Yonsei Med J.
2015 Nov;56(6):1503-1514. 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.6.1503.
Hypoxia Induces Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Follicular Thyroid Cancer: Involvement of Regulation of Twist by Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1alpha
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. strive1005@yuhs.ac, ywkohent@yuhs.ac
- 2Brain Korea 21 PLUS Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2345876
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.6.1503
Abstract
- PURPOSE
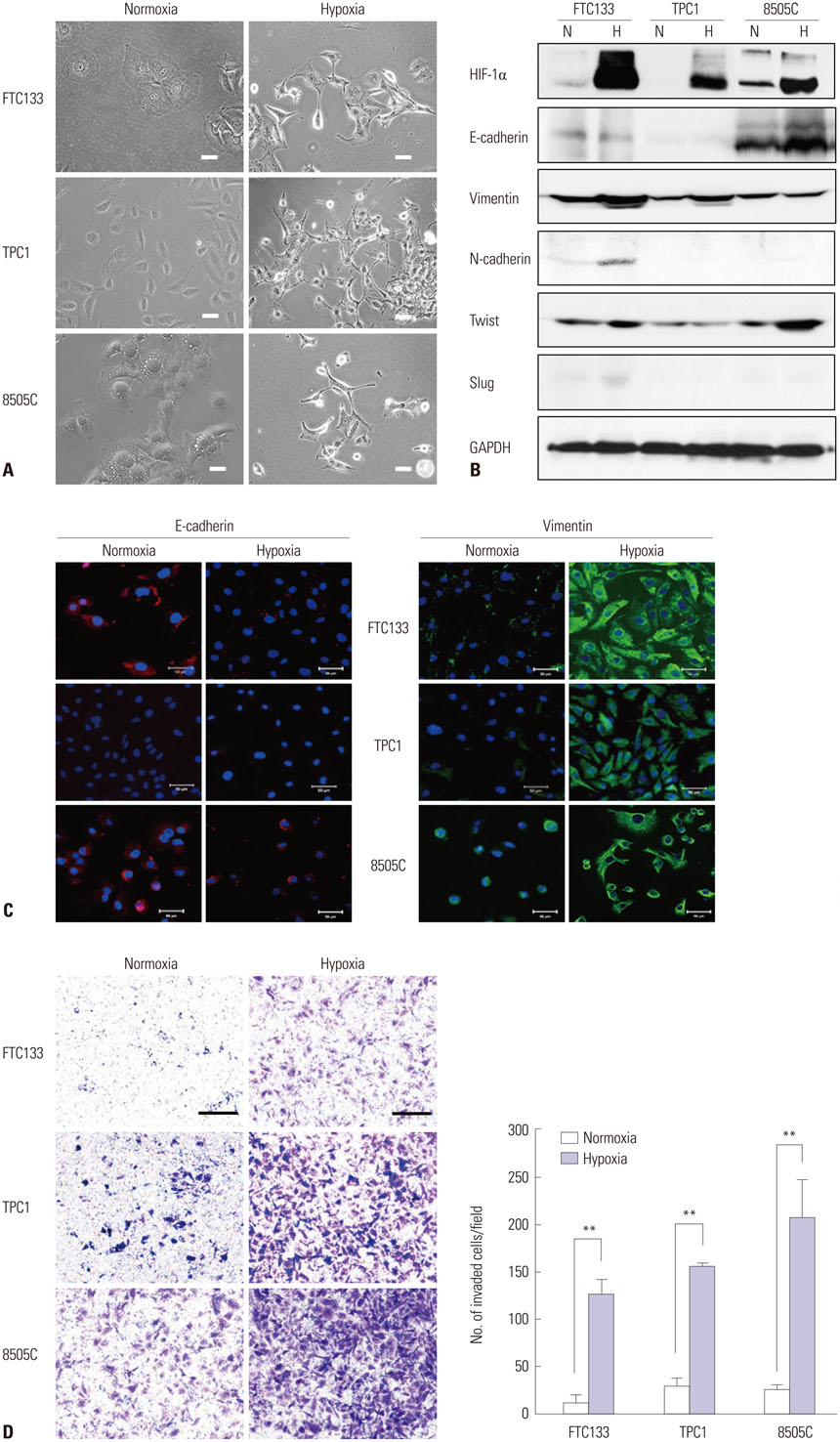
Although follicular thyroid cancer (FTC) has a relatively fair prognosis, distant metastasis sometimes results in poor prognosis and survival. There is little understanding