Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2016 Nov;8(6):505-511. 10.4168/aair.2016.8.6.505.
Clinical Significance of Component Allergens in Fagales Pollen-Sensitized Peanut Allergy in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Allergy and Immunology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. parkjw@yuhs.ac
- 2Institute of Allergy, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2349990
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2016.8.6.505
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Clinical features of peanut allergy can range from localized to systemic reactions. Because peanut and birch pollen have cross-reactivity, peanut can lead to localized allergic reaction in Fagales pollen-sensitized oral allergy syndrome (OAS) patients without peanut sensitization per se. The purpose of this study was to discriminate true peanut food allergy from cross-reactive hypersensitivity in birch-sensitized peanut allergy.
METHODS
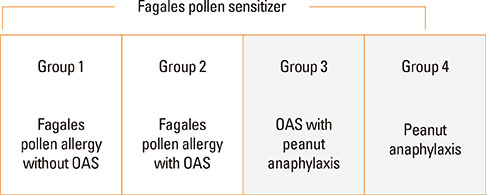
Birch-sensitized (n=81) and peanut anaphylaxis patients (n=12) were enrolled. Peanut-related allergic reactions and sensitization profiles were examined. Specific IgE to Fagales tree pollens (birch, oak), peanut, and their component allergens (Bet v 1, Bet v 2, Ara h 1, Ara h 2, Ara h 3, Ara h 8, and Ara h 9) were evaluated. Based on these specific IgEs and clinical features, the patients were classified into 4 groups: group 1 (Fagales pollen allergy without OAS), group 2 (Fagales pollen allergy with OAS), group 3 (OAS with peanut anaphylaxis), and group 4 (peanut anaphylaxis).
RESULTS
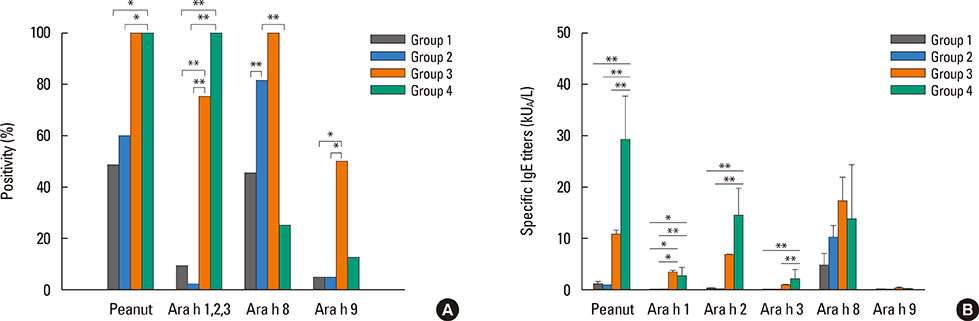
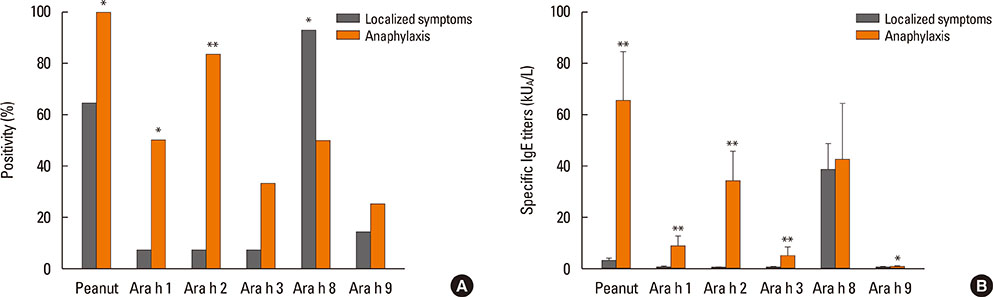
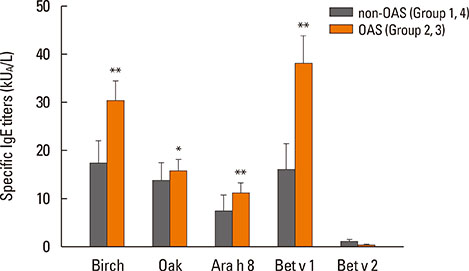
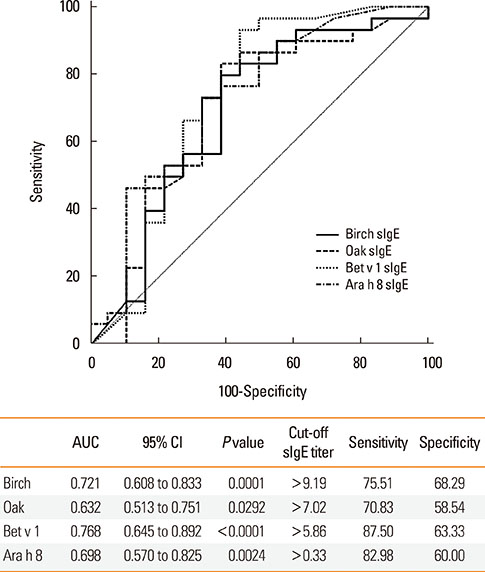
After peanut consumption, one-third of OAS patients experienced oral symptoms not associated with peanut sensitization. Ara h 1 or Ara h 2 was positive in peanut anaphylaxis patients, whereas Ara h 8 was positive in OAS patients. There were 4 patients with both peanut anaphylaxis and OAS (group 3). Both Ara h 2 and Ara h 8 were positive in these patients. Foods associated with OAS in Korea showed unique patterns compared to Westernized countries.
CONCLUSIONS
Ara h 2 and Ara h 8 may be important component allergens for discriminating peanut allergy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Comparison of the ImmunoCAP Assay and AdvanSure™ AlloScreen Advanced Multiplex Specific IgE Detection Assay
Kyung Hee Park, Jongsun Lee, Sang Chul Lee, Young Woong Son, Da Woon Sim, Jae-Hyun Lee, Jung-Won Park
Yonsei Med J. 2017;58(4):786-792. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.4.786.Subcutaneous Immunotherapy in Patients with Fagales Pollen-Induced Oral Allergy Syndrome
Nasil Kong, Sunyoung Kim, Sang Chul Lee, Kyung Hee Park, Jae-Hyun Lee, Jung-Won Park
Yonsei Med J. 2019;60(4):389-394. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.4.389.
Reference
-
