Lab Anim Res.
2016 Sep;32(3):151-159. 10.5625/lar.2016.32.3.151.
Fermented Pueraria Lobata extract ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines and recovering intestinal barrier function
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Gachon Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Gachon University, Incheon, Korea. eyeball@hanmail.net eyeball@gachon.ac.kr
- 3Research Institute, National Cancer Center, Gyeonggi-do, Korea.
- 4Graduate School of Biotechnology, College of Life Science, Kyung Hee University, Gyeonggi-do, Korea.
- 5Department of Oriental Medicine Biotechnology, College of Life Science, Kyung Hee University Global Campus, Gyeonggi-do, Korea.
- KMID: 2353590
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2016.32.3.151
Abstract
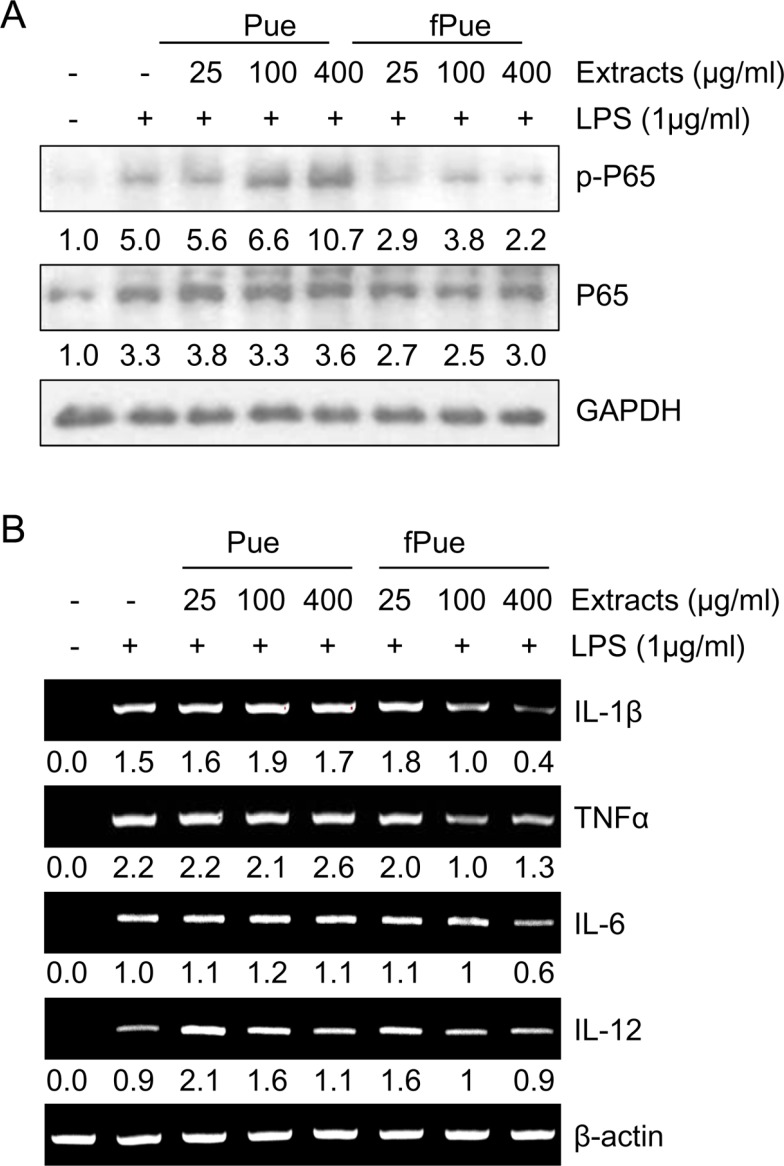
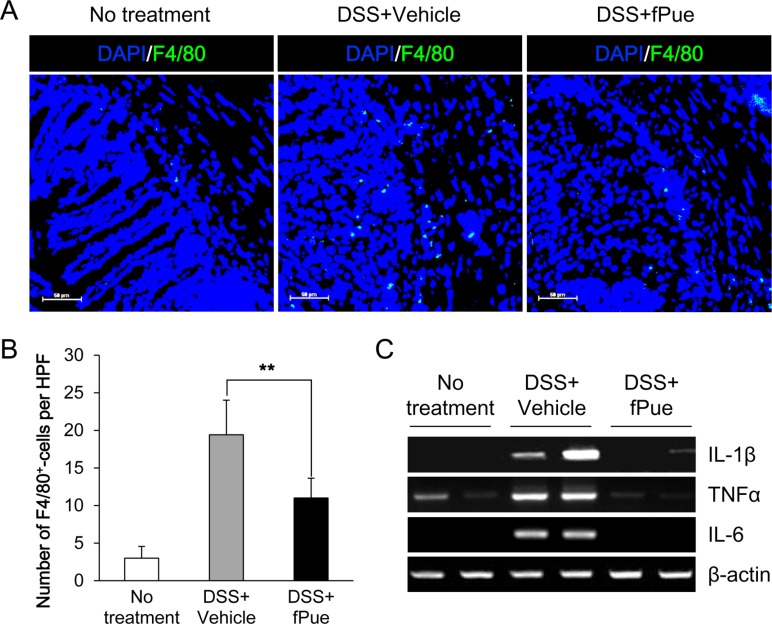
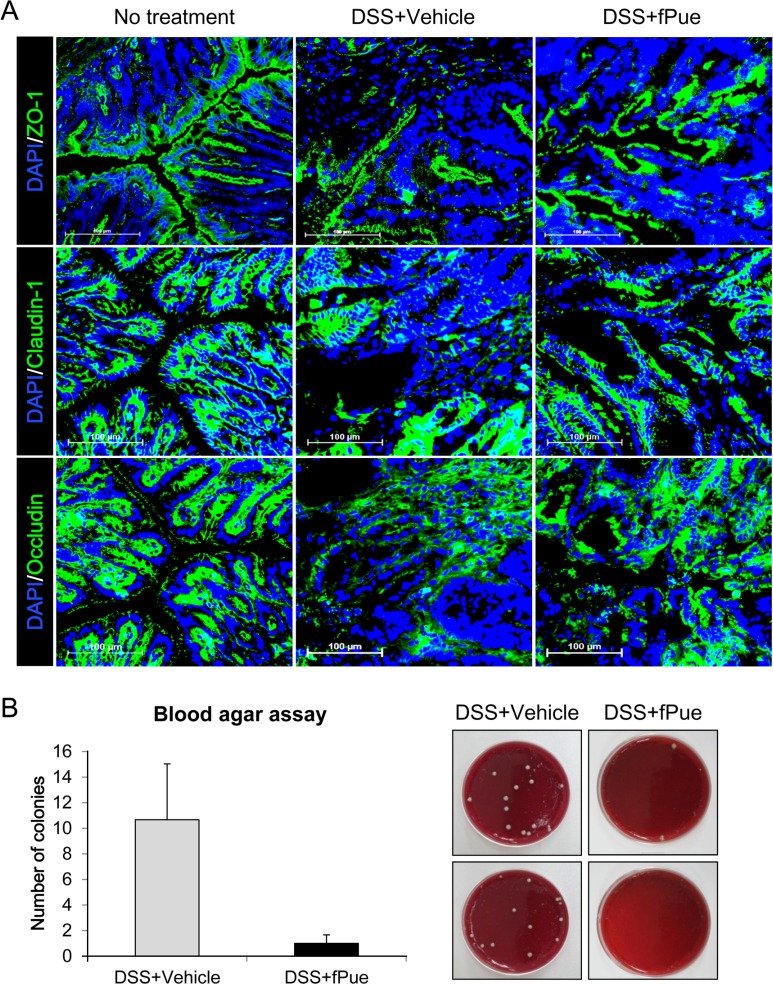
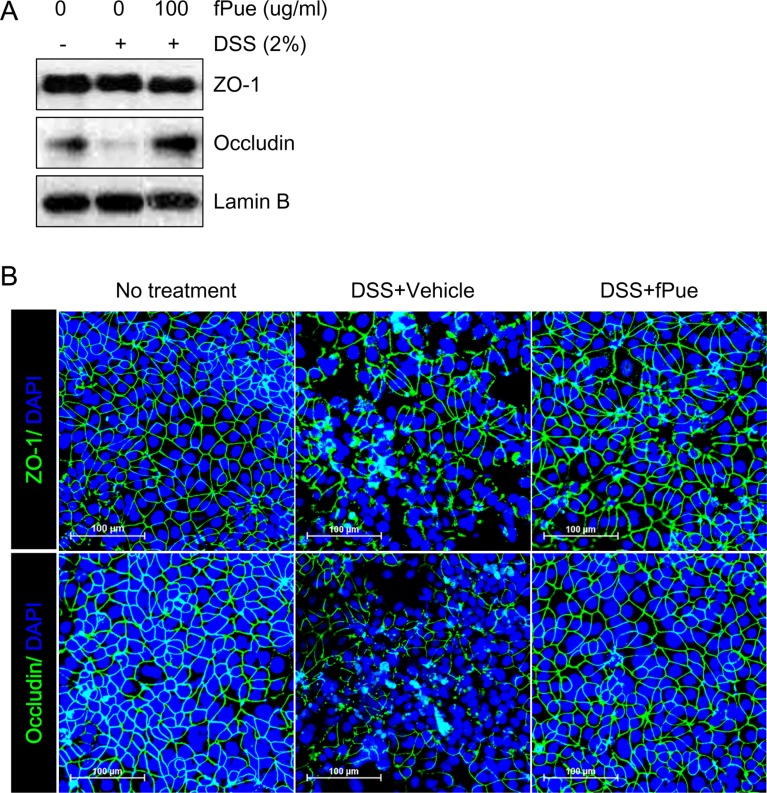
- Inflammatory bowel disease is a chronic inflammatory disorder occurring in the gastrointestinal track. However, the efficacy of current therapeutic strategies has been limited and accompanied by side effects. In order to eliminate the limitations, herbal medicines have recently been developed for treatment of IBD. Peuraria Lobata (Peuraria L.) is one of the traditional herbal medicines that have anti-inflammatory effects. Bioavailability of Peuraria L., which is rich in isoflavones, is lower than that of their fermented forms. In this study, we generated fermented Peuraria L. extracts (fPue) and investigated the role of fPue in