Yonsei Med J.
2015 Nov;56(6):1572-1581. 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.6.1572.
Thalidomide Accelerates the Degradation of Extracellular Matrix in Rat Hepatic Cirrhosis via Down-Regulation of Transforming Growth Factor-beta1
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Jining First People's Hospital, Jining, China. jnlvpeng@163.com
- KMID: 2345885
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.6.1572
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The degradation of the extracellular matrix has been shown to play an important role in the treatment of hepatic cirrhosis. In this study, the effect of thalidomide on the degradation of extracellular matrix was evaluated in a rat model of hepatic cirrhosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
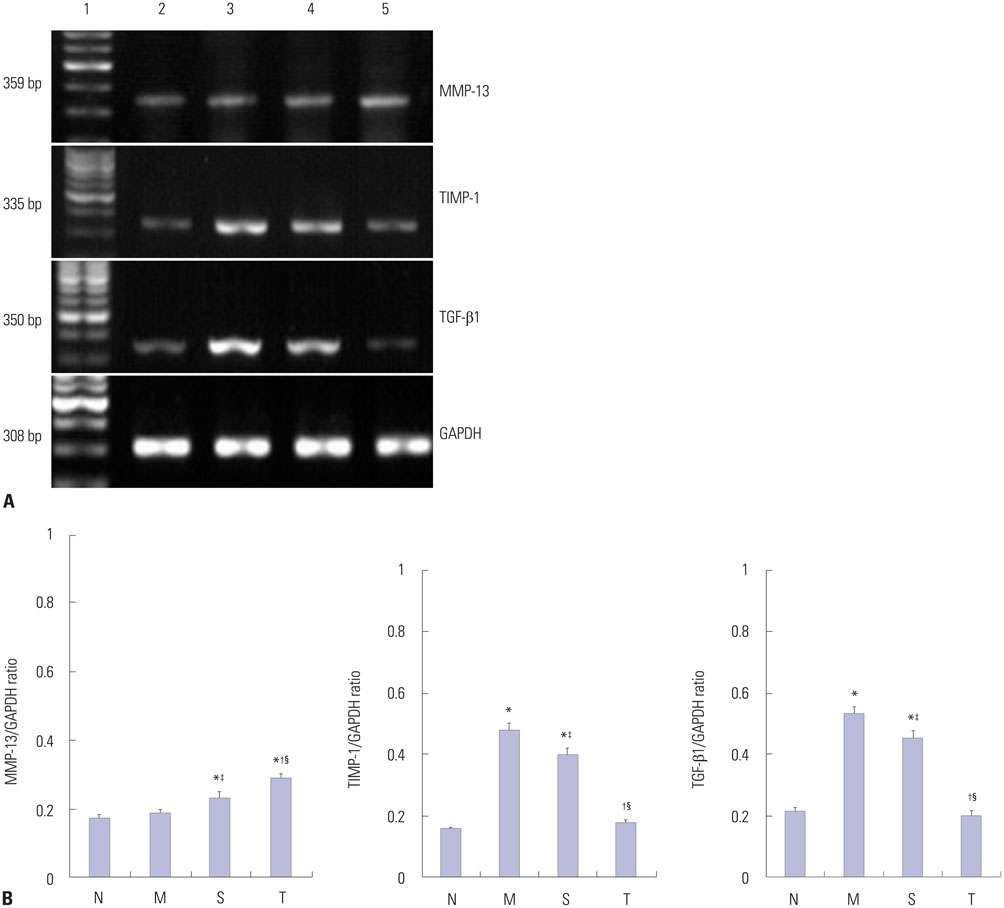
Cirrhosis was induced in Wistar rats by intraperitoneal injection of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) three times weekly for 8 weeks. Then CCl4 was discontinued and thalidomide (100 mg/kg) or its vehicle was administered daily by gavage for 6 weeks. Serum hyaluronic acid, laminin, procollagen type III, and collagen type IV were examined by using a radioimmunoassay. Matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13), tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1), and alpha-smooth muscle actin (alpha-SMA) protein in the liver, transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) protein in cytoplasm by using immunohistochemistry and Western blot analysis, and MMP-13, TIMP-1, and TGF-beta1 mRNA levels in the liver were studied using reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction.
