Korean J Radiol.
2013 Oct;14(5):743-753. 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.5.743.
Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography for Focal Hepatic Tumors: Usefulness for Differentiating Hemangiomas from Malignant Tumors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju 660-702, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology and Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-744, Korea. leejy4u@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1711428
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.5.743
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The purpose of this study is to investigate whether acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography with ARFI quantification and ARFI 2-dimensional (2D) imaging is useful for differentiating hepatic hemangiomas from malignant hepatic tumors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
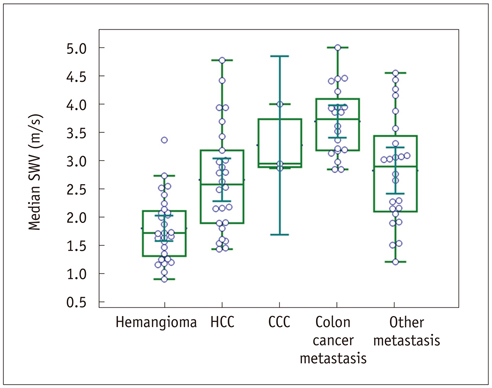
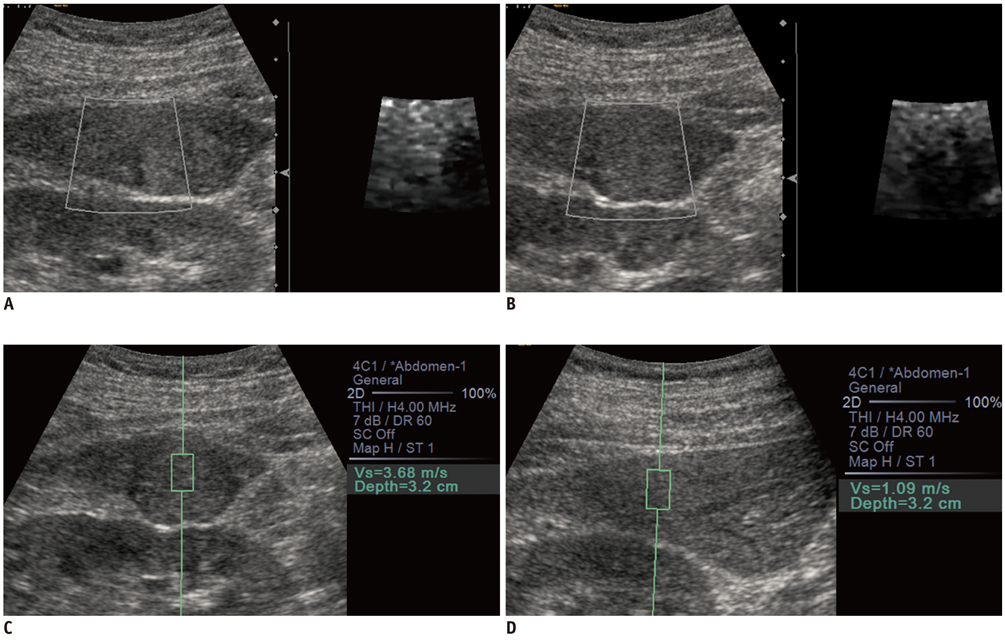
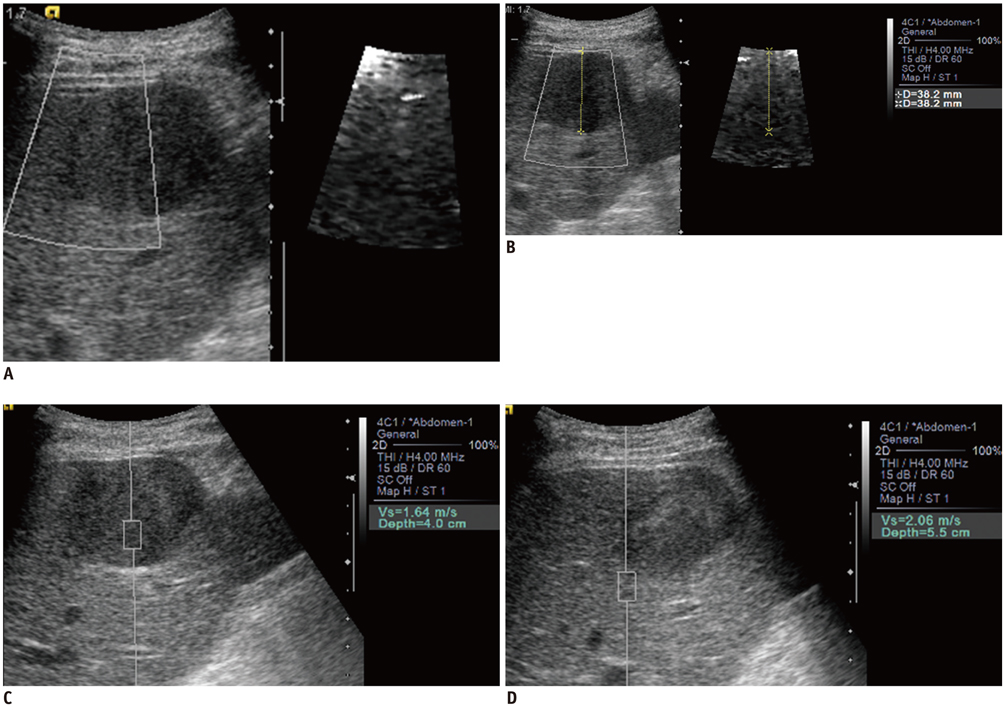
One-hundred-and-one tumors in 74 patients were included in this study: 28 hemangiomas, 26 hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs), three cholangiocarcinomas (CCCs), 20 colon cancer metastases and 24 other metastases. B-mode ultrasound, ARFI 2D imaging, and ARFI quantification were performed in all tumors. Shear wave velocities (SWVs) of the tumors and the adjacent liver and their SWV differences were compared among the tumor groups. The ARFI 2D images were compared with B-mode images regarding the stiffness, conspicuity and size of the tumors.
RESULTS
The mean SWV of the hemangiomas was significantly lower than the malignant hepatic tumor groups: hemangiomas, 1.80 +/- 0.57 m/sec; HCCs, 2.66 +/- 0.94 m/sec; CCCs, 3.27 +/- 0.64 m/sec; colon cancer metastases, 3.70 +/- 0.61 m/sec; and other metastases, 2.82 +/- 0.96 m/sec (p < 0.05). The area under the receiver operating characteristics curve of SWV for differentiating hemangiomas from malignant tumors was 0.86, with a sensitivity of 96.4% and a specificity of 65.8% at a cut-off value of 2.73 m/sec (p < 0.05). In the ARFI 2D images, the malignant tumors except HCCs were stiffer and more conspicuous as compared with the hemangiomas (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSION
ARFI elastography with ARFI quantification and ARFI 2D imaging may be useful for differentiating hepatic hemangiomas from malignant hepatic tumors.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Feldman M. Hemangioma of the liver; special reference to its association with cysts of the liver and pancreas. Am J Clin Pathol. 1958; 29:160–162.2. Moody AR, Wilson SR. Atypical hepatic hemangioma: a suggestive sonographic morphology. Radiology. 1993; 188:413–417.3. Semelka RC, Sofka CM. Hepatic hemangiomas. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 1997; 5:241–253.4. Vilgrain V, Boulos L, Vullierme MP, Denys A, Terris B, Menu Y. Imaging of atypical hemangiomas of the liver with pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2000; 20:379–397.5. Nelson RC, Chezmar JL. Diagnostic approach to hepatic hemangiomas. Radiology. 