Diabetes Metab J.
2016 Oct;40(5):386-395. 10.4093/dmj.2016.40.5.386.
Effects of Body Weight Reduction on Serum Irisin and Metabolic Parameters in Obese Subjects
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Health Science, Kansai Medical University Graduate School of Medicine, Hirakata, Japan. bsk-80@outlook.com
- 2Disease Prevention Center, Ijinkai Takeda General Hospital, Kyoto, Japan.
- 3Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Dokkyo Medical University, Tochigi, Japan.
- 4Health Science Center, Kansai Medical University, Hirakata, Japan.
- KMID: 2354612
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.5.386
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Irisin is a myokine implicated in lipid and glucose metabolism. The objective of this study is to examine the effect of a body weight reduction on the serum irisin level and physical indicators in obese Japanese patients without diabetes.
METHODS
The subjects were 22 patients (male/female, 5/17; age, 46.1±16.0 years; body mass index [BMI], 36.9±5.0 kg/m²) who completed a 6-month body weight reduction program at our clinic. The program included diet, exercise therapy and cognitive behavioral therapy. Blood parameters, body composition, exercise tolerance, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), and serum irisin were determined before and after intervention, and relationships among changes in these data were examined.
RESULTS
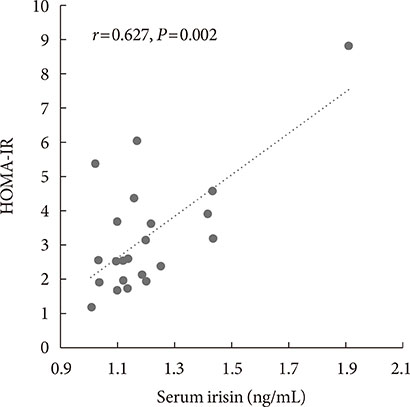
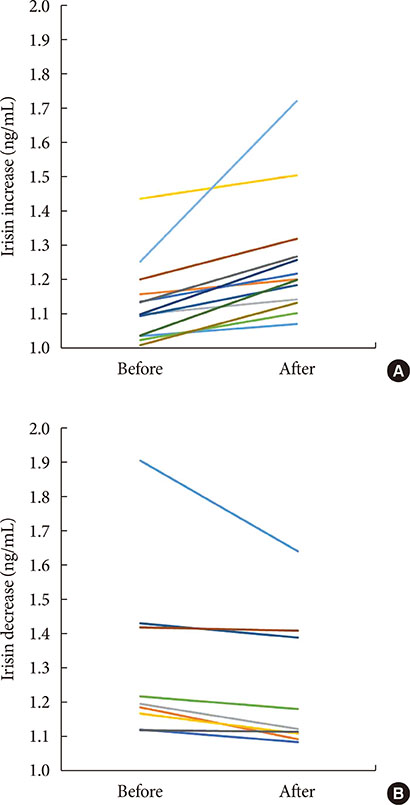
There were significant decreases in body weight and BMI after the intervention. Irisin before the intervention was significantly positively correlated with HOMA-IR (r=0.434, P<0.05). The mean irisin level showed no significant change after the intervention in all participants. However, improvements in % body fat, subcutaneous fat area, triglycerides, and fasting glucose were significantly greater in patients with an increase in irisin compared to those with a decrease in irisin after the intervention. Patients with an increase in irisin also had significantly lower fasting insulin (9.7±4.8 vs. 16.4±8.2, P<0.05) and HOMA-IR (2.2±1.1 vs. 3.7±1.6, P<0.05) after the intervention, compared to patients with a decrease in irisin.