inflammation and intestinal barrier function in vitro and in vivo. As the mice or intestinal epithelial cells were treated with DSS/fPue, mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines was reduced and the architecture and expression of tight junction proteins were recovered, compared to the DSS-treated group. In summary, fPue treatment resulted in amelioration of DSS-induced inflammation in the colon, and the disrupted intestinal barrier was recovered as the expression and architecture of tight junction proteins were retrieved. These results suggest that use of fPue could be a new therapeutic strategy for treatment of IBD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Molodecky NA, Soon IS, Rabi DM, Ghali WA, Ferris M, Chernoff G, Benchimol EI, Panaccione R, Ghosh S, Barkema HW, Kaplan GG. Increasing incidence and prevalence of the inflammatory bowel diseases with time, based on systematic review. Gastroenterology. 2012; 142(1):46–54.e42. PMID: 22001864.
Article2. Baumgart DC, Carding SR. Inflammatory bowel disease: cause and immunobiology. Lancet. 2007; 369(9573):1627–1640. PMID: 17499605.
Article3. Walker JR, Ediger JP, Graff LA, Greenfeld JM, Clara I, Lix L, Rawsthorne P, Miller N, Rogala L, McPhail CM, Bernstein CN. The Manitoba IBD cohort study: a population-based study of the prevalence of lifetime and 12-month anxiety and mood disorders. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008; 103(8):1989–1997. PMID: 18796096.
