J Korean Assoc Pediatr Surg.
2016 Dec;22(2):19-22. 10.13029/jkaps.2016.22.2.19.
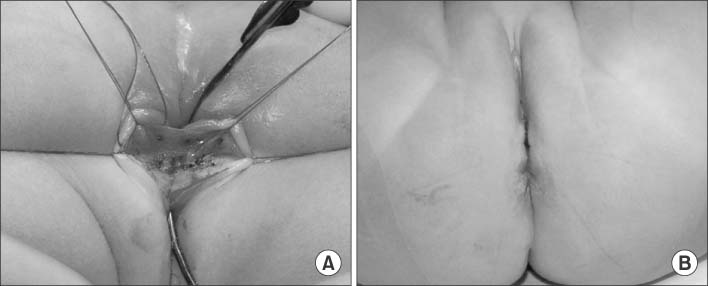
Diagnosis and Treatment of Congenital H-type Rectovestibular Fistula
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pediatric Surgery, Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jm0815.seo@samsung.com
- KMID: 2363018
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13029/jkaps.2016.22.2.19
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The congenital H-type rectovestibular fistula, a fistula between the anorectum and genital tract besides a normal anus is a rare variant of anorectal deformities. This disease needs proper treatment but there are no standard of diagnosis and treatment. The purpose of this report is to review a 13-year experience of approach and management for H-type rectovestibular fistula at a single institution.
METHODS
From February 2002 to August 2015, we cared for 11 patients who had congenital H-type rectovestibular fistula and reviewed their clinical presentation, accompanied anomalies, diagnostic modalities, operative technique, and postoperative progress.
RESULTS
Most patients with H-type rectovestibular fistula presented with symptoms including vestibular defecation and major labial abscess. We could find the fistula tract in most of patients by fistulography using contrast dye. All of the patients had been operated. There were 2 recurrences after surgical treatment who had inflammation and infection associated with the fistula. All other patients recovered without complications.
CONCLUSION
We think the operation including fistulectomy and repair of perineal body through a transanal approach can be a feasible option to the congenital H-type rectovestibular fistula. Also, combined inflammation and infection should be treated prior to surgery to reduce postoperative complications.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chatterjee SK, Talukder BC. Double termination of the alimentary tract in female infants. J Pediatr Surg. 1969; 4:237–243.
Article2. Tsuchida Y, Saito S, Honna T, Makino S, Kaneko M, Hazama H. Double termination of the alimentary tract in females: a report of 12 cases and a literature review. J Pediatr Surg. 1984; 19:292–296.
Article3. Holschneider A, Hutson J, Peña A, Beket E, Chatterjee S, Coran A, et al. Preliminary report on the international conference for the development of standards for the treatment of anorectal malformations. J Pediatr Surg. 2005; 40:1521–1526.
Article4. Rintala RJ, Mildh L, Lindahl H. H-type anorectal malformations: incidence and clinical characteristics. J Pediatr Surg. 1996; 31:559–562.
Article5. Willems M, Kluth D, Lambrecht W. Anorectal malformation: a new anatomic variant resembling an H-type fistula. J Pediatr Surg. 1996; 31:1682–1684.
Article6. Bryndorf J, Madsen CM. Ectopic anus in the female. Acta Chir Scand. 1960; 118:466–478.7. Li L, Zhang TC, Zhou CB, Pang WB, Chen YJ, Zhang JZ. Rectovestibular fistula with normal anus: a simple resection or an extensive perineal dissection? J Pediatr Surg. 2010; 45:519–524.
Article8. Sun L, Wang YX, Liu Y. Histopathological study of fistula-in-ano in female. Chin J Pediatr Surg. 1995; 16:136–137.9. Tsugawa C, Nishijima E, Muraji T, Satoh S, Kimura K. Surgical repair of rectovestibular fistula with normal anus. J Pediatr Surg. 1999; 34:1703–1705.
Article10. Lawal TA, Chatoorgoon K, Bischoff A, Peña A, Levitt MA. Management of H-type rectovestibular and rectovaginal fistulas. J Pediatr Surg. 2011; 46:1226–1230.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Tubular Colonic Duplication Presenting as Rectovestibular Fistula
- Infantile Vulvar Abscess with a Normal Anus: A Suspicious Sign of Rectovestibular Fistula
- Congenital Renal Arteriovenous Fistula
- Anterior Anorectocolonic Tubular Duplication Presenting as Rectovestibular Fistula in an Infant
- A Case of Congenital Urethrocutaneous Fistula