RESULTS
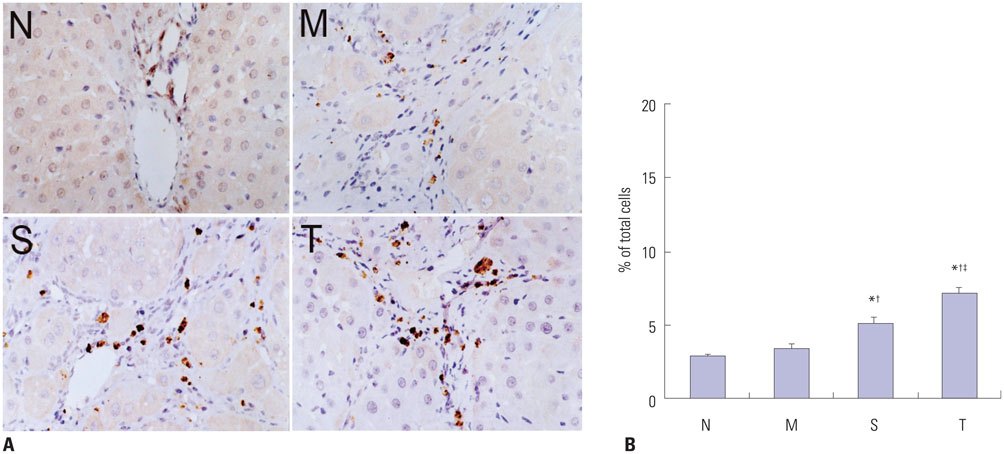
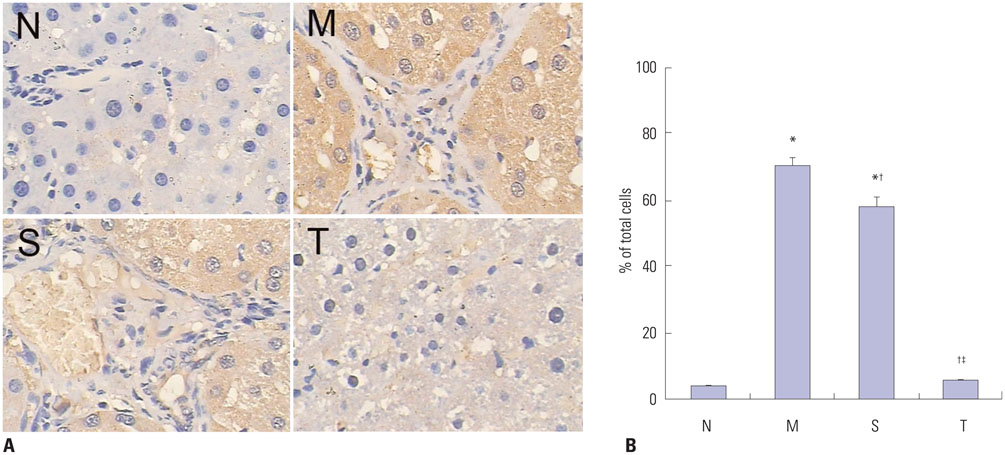
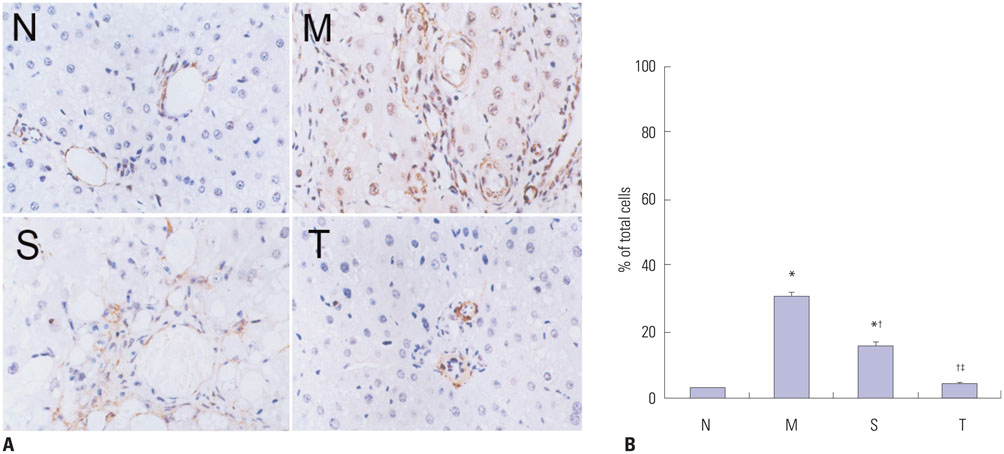
Liver histopathology was significantly better in rats given thalidomide than in the untreated model group. The levels of TIMP-1 and TGF-beta1 mRNA and protein expressions were decreased significantly and MMP-13 mRNA and protein in the liver were significantly elevated in the thalidomide-treated group.
CONCLUSION
Thalidomide may exert its effects on the regulation of MMP-13 and TIMP-1 via inhibition of the TGF-beta1 signaling pathway, which enhances the degradation of extracellular matrix and accelerates the regression of hepatic cirrhosis in rats.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Actins
Animals
Carbon Tetrachloride/toxicity
Collagen Type III/metabolism
Down-Regulation
Extracellular Matrix/metabolism
Immunohistochemistry
Immunosuppressive Agents/*pharmacology
Liver Cirrhosis, Experimental/chemically induced/*metabolism/pathology/*prevention & control
Male
RNA, Messenger/analysis/metabolism
Rats
Rats, Wistar
Thalidomide/*pharmacology
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1/biosynthesis/*drug effects
Transcription Factor RelA/biosynthesis/drug effects
Transforming Growth Factor beta1/biosynthesis/*drug effects
Transforming Growth Factors/metabolism
Actins
Carbon Tetrachloride
Collagen Type III
Immunosuppressive Agents
RNA, Messenger
Thalidomide
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1
Transcription Factor RelA
Transforming Growth Factor beta1