of the mechanisms contributing to the aggressiveness potential of thyroid cancer. We showed that hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) induced aggressiveness in FTC cells and identified the underlying mechanism of the HIF-1alpha-induced invasive characteristics.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
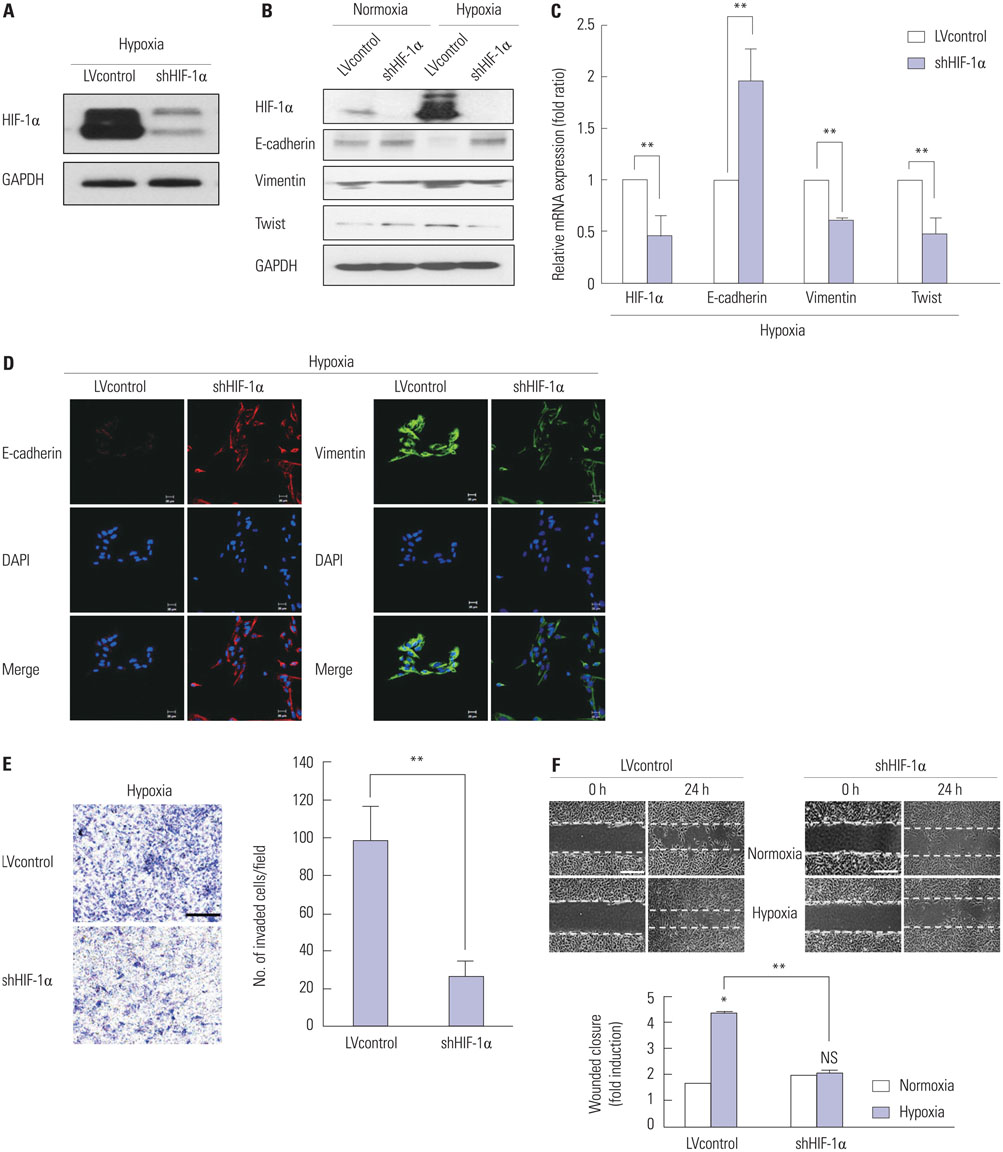
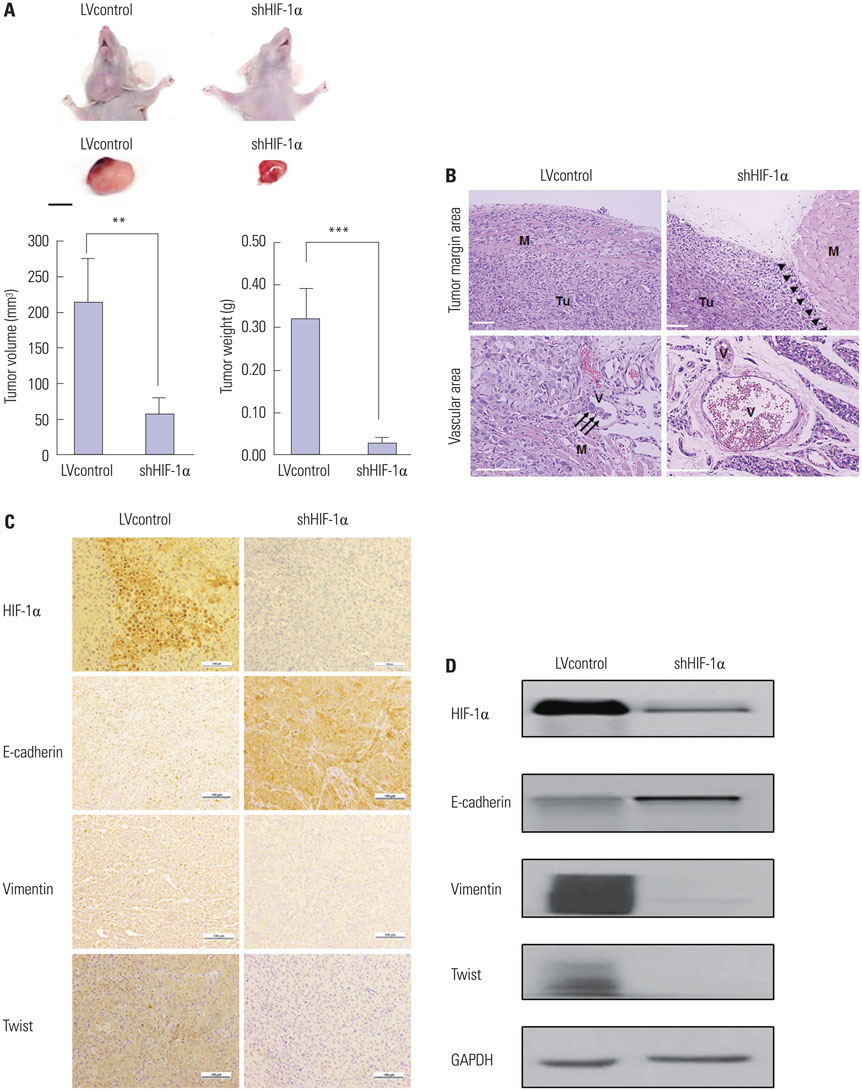
Cells were cultured under controlled hypoxic environments (1% O2) or normoxic conditions. The effect of hypoxia on HIF-1alpha, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) related markers were evaluated by quantitative real-time PCR, Western blot analysis and immunocytochemistry. Invasion and wound healing assay were conducted to identify functional character of EMT. The involvement of HIF-1alpha and Twist in EMT were studied using gene overexpression or silencing. After orthotopic nude mouse model was established using the cells transfected with lentiviral shHIF-1alpha, tissue analysis was done.
RESULTS
Hypoxia induces HIF-1alpha expression and EMT, including typical morphologic changes, cadherin shift, and increased vimentin expression. We showed that overexpression of HIF-1alpha via transfection resulted in the aforementioned changes without hypoxia, and repression of HIF-1alpha with RNA interference suppressed hypoxia-induced HIF-1alpha and EMT. Furthermore, we also observed that Twist expression was regulated by HIF-1alpha. These were confirmed in the orthotopic FTC model.
