J Breast Cancer.
2014 Mar;17(1):18-24.
Microgel-Encapsulated Methylene Blue for the Treatment of Breast Cancer Cells by Photodynamic Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Natural Science Department, Albany State University, Albany, GA, USA. seong.seo@asurams.edu
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is gaining increasing recognition for breast cancer treatment because it offers local selectivity and reduced toxic side effects compared to radiotherapy and chemotherapy. In PDT, photosensitizer drugs are loaded in different nanomaterials and used in combination with light exposure. However, the most representative issue with PDT is the difficulty of nanomaterials to encapsulate anticancer drugs at high doses, which results in low efficacy of the PDT treatment. Here, we proposed the development of the poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) microgel for the encapsulation of methylene blue, an anticancer drug, for its use as breast cancer treatment in MCF-7 cell line.
METHODS
We developed biocompatible microgels based on nonfunctionalized PNIPAM and its corresponding anionically functionalized PNIPAM and polyacrylic acid (PNIPAM-co-PAA) microgel. Methylene blue was used as the photosensitizer drug because of its ability to generate toxic reactive oxygen species upon exposure to light at 664 nm. Core PNIPAM and core/shell PNIPAM-co-PAA microgels were synthesized and characterized using ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy and dynamic light scattering. The effect of methylene blue was evaluated using the MCF-7 cell line.
RESULTS
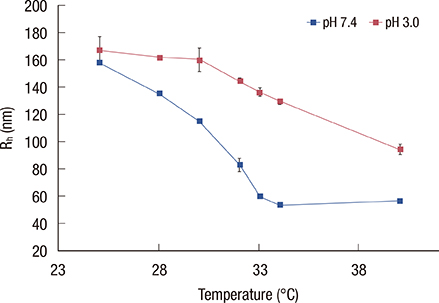
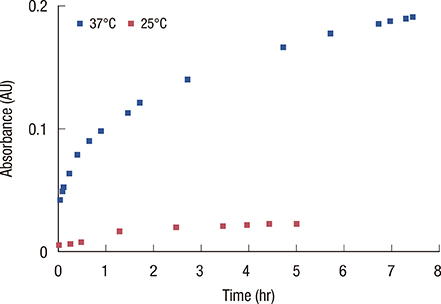
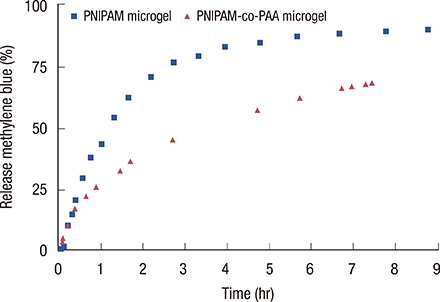
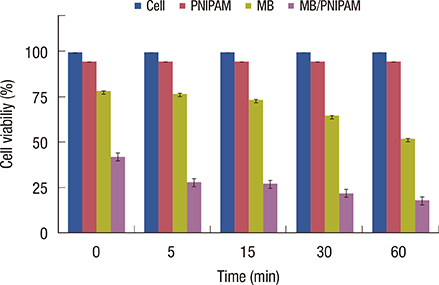
Loading of methylene blue in core PNIPAM microgel was higher than that in the core/shell PNIPAM-co-PAA microgel, indicating that electrostatic interactions did not play an important role in loading a cationic drug. This behavior is probably due to the skin layer inhibiting the high uptake of drugs in the PNIPAM-co-PAA microgel. Core PNIPAM microgel effectively retained the cationic drug (i.e., methylene blue) for several hours compared to core/shell PNIPAM-co-PAA and enhanced its photodynamic efficacy in vitro more than that of free methylene blue.
CONCLUSION
Our results showed that the employment of core PNIPAM and core/shell PNIPAM-co-PAA microgels enhanced the encapsulation of methylene blue. Core PNIPAM microgel released the drug more slowly than did core/shell PNIPAM-co-PAA, and it effectively inhibited the growth of MCF-7 cells.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ahmad A. Breast Cancer Metastasis and Drug Resistance: Progress and Prospects. New York: Springer;2013. p. 19–20.2. Weigelt B, Peterse JL, van't Veer LJ. Breast cancer metastasis: markers and models. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005; 5:591–602.
Article3. Buytaert E, Dewaele M, Agostinis P. Molecular effectors of multiple cell death pathways initiated by photodynamic therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007; 1776:86–107.
Article4. Siegel MM, Tabei K, Tsao R, Pastel MJ, Pandey RK, Berkenkamp S, et al. Comparative mass spectrometric analyses of Photofrin oligomers by fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry, UV and IR matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry, electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and laser desorption/jet-cooling photoionization mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom. 1999; 34:661–669.
Article5. Dolmans DE, Fukumura D, Jain RK. Photodynamic therapy for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003; 3:380–387.
Article6. Wilson BC, Patterson MS. The physics, biophysics and technology of photodynamic therapy. Phys Med Biol. 2008; 53:R61–R109.