Transforming Growth Factors
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mormone E, George J, Nieto N. Molecular pathogenesis of hepatic fibrosis and current therapeutic approaches. Chem Biol Interact. 2011; 193:225–231.
Article2. Iwaisako K, Brenner DA, Kisseleva T. What's new in liver fibrosis? The origin of myofibroblasts in liver fibrosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 27:Suppl 2. 65–68.
Article3. Rockey DC. Translating an understanding of the pathogenesis of hepatic fibrosis to novel therapies. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 11:224–231.
Article4. Yin C, Evason KJ, Asahina K, Stainier DY. Hepatic stellate cells in liver development, regeneration, and cancer. J Clin Invest. 2013; 123:1902–1910.
Article5. Kisseleva T, Brenner DA. Hepatic stellate cells and the reversal of fibrosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006; 21:Suppl 3. S84–S87.
Article6. Ramachandran P, Iredale JP. Liver fibrosis: a bidirectional model of fibrogenesis and resolution. QJM. 2012; 105:813–817.
Article7. Yata Y, Takahara T, Furui K, Zhang LP, Watanabe A. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-13 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in acute liver injury. J Hepatol. 1999; 30:419–424.
Article8. Watanabe T, Niioka M, Hozawa S, Kameyama K, Hayashi T, Arai M, et al. Gene expression of interstitial collagenase in both progressive and recovery phase of rat liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride. J Hepatol. 2000; 33:224–235.
