Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2016 Sep;20(5):459-466. 10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.5.459.
Lnk is an important modulator of insulin-like growth factor-1/Akt/peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma axis during adipogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Neuroregeneration and Stem Cell Programs, Institute for Cell Engineering, Department of Neurology, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA.
- 2Laboratory for Vascular Medicine and Stem Cell Biology, Medical Research Institute, Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, Pusan National University, Yangsan 50612, Korea. smkwon323@pusan.ac.kr
- 3Medical Science Research Institute, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital, Seoul 04401, Korea.
- 4Department of Biochemistry, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan 31151, Korea.
- 5Department of Physiology, Pusan Natinoal University, Yangsan 50612, Korea.
- 6Research Institute of Convergence Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University, Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan 50612, Korea.
- 7Department of Pharmacology, Gene and Cell Therapy Center for Vessel-Associated Disease, Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan 50612, Korea.
- KMID: 2350502
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.5.459
Abstract
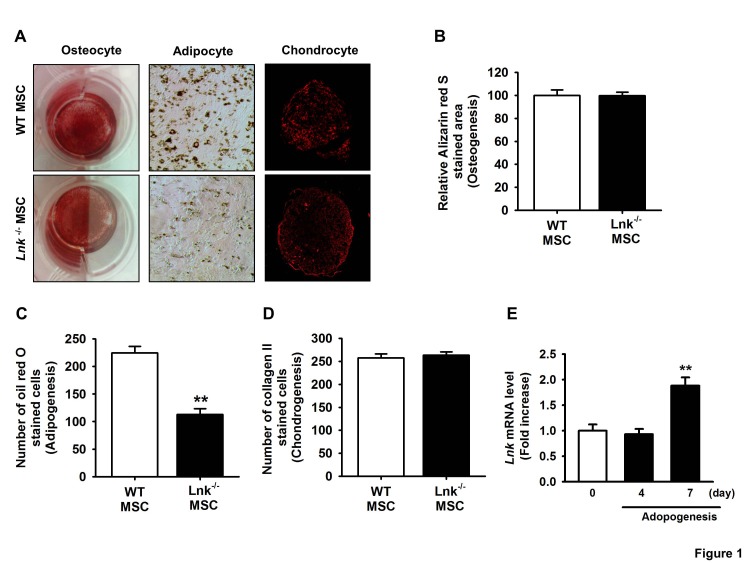
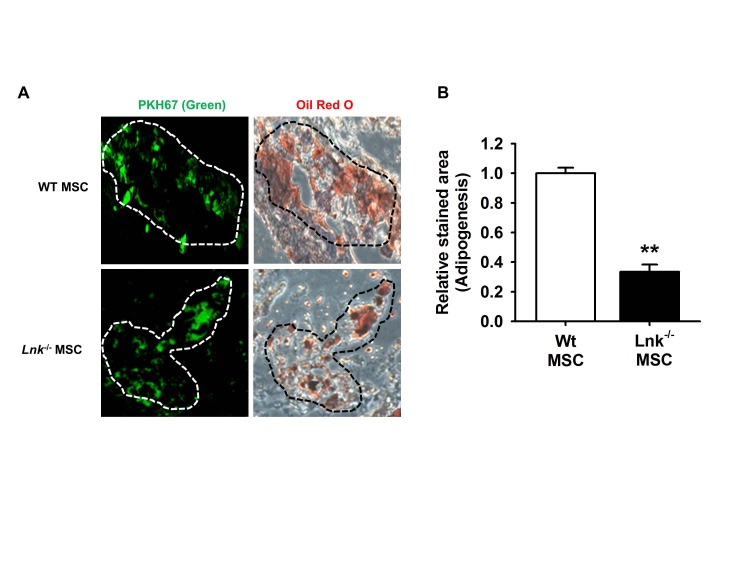
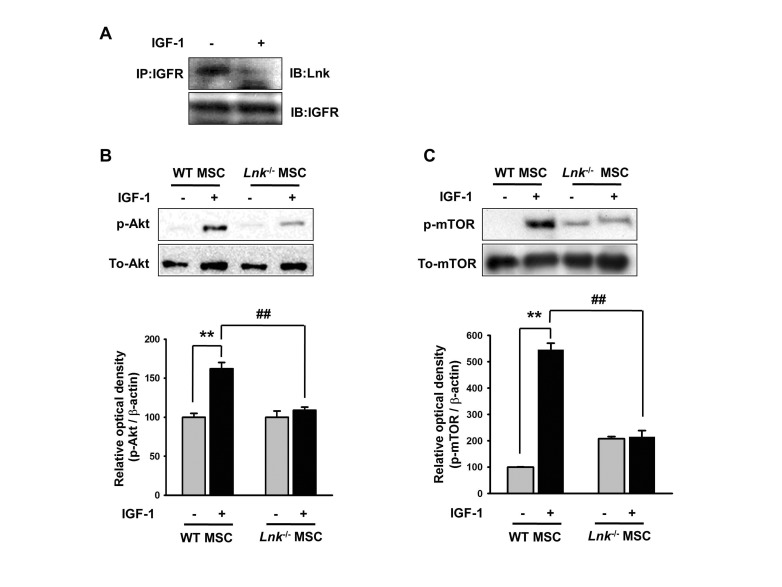
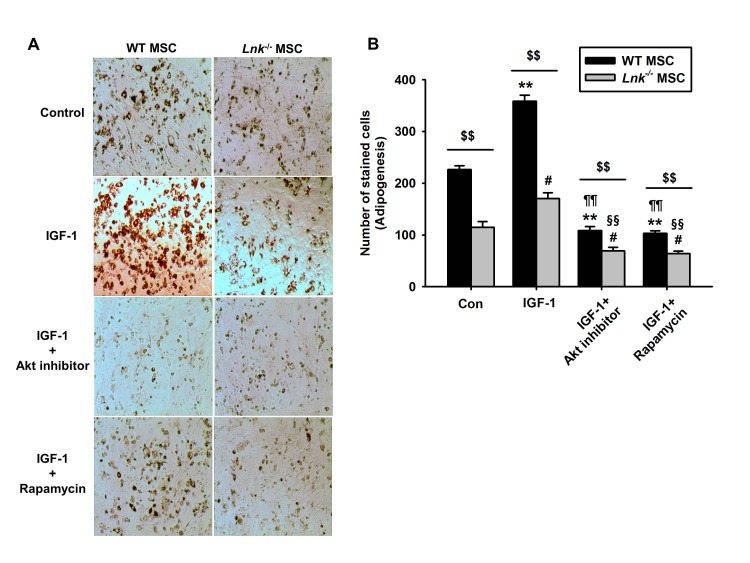
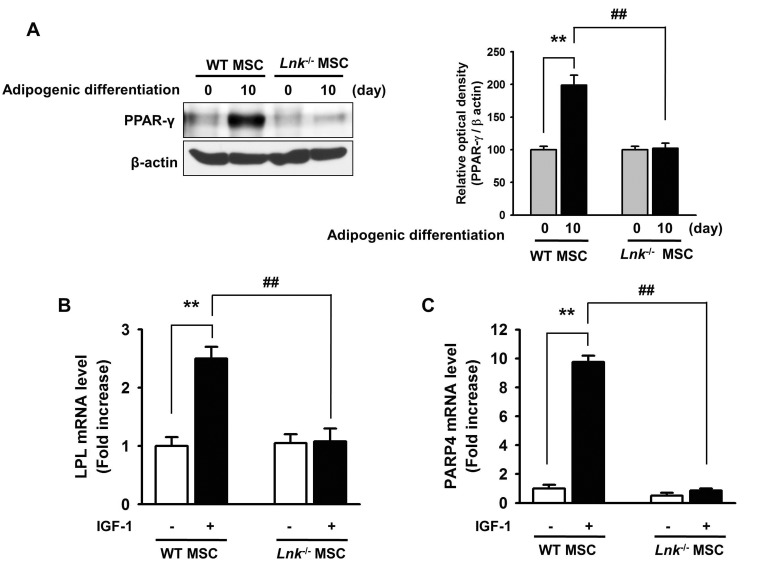
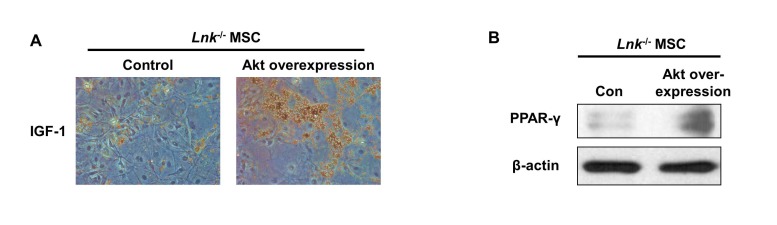
- Adipogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) is critical for metabolic homeostasis and nutrient signaling during development. However, limited information is available on the pivotal modulators of adipogenic differentiation of MSCs. Adaptor protein Lnk (Src homology 2B3 [SH2B3]), which belongs to a family of SH2-containing proteins, modulates the bioactivities of different stem cells, including hematopoietic stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells. In this study, we investigated whether an interaction between insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) and Lnk regulated IGF-1-induced adipogenic differentiation of MSCs. We found that wild-type MSCs showed greater adipogenic differentiation potential than Lnk(-/-) MSCs. An ex vivo adipogenic differentiation assay showed that Lnk(-/-) MSCs had decreased adipogenic differentiation potential compared with wild-type MSCs. Interestingly, we found that Lnk formed a complex with IGF-1R and that IGF-1 induced the dissociation of this complex. In addition, we observed that IGF-1-induced increase in the phosphorylation of Akt and mammalian target of rapamycin was triggered by the dissociation of the IGF-1R-Lnk complex. Expression levels of a pivotal transcription factor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ) and its adipogenic target genes (LPL and FABP4) significantly decreased in Lnk(-/-) MSCs. These results suggested that Lnk adaptor protein regulated the adipogenesis of MSCs through the IGF-1/Akt/PPAR-γ pathway.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chamberlain G, Fox J, Ashton B, Middleton J. Concise review: mesenchymal stem cells: their phenotype, differentiation capacity, immunological features, and potential for homing. Stem Cells. 2007; 25:2739–2749. PMID: 17656645.
Article2. Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S, Marshak DR. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999; 284:143–147. PMID: 10102814.