1. Ballmer-Weber BK, Lidholm J, Fernández-Rivas M, Seneviratne S, Hanschmann KM, Vogel L, et al. IgE recognition patterns in peanut allergy are age dependent: perspectives of the EuroPrevall study. Allergy. 2015; 70:391–407.2. Garcia-Blanca A, Aranda A, Blanca-Lopez N, Perez D, Gomez F, Mayorga C, et al. Influence of age on IgE response in peanut-allergic children and adolescents from the Mediterranean area. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2015; 26:497–502.3. Schmitz R, Ellert U, Kalcklösch M, Dahm S, Thamm M. Patterns of sensitization to inhalant and food allergens - findings from the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Children and Adolescents. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013; 162:263–270.4. Lee AJ, Thalayasingam M, Lee BW. Food allergy in Asia: how does it compare? Asia Pac Allergy. 2013; 3:3–14.5. Sicherer SH, Sampson HA. Peanut allergy: emerging concepts and approaches for an apparent epidemic. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 120:491–503.6. Chiang WC, Kidon MI, Liew WK, Goh A, Tang JP, Chay OM. The changing face of food hypersensitivity in an Asian community. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007; 37:1055–1061.7. Bajin MD, Cingi C, Oghan F, Gurbuz MK. Global warming and allergy in Asia Minor. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013; 270:27–31.8. Kim SH, Park HS, Jang JY. Impact of meteorological variation on hospital visits of patients with tree pollen allergy. BMC Public Health. 2011; 11:890.9. Codreanu F, Collignon O, Roitel O, Thouvenot B, Sauvage C, Vilain AC, et al. A novel immunoassay using recombinant allergens simplifies peanut allergy diagnosis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2011; 154:216–226.10. Vereda A, van Hage M, Ahlstedt S, Ibañez MD, Cuesta-Herranz J, van Odijk J, et al. Peanut allergy: clinical and immunologic differences among patients from 3 different geographic regions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 127:603–607.11. Sicherer SH. Clinical implications of cross-reactive food allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 108:881–890.12. Geroldinger-Simic M, Zelniker T, Aberer W, Ebner C, Egger C, Greiderer A, et al. Birch pollen-related food allergy: clinical aspects and the role of allergen-specific IgE and IgG4 antibodies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 127:616–622.e1.13. Yoon MG, Kim MA, Jin HJ, Shin YS, Park HS. Identification of immunoglobulin E binding components of two major tree pollens, birch and alder. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:216–220.14. Park HJ, Lim HS, Park KH, Lee JH, Park JW, Hong CS. Changes in allergen sensitization over the last 30 years in Korea respiratory allergic patients: a single-center. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:434–443.15. Weber RW. Patterns of pollen cross-allergenicity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 112:229–239.16. Oh JW, Lee HB, Kang IJ, Kim SW, Park KS, Kook MH, et al. The revised edition of Korean calendar for allergenic pollens. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:5–11.17. Choi K, Kim M, Lee WK, Gang HU, Chung DJ, Ko EJ, et al. Estimating radial growth response of major tree species using climatic and topographic condition in South Korea. J Clim Chang Res. 2014; 5:127–137.18. Cho KT, Jeong HM, Han YS, Lee SH. Variation of ecological niche of quercus serrata under elevated CO2 concentration and temperature. Korean J Environ Biol. 2014; 32:95–101.19. Nicolaou N, Poorafshar M, Murray C, Simpson A, Winell H, Kerry G, et al. Allergy or tolerance in children sensitized to peanut: prevalence and differentiation using component-resolved diagnostics. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:191–197.e1-13.20. Astier C, Morisset M, Roitel O, Codreanu F, Jacquenet S, Franck P, et al. Predictive value of skin prick tests using recombinant allergens for diagnosis of peanut allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 118:250–256.21. Kim J, Lee JY, Han Y, Ahn K. Significance of Ara h 2 in clinical reactivity and effect of cooking methods on allergenicity. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013; 110:34–38.22. Krause S, Reese G, Randow S, Zennaro D, Quaratino D, Palazzo P, et al. Lipid transfer protein (Ara h 9) as a new peanut allergen relevant for a Mediterranean allergic population. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124:771–778.e5.23. Ferreira F, Wolf M, Wallner M. Molecular approach to allergy diagnosis and therapy. Yonsei Med J. 2014; 55:839–852.24. Movérare R, Westritschnig K, Svensson M, Hayek B, Bende M, Pauli G, et al. Different IgE reactivity profiles in birch pollen-sensitive patients from six European populations revealed by recombinant allergens: an imprint of local sensitization. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2002; 128:325–335.25. Kim M, Choi E, Yoon T. Korean ginseng makes oral allergy syndrome in birch-sensitized respiratory allergy patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 121:Suppl 1. S187.26. Lee JY, Lee YD, Bahn JW, Park HS. A case of occupational asthma and rhinitis caused by Sanyak and Korean ginseng dusts. Allergy. 2006; 61:392–393.27. Lee JY, Jin HJ, Park JW, Jung SK, Jang JY, Park HS. A case of Korean ginseng-induced anaphylaxis confirmed by open oral challenge and basophil activation test. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:110–111.28. Blanco C. Latex-fruit syndrome. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2003; 3:47–53.29. Breiteneder H, Ebner C. Molecular and biochemical classification of plant-derived food allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000; 106:27–36.30. Sekerková A, Poláčková M. Detection of Bet v1, Bet v2 and Bet v4 specific IgE antibodies in the sera of children and adult patients allergic to birch pollen: evaluation of different IgE reactivity profiles depending on age and local sensitization. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2011; 154:278–285.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Utilization of Component-Resolved Diagnosis in Precision Allergology
- Are there any links between mugwort pollen and food allergens such as celery and carrot based upon allergy skin prick tests?
- Subcutaneous Immunotherapy in Patients with Fagales Pollen-Induced Oral Allergy Syndrome
- Etiology and clinical feature of oral allergy syndrome in children
- Change of causative inhalant allergens in respiratory allergic patients in Chungbuk district