Article4. Goodhand JR, Wahed M, Mawdsley JE, Farmer AD, Aziz Q, Rampton DS. Mood disorders in inflammatory bowel disease: relation to diagnosis, disease activity, perceived stress, and other factors. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012; 18(12):2301–2309. PMID: 22359369.
Article5. Itzkowitz SH, Yio X. Inflammation and cancer IV. Colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease: the role of inflammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004; 287(1):G7–G17. PMID: 15194558.
Article6. Jess T, Rungoe C, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Risk of colorectal cancer in patients with ulcerative colitis: a meta-analysis of population-based cohort studies. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 10(6):639–645. PMID: 22289873.
Article7. Reinecker HC, Steffen M, Witthoeft T, Pflueger I, Schreiber S, MacDermott RP, Raedler A. Enhanced secretion of tumour necrosis factor-alpha, IL-6, and IL-1 beta by isolated lamina propria mononuclear cells from patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993; 94(1):174–181. PMID: 8403503.8. Fries W, Renda MC, Lo Presti MA, Raso A, Orlando A, Oliva L, Giofre MR, Maggio A, Mattaliano A, Macaluso A, Cottone M. Intestinal permeability and genetic determinants in patients, first-degree relatives, and controls in a high-incidence area of Crohn's disease in Southern Italy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005; 100(12):2730–2736. PMID: 16393227.
Article9. Reuter BK, Pizarro TT. Mechanisms of tight junction dysregulation in the SAMP1/YitFc model of Crohn's disease-like ileitis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009; 1165:301–307. PMID: 19538320.