Article9. Schaefer B, Rivas-Estilla AM, Meraz-Cruz N, Reyes-Romero MA, Hernández-Nazara ZH, DomÍnguez-Rosales JA, et al. Reciprocal modulation of matrix metalloproteinase-13 and type I collagen genes in rat hepatic stellate cells. Am J Pathol. 2003; 162:1771–1780.
Article10. Hemmann S, Graf J, Roderfeld M, Roeb E. Expression of MMPs and TIMPs in liver fibrosis - a systematic review with special emphasis on anti-fibrotic strategies. J Hepatol. 2007; 46:955–975.
Article11. Klironomos S, Notas G, Sfakianaki O, Kiagiadaki F, Xidakis C, Kouroumalis E. Octreotide modulates the effects on fibrosis of TNF-α, TGF-β and PDGF in activated rat hepatic stellate cells. Regul Pept. 2014; 188:5–12.
Article12. Sun X, He Y, Ma TT, Huang C, Zhang L, Li J. Participation of miR-200a in TGF-β1-mediated hepatic stellate cell activation. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014; 388:11–23.
Article13. Knittel T, Mehde M, Kobold D, Saile B, Dinter C, Ramadori G. Expression patterns of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells of rat liver: regulation by TNF-alpha and TGF-beta1. J Hepatol. 1999; 30:48–60.
Article14. Lechuga CG, Hernández-Nazara ZH, Domínguez Rosales JA, Morris ER, Rincón AR, Rivas-Estilla AM, et al. TGF-beta1 modulates matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in hepatic stellate cells by complex mechanisms involving p38MAPK, PI3-kinase, AKT, and p70S6k. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004; 287:G974–G987.15. Prakobwong S, Pinlaor S, Yongvanit P, Sithithaworn P, Pairojkul C, Hiraku Y. Time profiles of the expression of metalloproteinases, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteases, cytokines and collagens in hamsters infected with Opisthorchis viverrini with special reference to peribiliary fibrosis and liver injury. Int J Parasitol. 2009; 39:825–835.
Article16. Singh MK, Bhattacharya D, Chaudhuri S, Acharya S, Kumar P, Santra P, et al. T11TS inhibits glioma angiogenesis by modulation of MMPs, TIMPs, with related integrin αv and TGF-β1 expressions. Tumour Biol. 2014; 35:2231–2246.
Article17. De Sanctis JB, Mijares M, Suárez A, Compagnone R, Garmendia J, Moreno D, et al. Pharmacological properties of thalidomide and its analogues. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2010; 4:144–148.
Article18. Kumar V, Chhibber S. Thalidomide: an old drug with new action. J Chemother. 2011; 23:326–334.
Article19. Kumar N, Sharma U, Singh C, Singh B. Thalidomide: chemistry, therapeutic potential and oxidative stress induced teratogenicity. Curr Top Med Chem. 2012; 12:1436–1455.
Article20. Muriel P, Fernández-Martínez E, Pérez-Alvarez V, Lara-Ochoa F, Ponce S, García J, et al. Thalidomide ameliorates carbon tetrachloride induced cirrhosis in the rat. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003; 15:951–957.
Article21. Yang YY, Huang YT, Lin HC, Lee FY, Lee KC, Chau GY, et al. Thalidomide decreases intrahepatic resistance in cirrhotic rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009; 380:666–672.
Article22. Desmet VJ, Gerber M, Hoofnagle JH, Manns M, Scheuer PJ. Classification of chronic hepatitis: diagnosis, grading and staging. Hepatology. 1994; 19:1513–1520.
Article23. Chao YC, Nylander-French LA. Determination of keratin protein in a tape-stripped skin sample from jet fuel exposed skin. Ann Occup Hyg. 2004; 48:65–73.24. Lee UE, Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2011; 25:195–206.