CONCLUSION
Body weight reduction did not alter irisin levels. However, irisin may play important roles in fat and glucose metabolism and insulin resistance, and the effects of body weight reduction on irisin kinetics may be a key for obesity treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pedersen BK. Muscle as a secretory organ. Compr Physiol. 2013; 3:1337–1362.2. Moon SS. Low skeletal muscle mass is associated with insulin resistance, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome in the Korean population: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2009-2010. Endocr J. 2014; 61:61–70.3. Lee CG, Boyko EJ, Strotmeyer ES, Lewis CE, Cawthon PM, Hoffman AR, Everson-Rose SA, Barrett-Connor E, Orwoll ES. Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Study Research Group. Association between insulin resistance and lean mass loss and fat mass gain in older men without diabetes mellitus. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011; 59:1217–1224.4. Bostrom P, Wu J, Jedrychowski MP, Korde A, Ye L, Lo JC, Rasbach KA, Bostrom EA, Choi JH, Long JZ, Kajimura S, Zingaretti MC, Vind BF, Tu H, Cinti S, Hojlund K, Gygi SP, Spiegelman BM. A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 2012; 481:463–468.5. Elsen M, Raschke S, Eckel J. Browning of white fat: does irisin play a role in humans? J Endocrinol. 2014; 222:R25–R38.6. Novelle MG, Contreras C, Romero-Pico A, Lopez M, Dieguez C. Irisin, two years later. Int J Endocrinol. 2013; 2013:746281.7. Kerstholt N, Ewert R, Nauck M, Spielhagen T, Bollmann T, Stubbe B, Felix SB, Wallaschofski H, Glaser S, Friedrich N. Association of circulating irisin and cardiopulmonary exercise capacity in healthy volunteers: results of the Study of Health in Pomerania. BMC Pulm Med. 2015; 15:41.8. Hecksteden A, Wegmann M, Steffen A, Kraushaar J, Morsch A, Ruppenthal S, Kaestner L, Meyer T. Irisin and exercise training in humans: results from a randomized controlled training trial. BMC Med. 2013; 11:235.9. Park KH, Zaichenko L, Brinkoetter M, Thakkar B, Sahin-Efe A, Joung KE, Tsoukas MA, Geladari EV, Huh JY, Dincer F, Davis CR, Crowell JA, Mantzoros CS. Circulating irisin in relation to insulin resistance and the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98:4899–4907.10. Crujeiras AB, Zulet MA, Lopez-Legarrea P, de la Iglesia R, Pardo M, Carreira MC, Martinez JA, Casanueva FF. Association between circulating irisin levels and the promotion of insulin resistance during the weight maintenance period after a dietary weight-lowering program in obese patients. Metabolism. 2014; 63:520–531.11. Sesti G, Andreozzi F, Fiorentino TV, Mannino GC, Sciacqua A, Marini MA, Perticone F. High circulating irisin levels are associated with insulin resistance and vascular atherosclerosis in a cohort of nondiabetic adult subjects. Acta Diabetol. 2014; 51:705–713.12. Ebert T, Focke D, Petroff D, Wurst U, Richter J, Bachmann A, Lossner U, Kralisch S, Kratzsch J, Beige J, Bast I, Anders M, Bluher M, Stumvoll M, Fasshauer M. Serum levels of the myokine irisin in relation to metabolic and renal function. Eur J Endocrinol. 2014; 170:501–506.13. Fukushima Y, Kurose S, Shinno H, Cao Thi, Tamanoi A, Tsutsumi H, Hasegawa T, Nakajima T, Kimura Y. Relationships between serum irisin levels and metabolic parameters in Japanese patients with obesity. Obes Sci Pract. 2016; 2:203–209.14. Kurose S, Tsutsumi H, Yamanaka Y, Shinno H, Miyauchi T, Tamanoi A, Imai M, Masuda I, Kimura Y. Improvement in endothelial function by lifestyle modification focused on exercise training is associated with insulin resistance in obese patients. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2014; 8:e106–e114.15. Saito H, Kimura Y, Tashima S, Takao N, Nakagawa A, Baba T, Sato S. Psychological factors that promote behavior modification by obese patients. Biopsychosoc Med. 2009; 3:9.16. Kimura Y. Dietary instruction and cognitive behavioral therapy. J Clin Sports Med. 2009; 26:225–230.17. Fukushima Y, Kurose S, Shinno H, Cao Thu H, Takao N, Tsutsumi H, Kimura Y. Importance of lean muscle maintenance to improve insulin resistance by body weight reduction in female patients with obesity. Diabetes Metab J. 2016; 40:147–153.18. Beaver WL, Wasserman K, Whipp BJ. A new method for detecting anaerobic threshold by gas exchange. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1986; 60:2020–2027.19. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985; 28:412–419.20. Aydin S, Aydin S, Kuloglu T, Yilmaz M, Kalayci M, Sahin I, Cicek D. Alterations of irisin concentrations in saliva and serum of obese and normal-weight subjects, before and after 45 min of a Turkish bath or running. Peptides. 2013; 50:13–18.21. Pekkala S, Wiklund PK, Hulmi JJ, Ahtiainen JP, Horttanainen M, Pollanen E, Makela KA, Kainulainen H, Hakkinen K, Nyman K, Alen M, Herzig KH, Cheng S. Are skeletal muscle FNDC5 gene expression and irisin release regulated by exercise and related to health? J Physiol. 2013; 591:5393–5400.22. Huh JY, Panagiotou G, Mougios V, Brinkoetter M, Vamvini MT, Schneider BE, Mantzoros CS. FNDC5 and irisin in humans. I. Predictors of circulating concentrations in serum and plasma and II. mRNA expression and circulating concentrations in response to weight loss and exercise. Metabolism. 2012; 61:1725–1738.23. Besse-Patin A, Montastier E, Vinel C, Castan-Laurell I, Louche K, Dray C, Daviaud D, Mir L, Marques MA, Thalamas C, Valet P, Langin D, Moro C, Viguerie N. Effect of endurance training on skeletal muscle myokine expression in obese men: identification of apelin as a novel myokine. Int J Obes (Lond). 2014; 38:707–713.24. Norheim F, Langleite TM, Hjorth M, Holen T, Kielland A, Stadheim HK, Gulseth HL, Birkeland KI, Jensen J, Drevon CA. The effects of acute and chronic exercise on PGC-1α, irisin and browning of subcutaneous adipose tissue in humans. FEBS J. 2014; 281:739–749.25. Kurdiova T, Balaz M, Vician M, Maderova D, Vlcek M, Valkovic L, Srbecky M, Imrich R, Kyselovicova O, Belan V, Jelok I, Wolfrum C, Klimes I, Krssak M, Zemkova E, Gasperikova D, Ukropec J, Ukropcova B. Effects of obesity, diabetes and exercise on Fndc5 gene expression and irisin release in human skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: in vivo and in vitro studies. J Physiol. 2014; 592:1091–1107.26. Huerta AE, Prieto-Hontoria PL, Fernandez-Galilea M, Sainz N, Cuervo M, Martinez JA, Moreno-Aliaga MJ. Circulating irisin and glucose metabolism in overweight/obese women: effects of α-lipoic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid. J Physiol Biochem. 2015; 71:547–558.27. de la Iglesia R, Lopez-Legarrea P, Crujeiras AB, Pardo M, Casanueva FF, Zulet MA, Martinez JA. Plasma irisin depletion under energy restriction is associated with improvements in lipid profile in metabolic syndrome patients. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2014; 81:306–311.28. Moreno-Navarrete JM, Ortega F, Serrano M, Guerra E, Pardo G, Tinahones F, Ricart W, Fernandez-Real JM. Irisin is expressed and produced by human muscle and adipose tissue in association with obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98:E769–E778.29. Stengel A, Hofmann T, Goebel-Stengel M, Elbelt U, Kobelt P, Klapp BF. Circulating levels of irisin in patients with anorexia nervosa and different stages of obesity: correlation with body mass index. Peptides. 2013; 39:125–130.30. Pardo M, Crujeiras AB, Amil M, Aguera Z, Jimenez-Murcia S, Banos R, Botella C, de la Torre R, Estivill X, Fagundo AB, Fernandez-Real JM, Fernandez-Garcia JC, Fruhbeck G, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Rodriguez R, Tinahones FJ, Fernandez-Aranda F, Casanueva FF. Association of irisin with fat mass, resting energy expenditure, and daily activity in conditions of extreme body mass index. Int J Endocrinol. 2014; 2014:857270.31. Peter PR, Park KH, Huh JY, Wedick NM, Mantzoros CS. Circulating irisin levels are not affected by coffee intake: a randomized controlled trial. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e94463.32. Moreno M, Moreno-Navarrete JM, Serrano M, Ortega F, Delgado E, Sanchez-Ragnarsson C, Valdes S, Botas P, Ricart W, Fernandez-Real JM. Circulating irisin levels are positively associated with metabolic risk factors in sedentary subjects. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0124100.33. Huth C, Dubois MJ, Marette A, Tremblay A, Weisnagel SJ, Lacaille M, Mauriege P, Joanisse DR. Irisin is more strongly predicted by muscle oxidative potential than adiposity in non-diabetic men. J Physiol Biochem. 2015; 71:559–568.34. Choi YK, Kim MK, Bae KH, Seo HA, Jeong JY, Lee WK, Kim JG, Lee IK, Park KG. Serum irisin levels in new-onset type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2013; 100:96–101.35. Polyzos SA, Kountouras J, Anastasilakis AD, Geladari EV, Mantzoros CS. Irisin in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism. 2014; 63:207–217.36. Yan B, Shi X, Zhang H, Pan L, Ma Z, Liu S, Liu Y, Li X, Yang S, Li Z. Association of serum irisin with metabolic syndrome in obese Chinese adults. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e94235.37. Liu JJ, Wong MD, Toy WC, Tan CS, Liu S, Ng XW, Tavintharan S, Sum CF, Lim SC. Lower circulating irisin is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Complications. 2013; 27:365–369.38. Al-Daghri NM, Alkharfy KM, Rahman S, Amer OE, Vinodson B, Sabico S, Piya MK, Harte AL, McTernan PG, Alokail MS, Chrousos GP. Irisin as a predictor of glucose metabolism in children: sexually dimorphic effects. Eur J Clin Invest. 2014; 44:119–124.39. Gouni-Berthold I, Berthold HK, Huh JY, Berman R, Spenrath N, Krone W, Mantzoros CS. Effects of lipid-lowering drugs on irisin in human subjects in vivo and in human skeletal muscle cells ex vivo. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e72858.40. Staiger H, Bohm A, Scheler M, Berti L, Machann J, Schick F, Machicao F, Fritsche A, Stefan N, Weigert C, Krook A, Haring HU, de Angelis MH. Common genetic variation in the human FNDC5 locus, encoding the novel muscle-derived 'browning' factor irisin, determines insulin sensitivity. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e61903.41. Roca-Rivada A, Castelao C, Senin LL, Landrove MO, Baltar J, Belen Crujeiras A, Seoane LM, Casanueva FF, Pardo M. FNDC5/irisin is not only a myokine but also an adipokine. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e60563.42. Chen JQ, Huang YY, Gusdon AM, Qu S. Irisin: a new molecular marker and target in metabolic disorder. Lipids Health Dis. 2015; 14:2.43. Reinehr T, Elfers C, Lass N, Roth CL. Irisin and its relation to insulin resistance and puberty in obese children: a longitudinal analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015; 100:2123–2130.44. Sanchis-Gomar F, Alis R, Pareja-Galeano H, Sola E, Victor VM, Rocha M, Hernandez-Mijares A, Romagnoli M. Circulating irisin levels are not correlated with BMI, age, and other biological parameters in obese and diabetic patients. Endocrine. 2014; 46:674–677.45. Tang S, Zhang R, Jiang F, Wang J, Chen M, Peng D, Yan J, Bao Y, Hu C, Jia W. An interaction between a FNDC5 variant and obesity modulates glucose metabolism in a Chinese Han population. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e109957.46. Tanisawa K, Taniguchi H, Sun X, Ito T, Cao ZB, Sakamoto S, Higuchi M. Common single nucleotide polymorphisms in the FNDC5 gene are associated with glucose metabolism but do not affect serum irisin levels in Japanese men with low fitness levels. Metabolism. 2014; 63:574–583.47. Kerstholt N, Ewert R, Nauck M, Spielhagen T, Bollmann T, Stubbe B, Felix SB, Wallaschofski H, Glaser S, Friedrich N. Association of circulating irisin and cardiopulmonary exercise capacity in healthy volunteers: results of the Study of Health in Pomerania. BMC Pulm Med. 2015; 15:41.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Thermotherapy as an alternative to exercise for metabolic health in obese postmenopausal women: focus on circulating irisin level
- Short-term Changes in Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Level after Body Fat Reduction via Partial Meal Replacement
- Correlation between Serum Lipid Parameters and Interleukin-10 Concentration in Obese Individuals
- Relationship between Circulating Obestatin Levels and Obesity Index in Obese Patients
- Effect of Orlistat on the Metabolic Syndrome in Obese Patients