Article10. Zeissig S, Burgel N, Gunzel D, Richter J, Mankertz J, Wahnschaffe U, Kroesen AJ, Zeitz M, Fromm M, Schulzke JD. Changes in expression and distribution of claudin 2, 5 and 8 lead to discontinuous tight junctions and barrier dysfunction in active Crohn's disease. Gut. 2007; 56(1):61–72. PMID: 16822808.
Article11. Bruewer M, Samarin S, Nusrat A. Inflammatory bowel disease and the apical junctional complex. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006; 1072:242–252. PMID: 17057204.
Article12. Zareie M, Johnson-Henry K, Jury J, Yang PC, Ngan BY, McKay DM, Soderholm JD, Perdue MH, Sherman PM. Probiotics prevent bacterial translocation and improve intestinal barrier function in rats following chronic psychological stress. Gut. 2006; 55(11):1553–1560. PMID: 16638791.
Article13. Fakhoury M, Negrulj R, Mooranian A, Al-Salami H. Inflammatory bowel disease: clinical aspects and treatments. J Inflamm Res. 2014; 7:113–120. PMID: 25075198.
Article14. Peyrin-Biroulet L, Lemann M. Review article: remission rates achievable by current therapies for inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011; 33(8):870–879. PMID: 21323689.
Article15. Clark M, Colombel JF, Feagan BC, Fedorak RN, Hanauer SB, Kamm MA, Mayer L, Regueiro C, Rutgeerts P, Sandborn WJ, Sands BE, Schreiber S, Targan S, Travis S, Vermeire S. American gastroenterological association consensus development conference on the use of biologics in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease, June 21-23, 2006. Gastroenterology. 2007; 133(1):312–339. PMID: 17631151.
Article16. Neurath MF. Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014; 14(5):329–342. PMID: 24751956.
Article17. Gisbert JP, Panes J. Loss of response and requirement of infliximab dose intensification in Crohn's disease: a review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009; 104(3):760–767. PMID: 19174781.
Article18. Billioud V, Sandborn WJ, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Loss of response and need for adalimumab dose intensification in Crohn's disease: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011; 106(4):674–684. PMID: 21407178.
Article19. Langmead L, Rampton DS. Review article: complementary and alternative therapies for inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006; 23(3):341–349. PMID: 16422993.
Article20. Jackson LN, Zhou Y, Qiu S, Wang Q, Evers BM. Alternative medicine products as a novel treatment strategy for inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Chin Med. 2008; 36(5):953–965. PMID: 19051360.
Article21. Jun M, Hong J, Jeong WS, Ho CT. Suppression of arachidonic acid metabolism and nitric oxide formation by kudzu isoflavones in murine macrophages. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2005; 49(12):1154–1159. PMID: 16254887.
Article22. Bebrevska L, Foubert K, Hermans N, Chatterjee S, Van Marck E, De Meyer G, Vlietinck A, Pieters L, Apers S. In vivo antioxidative activity of a quantified Pueraria lobata root extract. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010; 127(1):112–117. PMID: 19799984.
Article23. Jiang RW, Lau KM, Lam HM, Yam WS, Leung LK, Choi KL, Waye MM, Mak TC, Woo KS, Fung KP. A comparative study on aqueous root extracts of Pueraria thomsonii and Pueraria lobata by antioxidant assay and HPLC fingerprint analysis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005; 96(1-2):133–138. PMID: 15588661.
Article24. Izumi T, Piskula MK, Osawa S, Obata A, Tobe K, Saito M, Kataoka S, Kubota Y, Kikuchi M. Soy isoflavone aglycones are absorbed faster and in higher amounts than their glucosides in humans. J Nutr. 2000; 130(7):1695–1699. PMID: 10867038.
Article25. Boismenu R, Chen Y. Insights from mouse models of colitis. J Leukoc Biol. 2000; 67(3):267–278. PMID: 10733087.
Article26. Nishiyama Y, Kataoka T, Yamato K, Taguchi T, Yamaoka K. Suppression of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by radon inhalation. Mediators Inflamm. 2012; 2012:239617. PMID: 23365486.
Article27. Stillie R, Stadnyk AW. Role of TNF receptors, TNFR1 and TNFR2, in dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009; 15(10):1515–1525. PMID: 19479745.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Using Murine Intestinal Organoids
- T Cell-Specific Knockout of STAT3 Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis by Reducing the Inflammatory Response
- Histological Study of Experimental Colitis Induced by Dextran Sulfate Sodium
- The Therapeutic Efficacy of Tonsil-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Dextran Sulfate Sodium-induced Acute Murine Colitis Model
- Long Noncoding RNA FBXL19-AS1-Mediated Ulcerative Colitis-Associated Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Defect