Article3. Singer NG, Caplan AI. Mesenchymal stem cells: mechanisms of inflammation. Annu Rev Pathol. 2011; 6:457–478. PMID: 21073342.
Article4. Woldt E, Matz RL, Terrand J, Mlih M, Gracia C, Foppolo S, Martin S, Bruban V, Ji J, Velot E, Herz J, Boucher P. Differential signaling by adaptor molecules LRP1 and ShcA regulates adipogenesis by the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. J Biol Chem. 2011; 286:16775–16782. PMID: 21454706.
Article5. Laviola L, Natalicchio A, Giorgino F. The IGF-I signaling pathway. Curr Pharm Des. 2007; 13:663–669. PMID: 17346182.
Article6. Garten A, Schuster S, Kiess W. The insulin-like growth factors in adipogenesis and obesity. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2012; 41:283–295. v–vi. PMID: 22682631.
Article7. Chen Q, Shou P, Zheng C, Jiang M, Cao G, Yang Q, Cao J, Xie N, Velletri T, Zhang X, Xu C, Zhang L, Yang H, Hou J, Wang Y, Shi Y. Fate decision of mesenchymal stem cells: adipocytes or osteoblasts? Cell Death Differ. 2016; (7):1128–1139. PMID: 26868907.
Article8. James AW. Review of signaling pathways governing MSC osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation. Scientifica (Cairo). 2013; 2013:684736. PMID: 24416618.
Article9. Muruganandan S, Roman AA, Sinal CJ. Adipocyte differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: cross talk with the osteoblastogenic program. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009; 66:236–253. PMID: 18854943.
Article10. Devallière J, Charreau B. The adaptor Lnk (SH2B3): an emerging regulator in vascular cells and a link between immune and inflammatory signaling. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011; 82:1391–1402. PMID: 21723852.
