigree
Phenotype
Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide
Proteins/*genetics
Republic of Korea
DNA
Proteins
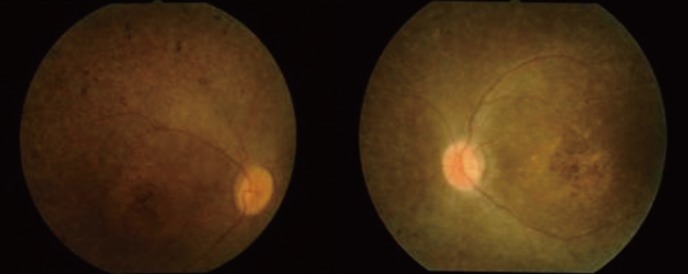
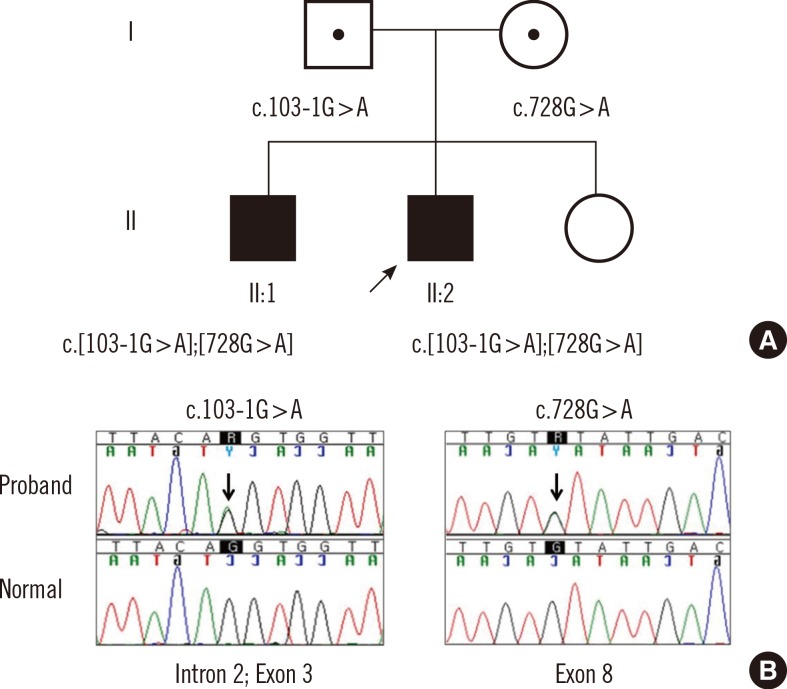
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Retinitis Pigmentosa Associated with Bardet-Biedl Syndrome with BBS9 Gene Mutation in a Korean Patient
Yong Hoon Kim, Kwang Sic Joo, Moon-Woo Seong, Sung Sup Park, Se Joon Woo
Korean J Ophthalmol. 2020;34(1):94-95. doi: 10.3341/kjo.2019.0083.
Reference
-
1. Beales PL, Elcioglu N, Woolf AS, Parker D, Flinter FA. New criteria for improved diagnosis of Bardet-Biedl syndrome: results of a population survey. J Med Genet. 1999; 36:437–446. PMID: 10874630.2. Baker K. Making sense of cilia in disease: the human ciliopathies. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2009; 151C:281–295. PMID: 19876933.
Article3. Deveault C, Billingsley G, Duncan JL, Bin J, Theal R, Vincent A, et al. BBS genotype-phenotype assessment of a multiethnic patient cohort calls for a revision of the disease definition. Hum Mutat. 2011; 32:610–619. PMID: 21344540.
Article4. Chen J, Smaoui N, Hammer MB, Jiao X, Riazuddin SA, Harper S, et al. Molecular analysis of Bardet-Biedl syndrome families: report of 21 new mutations in 10 genes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011; 52:5317–5324. PMID: 21642631.5. Billingsley G, Deveault C, Héon E. BBS mutational analysis: a strategic approach. Ophthalmic Genet. 2011; 32:181–187. PMID: 21463199.
Article6. Wang X, Wang H, Sun V, Tuan HF, Keser V, Wang K, et al. Comprehensive molecular diagnosis of 179 Leber congenital amaurosis and juvenile retinitis pigmentosa patients by targeted next generation sequencing. J Med Genet. 2013; 50:674–688. PMID: 23847139.
Article7. Katsanis N, Ansley SJ, Badano JL, Eichers ER, Lewis RA, Hoskins BE, et al. Triallelic inheritance in Bardet-Biedl syndrome, a Mendelian recessive disorder. Science. 2001; 293:2256–2259. PMID: 11567139.
Article8. Nachury MV, Loktev AV, Zhang Q, Westlake CJ, Peränen J, Merdes A, et al. A core complex of BBS proteins cooperates with the GTPase Rab8 to promote ciliary membrane biogenesis. Cell. 2007; 129:1201–1203. PMID: 17574030.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Identification of Two Cases of Ciliopathy-Associated Diabetes and Their Mutation Analysis Using Whole Exome Sequencing
- Two siblings with Bardet-Biedl syndrome caused by mutations in BBS10: the first case identified in Korea
- Retinitis Pigmentosa Associated with Bardet-Biedl Syndrome with BBS9 Gene Mutation in a Korean Patient
- Novel Compound Heterozygous Mutations in CTSC Gene in a Chinese Family with Papillon–Lefevre Syndrome
- A compound heterozygous mutation in the FMO3 gene: the first pediatric case causes fish odor syndrome in Korea