Korean J Radiol.
2016 Apr;17(2):218-223. 10.3348/kjr.2016.17.2.218.
Assessment of Placental Stiffness Using Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography in Pregnant Women with Fetal Anomalies
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Dicle University Medical Faculty, Diyarbakir 21280, Turkey. bircanalan@hotmail.com
- 2Department of Gynecology and Obstetric, Dicle University Medical Faculty, Diyarbakir 21280, Turkey.
- KMID: 2360206
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.2.218
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
We aimed to evaluate placental stiffness measured by acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography in pregnant women in the second trimester with a normal fetus versus those with structural anomalies and non-structural findings.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Forty pregnant women carrying a fetus with structural anomalies diagnosed sonographically at 18-28 weeks of gestation comprised the study group. The control group consisted of 34 healthy pregnant women with a sonographically normal fetus at a similar gestational age. Placental shear wave velocity (SWV) was measured by ARFI elastography and compared between the two groups. Structural anomalies and non-structural findings were scored based on sonographic markers. Placental stiffness measurements were compared among fetus anomaly categories. Doppler parameters of umbilical and uterine arteries were compared with placental SWV measurements.
RESULTS
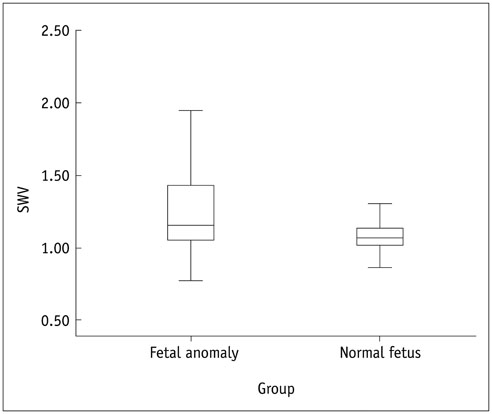
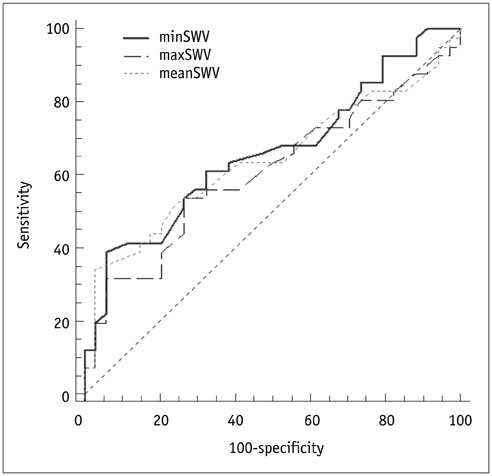
All placental SWV measurements, including minimum SWV, maximum SWV, and mean SWV were significantly higher in the study group than the control group ([0.86 ± 0.2, 0.74 ± 0.1; p < 0.001], [1.89 ± 0.7, 1.59 ± 0.5; p = 0.04], and [1.26 ± 0.4, 1.09 ± 0.2; p = 0.01]), respectively.
CONCLUSION
Placental stiffness evaluated by ARFI elastography during the second trimester in pregnant women with fetuses with congenital structural anomalies is higher than that of pregnant women with normal fetuses.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bowman ZS, Kennedy AM. Sonographic appearance of the placenta. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2014; 43:356–373.2. Arizawa M, Nakayama M. [Pathological analysis of the placenta in trisomies 21, 18 and 13]. Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 1992; 44:9–13.3. Zhi H, Ou B, Xiao XY, Peng YL, Wang Y, Liu LS, et al. Ultrasound elastography of breast lesions in chinese women: a multicenter study in China. Clin Breast Cancer. 2013; 13:392–400.4. Goddi A, Bonardi M, Alessi S. Breast elastography: a literature review. J Ultrasound. 2012; 15:192–198.5. Kuroda H, Kakisaka K, Oikawa T, Onodera M, Miyamoto Y, Sawara K, et al. Liver stiffness measured by acoustic radiation force impulse elastography reflects the severity of liver damage and prognosis in patients with acute liver failure. Hepatol Res. 2015; 45:571–577.6. Calvete AC, Mestre JD, Gonzalez JM, Martinez ES, Sala BT, Zambudio AR. Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging for evaluation of the thyroid gland. J Ultrasound Med. 2014; 33:1031–1040.7. Göya C, Hamidi C, Okur MH, Içer M, Ogğuz A, Hattapogğlu S, et al. The utility of acoustic radiation force impulse imaging in diagnosing acute appendicitis and staging its severity. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2014; 20:453–458.8. Bromley B, Shipp T, Benacerraf BR. Genetic sonogram scoring index: accuracy and clinical utility. J Ultrasound Med. 1999; 18:523–528. quiz 529-5309. Bromley B, Benacerraf BR. The Genetic Sonogram Scoring Index. Semin Perinatol. 2003; 27:124–129.10. Benacerraf BR, Neuberg D, Bromley B, Frigoletto FD Jr. Sonographic scoring index for prenatal detection of chromosomal abnormalities. J Ultrasound Med. 1992; 11:449–458.11. Sugitani M, Fujita Y, Yumoto Y, Fukushima K, Takeuchi T, Shimokawa M, et al. A new method for measurement of placental elasticity: acoustic radiation force impulse imaging. Placenta. 2013; 34:1009–1013.12. Ohmaru T, Fujita Y, Sugitani M, Shimokawa M, Fukushima K, Kato K. Placental elasticity evaluation using virtual touch tissue quantification during pregnancy. Placenta. 2015; 36:915–920.13. Li WJ, Wei ZT, Yan RL, Zhang YL. Detection of placenta elasticity modulus by quantitative real-time shear wave imaging. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol. 2012; 39:470–473.14. Cimsit C, Yoldemir T, Akpinar IN. Shear wave elastography in placental dysfunction: comparison of elasticity values in normal and preeclamptic pregnancies in the second trimester. J Ultrasound Med. 2015; 34:151–159.15. Cimsit C, Yoldemir T, Akpinar IN. Strain elastography in placental dysfunction: placental elasticity differences in normal and preeclamptic pregnancies in the second trimester. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2015; 291:811–817.16. Papageorghiou AT, Yu CK, Bindra R, Pandis G, Nicolaides KH. Fetal Medicine Foundation Second Trimester Screening Group. Multicenter screening for pre-eclampsia and fetal growth restriction by transvaginal uterine artery Doppler at 23 weeks of gestation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2001; 18:441–449.17. Papageorghiou AT, Yu CK, Nicolaides KH. The role of uterine artery Doppler in predicting adverse pregnancy outcome. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2004; 18:383–396.18. Cnossen JS, Morris RK, ter Riet G, Mol BW, van der, Coomarasamy A, et al. Use of uterine artery Doppler ultrasonography to predict pre-eclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction: a systematic review and bivariable meta-analysis. CMAJ. 2008; 178:701–711.19. Afrakhteh M, Moeini A, Taheri MS, Haghighatkhah HR, Fakhri M, Masoom N. Uterine Doppler velocimetry of the uterine arteries in the second and third trimesters for the prediction of gestational outcome. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2014; 36:35–39.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasound-based Liver Elastography: Recent Advances
- Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules by Elastography
- Ultrasound elastography for thyroid nodules: recent advances
- Applications of acoustic radiation force impulse quantification in chronic kidney disease: a review
- Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography for Focal Hepatic Tumors: Usefulness for Differentiating Hemangiomas from Malignant Tumors