1990; 176:11–13.6. Yamashita Y, Hatanaka Y, Yamamoto H, Arakawa A, Matsukawa T, Miyazaki T, et al. Differential diagnosis of focal liver lesions: role of spin-echo and contrast-enhanced dynamic MR imaging. Radiology. 1994; 193:59–65.7. Claudon M, Cosgrove D, Albrecht T, Bolondi L, Bosio M, Calliada F, et al. Guidelines and good clinical practice recommendations for contrast enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) - update 2008. Ultraschall Med. 2008; 29:28–44.8. Leslie DF, Johnson CD, MacCarty RL, Ward EM, Ilstrup DM, Harmsen WS. Single-pass CT of hepatic tumors: value of globular enhancement in distinguishing hemangiomas from hypervascular metastases. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995; 165:1403–1406.9. Quinn SF, Benjamin GG. Hepatic cavernous hemangiomas: simple diagnostic sign with dynamic bolus CT. Radiology. 1992; 182:545–548.10. Soyer P, Dufresne AC, Somveille E, Scherrer A. Hepatic cavernous hemangioma: appearance on T2-weighted fast spine-cho MR imaging with and without fat suppression. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997; 168:461–465.11. Yoon JH, Lee JM, Woo HS, Yu MH, Joo I, Lee ES, et al. Staging of hepatic fibrosis: comparison of magnetic resonance elastography and shear wave elastography in the same individuals. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:202–212.12. Cho N, Moon WK, Park JS, Cha JH, Jang M, Seong MH. Nonpalpable breast masses: evaluation by US elastography. Korean J Radiol. 2008; 9:111–118.13. Lalitha P, Reddy MCh, Reddy KJ. Musculoskeletal applications of elastography: a pictorial essay of our initial experience. Korean J Radiol. 2011; 12:365–375.14. Lee TH, Cha SW, Cho YD. EUS elastography: advances in diagnostic EUS of the pancreas. Korean J Radiol. 2012; 13:Suppl 1. S12–S16.15. Kantarci F, Cebi Olgun D, Mihmanli I. Shear-wave elastography of segmental infarction of the testis. Korean J Radiol. 2012; 13:820–822.16. Nightingale K, McAleavey S, Trahey G. Shear-wave generation using acoustic radiation force: in vivo and ex vivo results. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2003; 29:1715–1723.17. Cho SH, Lee JY, Han JK, Choi BI. Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography for the evaluation of focal solid hepatic lesions: preliminary findings. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2010; 36:202–208.18. Davies G, Koenen M. Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography in distinguishing hepatic haemangiomata from metastases: preliminary observations. Br J Radiol. 2011; 84:939–943.19. Fahey BJ, Nelson RC, Bradway DP, Hsu SJ, Dumont DM, Trahey GE. In vivo visualization of abdominal malignancies with acoustic radiation force elastography. Phys Med Biol. 2008; 53:279–293.20. Heide R, Strobel D, Bernatik T, Goertz RS. Characterization of focal liver lesions (FLL) with acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastometry. Ultraschall Med. 2010; 31:405–409.21. Gallotti A, D'Onofrio M, Romanini L, Cantisani V, Pozzi Mucelli R. Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) ultrasound imaging of solid focal liver lesions. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:451–455.22. Frulio N, Laumonier H, Carteret T, Laurent C, Maire F, Balabaud C, et al. Evaluation of liver tumors using acoustic radiation force impulse elastography and correlation with histologic data. J Ultrasound Med. 2013; 32:121–130.23. Shuang-Ming T, Ping Z, Ying Q, Li-Rong C, Ping Z, Rui-Zhen L. Usefulness of acoustic radiation force impulse imaging in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant liver lesions. Acad Radiol. 2011; 18:810–815.24. Yu H, Wilson SR. Differentiation of benign from malignant liver masses with Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse technique. Ultrasound Q. 2011; 27:217–223.25. Leslie DF, Johnson CD, Johnson CM, Ilstrup DM, Harmsen WS. Distinction between cavernous hemangiomas of the liver and hepatic metastases on CT: value of contrast enhancement patterns. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995; 164:625–629.26. Van Hoe L, Baert AL, Gryspeerdt S, Vandenbosh G, Nevens F, Van Steenbergen W, et al. Dual-phase helical CT of the liver: value of an early-phase acquisition in the differential diagnosis of noncystic focal lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997; 168:1185–1192.27. Bruix J, Sherman M. Practice Guidelines Committee, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2005; 42:1208–1236.28. Friedrich-Rust M, Wunder K, Kriener S, Sotoudeh F, Richter S, Bojunga J, et al. Liver fibrosis in viral hepatitis: noninvasive assessment with acoustic radiation force impulse imaging versus transient elastography. Radiology. 2009; 252:595–604.29. Venkatesh SK, Yin M, Glockner JF, Takahashi N, Araoz PA, Talwalkar JA, et al. MR elastography of liver tumors: preliminary results. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 190:1534–1540.30. Ishak KG, Rabin L. Benign tumors of the liver. Med Clin North Am. 1975; 59:995–1013.31. DeWall RJ, Bharat S, Varghese T, Hanson ME, Agni RM, Kliewer MA. Characterizing the compression-dependent viscoelastic properties of human hepatic pathologies using dynamic compression testing. Phys Med Biol. 2012; 57:2273–2286.32. D'Onofrio M, Gallotti A, Mucelli RP. Tissue quantification with acoustic radiation force impulse imaging: measurement repeatability and normal values in the healthy liver. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 195:132–136.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasound elastography for thyroid nodules: recent advances
- Usefulness of acoustic radiation force impulse elastography in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant solid pancreatic lesions
- Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules by Elastography
- The Diagnostic Performance of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elasticity Imaging to Differentiate Malignant from Benign Thyroid Nodules: Comparison with Conventional B-Mode Sonographic Findings
- Assessment of Placental Stiffness Using Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography in Pregnant Women with Fetal Anomalies