Article7. Bechet D, Couleaud P, Frochot C, Viriot ML, Guillemin F, Barberi-Heyob M. Nanoparticles as vehicles for delivery of photodynamic therapy agents. Trends Biotechnol. 2008; 26:612–621.
Article8. Wainwright M. Non-porphyrin photosensitizers in biomedicine. Chem Soc Rev. 1996; 25:351–359.
Article9. Sharman WM, Allen CM, van Lier JE. Photodynamic therapeutics: basic principles and clinical applications. Drug Discov Today. 1999; 4:507–517.
Article10. Tuite EM, Kelly JM. Photochemical interactions of methylene blue and analogues with DNA and other biological substrates. J Photochem Photobiol B. 1993; 21:103–124.11. Orth K, Beck G, Genze F, Rück A. Methylene blue mediated photodynamic therapy in experimental colorectal tumors in mice. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2000; 57:186–192.
Article12. Davis ME, Chen ZG, Shin DM. Nanoparticle therapeutics: an emerging treatment modality for cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008; 7:771–782.
Article13. Tang W, Xu H, Park EJ, Philbert MA, Kopelman R. Encapsulation of methylene blue in polyacrylamide nanoparticle platforms protects its photodynamic effectiveness. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008; 369:579–583.
Article14. Derycke AS, de Witte PA. Liposomes for photodynamic therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004; 56:17–30.
Article15. Regehly M, Greish K, Rancan F, Maeda H, Böhm F, Röder B. Water-soluble polymer conjugates of ZnPP for photodynamic tumor therapy. Bioconjug Chem. 2007; 18:494–499.
Article16. Roy I, Ohulchanskyy TY, Pudavar HE, Bergey EJ, Oseroff AR, Morgan J, et al. Ceramic-based nanoparticles entrapping water-insoluble photosensitizing anticancer drugs: a novel drug-carrier system for photodynamic therapy. J Am Chem Soc. 2003; 125:7860–7865.
Article17. Barbucci R, Magnani A, Consumi M. Swelling behavior of carboxymethylcellulose hydrogels in relation to cross-linking, pH, and charge density. Macromolecules. 2000; 33:7475–7480.
Article18. Matsumura Y, Maeda H. A new concept for macromolecular therapeutics in cancer chemotherapy: mechanism of tumoritropic accumulation of proteins and the antitumor agent smancs. Cancer Res. 1986; 46(12 Pt 1):6387–6392.19. Maeda H. The enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect in tumor vasculature: the key role of tumor-selective macromolecular drug targeting. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2001; 41:189–207.
Article20. Grabstain V, Bianco-Peled H. Mechanisms controlling the temperature-dependent binding of proteins to poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgels. Biotechnol Prog. 2003; 19:1728–1733.
Article21. Schmitz KS. An Introduction to Dynamic Light Scattering by Macromolecules. Oxford: Academic Press;1990. p. 11–42.22. Hoare T, Pelton R. Impact of microgel morphology on functionalized microgel-drug interactions. Langmuir. 2008; 24:1005–1012.
Article23. Fernández-Nieves A, Fernández-Barbero A, Vincent B, de las Nieves FJ. Charge controlled swelling of microgel particles. Macromolecules. 2000; 33:2114–2118.
Article24. Deka SR, Quarta A, Di Corato R, Falqui A, Manna L, Cingolani R, et al. Acidic pH-responsive nanogels as smart cargo systems for the simultaneous loading and release of short oligonucleotides and magnetic nanoparticles. Langmuir. 2010; 26:10315–10324.
Article25. Komine C, Tsujimoto Y. A small amount of singlet oxygen generated via excited methylene blue by photodynamic therapy induces the sterilization of Enterococcus faecalis. J Endod. 2013; 39:411–414.
Article26. Khdair A, Gerard B, Handa H, Mao G, Shekhar MP, Panyam J. Surfactant-polymer nanoparticles enhance the effectiveness of anticancer photodynamic therapy. Mol Pharm. 2008; 5:795–807.
Article27. Qin M, Hah HJ, Kim G, Nie G, Lee YE, Kopelman R. Methylene blue covalently loaded polyacrylamide nanoparticles for enhanced tumor-targeted photodynamic therapy. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2011; 10:832–841.
Article28. Chen Y, Zheng W, Li Y, Zhong J, Ji J, Shen P. Apoptosis induced by methylene-blue-mediated photodynamic therapy in melanomas and the involvement of mitochondrial dysfunction revealed by proteomics. Cancer Sci. 2008; 99:2019–2027.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Methylene Blue-mediated Photodynamic Therapy on Wild-type and Ciprofloxacin-resistant Mycobacterium smegmatis
- Methylene Blue for Localization of Sentinel Lymph Nodes in Breast Cancer: A Comparison with Isosulfan Blue
- The Dye-injection Microdochectomy for Intraductal Papilloma of the Breast
- Localization of Nonpalpable Breast lesion with Ultrasonoguided Dye Injection
- Effect of Photodynamic Therapy Enhanced by Methylene Blue on Drug-resistant Mycobacterium smegmatis