Article25. Ahmad A, Ahmad R. Understanding the mechanism of hepatic fibrosis and potential therapeutic approaches. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18:155–167.
Article26. Inagaki Y, Higashiyama R, Higashi K. Novel anti-fibrotic modalities for liver fibrosis: molecular targeting and regenerative medicine in fibrosis therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 27:Suppl 2. 85–88.
Article27. Enomoto N, Takei Y, Hirose M, Ikejima K, Miwa H, Kitamura T, et al. Thalidomide prevents alcoholic liver injury in rats through suppression of Kupffer cell sensitization and TNF-alpha production. Gastroenterology. 2002; 123:291–300.
Article28. Hung KC, Hsieh PM, Yang KL, Lin KJ, Chen YS, Hung CH. Effect of thalidomide on the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in a rat model of liver regeneration. Oncol Lett. 2013; 5:852–856.
Article29. Nunes de Carvalho S, Helal-Neto E, de Andrade DC, Costa Cortez EA, Thole AA, Barja-Fidalgo C, et al. Bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation increases metalloproteinase-9 and 13 and decreases tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase-1 and 2 expression in the liver of cholestatic rats. Cells Tissues Organs. 2013; 198:139–148.
Article30. Endo H, Niioka M, Sugioka Y, Itoh J, Kameyama K, Okazaki I, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-13 promotes recovery from experimental liver cirrhosis in rats. Pathobiology. 2011; 78:239–252.
Article31. Arthur MJ. Fibrogenesis II. Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in liver fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000; 279:G245–G249.
Article32. Cong M, Liu T, Wang P, Fan X, Yang A, Bai Y, et al. Antifibrotic effects of a recombinant adeno-associated virus carrying small interfering RNA targeting TIMP-1 in rat liver fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 2013; 182:1607–1616.
Article33. Cong M, Liu T, Wang P, Xu Y, Tang S, Wang B, et al. Suppression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 by recombinant adeno-associated viruses carrying siRNAs in hepatic stellate cells. Int J Mol Med. 2009; 24:685–692.
Article34. Peng J, Li X, Feng Q, Chen L, Xu L, Hu Y. Anti-fibrotic effect of Cordyceps sinensis polysaccharide: Inhibiting HSC activation, TGF-β1/Smad signalling, MMPs and TIMPs. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2013; 238:668–677.
Article35. Cong M, Liu T, Wang P, Fan X, Yang A, Bai Y, et al. Antifibrotic effects of a recombinant adeno-associated virus carrying small interfering RNA targeting TIMP-1 in rat liver fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 2013; 182:1607–1616.
Article36. Baghy K, Iozzo RV, Kovalszky I. Decorin-TGFβ axis in hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. J Histochem Cytochem. 2012; 60:262–268.
Article37. Arriola Benitez PC, Scian R, Comerci DJ, Serantes DR, Vanzulli S, Fossati CA, et al. Brucella abortus induces collagen deposition and MMP-9 down-modulation in hepatic stellate cells via TGF-β1 production. Am J Pathol. 2013; 183:1918–1927.
Article38. Lin N, Chen S, Pan W, Xu L, Hu K, Xu R. NP603, a novel and potent inhibitor of FGFR1 tyrosine kinase, inhibits hepatic stellate cell proliferation and ameliorates hepatic fibrosis in rats. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011; 301:C469–C477.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of Transforming Growth Factor-beta1 and Its Effects on the Extracellular Matrix Formation and Angiogenesis in Gastric Carcinoma
- Upregulation of Transforming Growth Factor-beta Receptors in the Rat Remnant Kidney
- Transcriptional Regulation of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation by siRNA for TGF-beta1
- Cellular Distribution of TGF-beta1 Peptide in Dimethylnitrosamine Induced Fibrosis of Rat Liver
- Regulation of the Levels of Trabecular Matrix Metalloproteinase and Inhibitor by Transforming Growth Factor-beta1