Article11. Takaki S, Sauer K, Iritani BM, Chien S, Ebihara Y, Tsuji K, Takatsu K, Perlmutter RM. Control of B cell production by the adaptor protein ink. Definition of a conserved family of signal-modulating proteins. Immunity. 2000; 13:599–609. PMID: 11114373.12. Matsumoto T, Ii M, Nishimura H, Shoji T, Mifune Y, Kawamoto A, Kuroda R, Fukui T, Kawakami Y, Kuroda T, Kwon SM, Iwasaki H, Horii M, Yokoyama A, Oyamada A, Lee SY, Hayashi S, Kurosaka M, Takaki S, Asahara T. Lnk-dependent axis of SCF-cKit signal for osteogenesis in bone fracture healing. J Exp Med. 2010; 207:2207–2223. PMID: 20855498.
Article13. Lee SH, Lee KB, Lee JH, Kang S, Kim HG, Asahara T, Kwon SM. Selective interference targeting of Lnk in umbilical cord-derived late endothelial progenitor cells improves vascular repair, following hind limb ischemic injury, via regulation of JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Stem Cells. 2015; 33:1490–1500. PMID: 25537795.
Article14. Ahmed Z, Pillay TS. Adapter protein with a pleckstrin homology (PH) and an Src homology 2 (SH2) domain (APS) and SH2-B enhance insulin-receptor autophosphorylation, extracellular-signal-regulated kinase and phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent signalling. Biochem J. 2003; 371:405–412. PMID: 12521378.
Article15. Bae SS, Cho H, Mu J, Birnbaum MJ. Isoform-specific regulation of insulin-dependent glucose uptake by Akt/protein kinase B. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278:49530–49536. PMID: 14522993.
Article16. Velazquez L. The Lnk adaptor protein: a key regulator of normal and pathological hematopoiesis. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2012; 60:415–429. PMID: 22990499.
Article17. Wang J, Riedel H. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor and insulin receptor association with a Src homology-2 domain-containing putative adapter. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273:3136–3139. PMID: 9452421.
Article18. Scott A, Cook JL, Hart DA, Walker DC, Duronio V, Khan KM. Tenocyte responses to mechanical loading in vivo: a role for local insulin-like growth factor 1 signaling in early tendinosis in rats. Arthritis Rheum. 2007; 56:871–881. PMID: 17328060.
Article19. Yu W, Chen Z, Zhang J, Zhang L, Ke H, Huang L, Peng Y, Zhang X, Li S, Lahn BT, Xiang AP. Critical role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase cascade in adipogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2008; 310:11–18. PMID: 18060476.
Article20. Rosen ED, MacDougald OA. Adipocyte differentiation from the inside out. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006; 7:885–896. PMID: 17139329.
Article21. Tontonoz P, Hu E, Spiegelman BM. Regulation of adipocyte gene expression and differentiation by peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995; 5:571–576. PMID: 8664544.22. Kamei N, Kwon SM, Alev C, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama A, Nakanishi K, Yamada K, Horii M, Nishimura H, Takaki S, Kawamoto A, Ii M, Akimaru H, Tanaka N, Nishikawa S, Ochi M, Asahara T. Lnk deletion reinforces the function of bone marrow progenitors in promoting neovascularization and astrogliosis following spinal cord injury. Stem Cells. 2010; 28:365–375. PMID: 19859984.
Article23. Saleh MA, McMaster WG, Wu J, Norlander AE, Funt SA, Thabet SR, Kirabo A, Xiao L, Chen W, Itani HA, Michell D, Huan T, Zhang Y, Takaki S, Titze J, Levy D, Harrison DG, Madhur MS. Lymphocyte adaptor protein LNK deficiency exacerbates hypertension and end-organ inflammation. J Clin Invest. 2015; 125:1189–1202. PMID: 25664851.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Macakurzin C Derivatives as a Novel Pharmacophore for Pan-Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Modulator
- Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor gammaActivation Promotes Adipogenesis in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor-delta (PPAR-delta)
- Effects of Sulfonylureas on Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor gamma Activity and on Glucose Uptake by Thiazolidinediones
- Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor (PPAR) alpha/gamma Agonist