CONCLUSION
Hypoxia induced HIF-1alpha, which in turn induced EMT, resulting in the increased capacity for invasion and migration of cells via regulation of the Twist signal pathway in FTC cells. These findings provide insight into a possible therapeutic strategy to prevent invasive and metastatic FTC.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adenocarcinoma, Follicular/*genetics/metabolism
Animals
Anoxia/*genetics
Cadherins/genetics
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition/*genetics
Gene Expression Regulation, Neoplastic
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1, alpha Subunit/*genetics/metabolism
Lymphokines
Mice
Neoplasm Invasiveness
Phenotype
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
Signal Transduction/drug effects
Thyroid Neoplasms/*genetics/metabolism
Transcriptional Activation
Twist Transcription Factor/*genetics/metabolism
Vimentin/metabolism
Cadherins
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1, alpha Subunit
Lymphokines
Twist Transcription Factor
Vimentin
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Development of Inhibitors Targeting Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 and 2 for Cancer Therapy
Tianchi Yu, Bo Tang, Xueying Sun
Yonsei Med J. 2017;58(3):489-496. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.3.489.
Reference
-
1. Phay JE, Ringel MD. Metastatic mechanisms in follicular cell-derived thyroid cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2013; 20:R307–R319.
Article2. Carling T, Udelsman R. Thyroid cancer. Annu Rev Med. 2014; 65:125–137.
Article3. Chang JW, Kang SU, Shin YS, Kim KI, Seo SJ, Yang SS, et al. Non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma inhibits thyroid papillary cancer cell invasion via cytoskeletal modulation, altered MMP-2/-9/uPA activity. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e92198.
Article4. Rahmani N, Abbas Hashemi S, Fazli M, Raisian M. Clinical management and outcomes of papillary, follicular and medullary thyroid cancer surgery. Med Glas (Zenica). 2013; 10:164–167.5. Zhao JH, Luo Y, Jiang YG, He DL, Wu CT. Knockdown of β-Catenin through shRNA cause a reversal of EMT and metastatic phenotypes induced by HIF-1α. Cancer Invest. 2011; 29:377–382.
Article6. Xiao W, Jiang M, Li H, Li C, Su R, Huang K. Knockdown of FAK inhibits the invasion and metastasis of Tca8113 cells in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2013; 8:703–707.
Article7. Marie-Egyptienne DT, Lohse I, Hill RP. Cancer stem cells, the epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) and radioresistance: potential role of hypoxia. Cancer Lett. 2013; 341:63–72.
Article8. De Craene B, Berx G. Regulatory networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013; 13:97–110.
Article9. Cavallaro U, Christofori G. Cell adhesion and signalling by cadherins and Ig-CAMs in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004; 4:118–132.
Article10. Burrows N, Resch J, Cowen RL, von Wasielewski R, Hoang-Vu C, West CM, et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in thyroid carcinomas. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2010; 17:61–72.11. Kim DH, Hossain MA, Kim MY, Kim JA, Yoon JH, Suh HS, et al. A novel resveratrol analogue, HS-1793, inhibits hypoxia-induced HIF-1α and VEGF expression, and migration in human prostate cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2013; 43:1915–1924.
Article12. Melstrom LG, Salabat MR, Ding XZ, Strouch MJ, Grippo PJ, Mirzoeva S, et al. Apigenin down-regulates the hypoxia response genes: HIF-1α, GLUT-1, and VEGF in human pancreatic cancer cells. J Surg Res. 2011; 167:173–181.
Article13. Kockar F, Yildrim H, Sagkan RI, Hagemann C, Soysal Y, Anacker J, et al. Hypoxia and cytokines regulate carbonic anhydrase 9 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro. World J Clin Oncol. 2012; 3:82–91.
Article14. Sendoel A, Kohler I, Fellmann C, Lowe SW, Hengartner MO. HIF-1 antagonizes p53-mediated apoptosis through a secreted neuronal tyrosinase. Nature. 2010; 465:577–583.
Article15. Culver C, Melvin A, Mudie S, Rocha S. HIF-1α depletion results in SP1-mediated cell cycle disruption and alters the cellular response to chemotherapeutic drugs. Cell Cycle. 2011; 10:1249–1260.
Article16. Burrows N, Babur M, Resch J, Williams KJ, Brabant G. Hypoxia-inducible factor in thyroid carcinoma. J Thyroid Res. 2011; 2011:762905.
Article17. Li H, Liang CZ, Chen QX. Regulatory role of hypoxia inducible factor in the biological behavior of nucleus pulposus cells. Yonsei Med J. 2013; 54:807–812.
Article18. Semenza GL. HIF-1: upstream and downstream of cancer metabolism. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2010; 20:51–56.
Article19. Semenza GL. Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003; 3:721–732.
Article20. Warfel NA, El-Deiry WS. HIF-1 signaling in drug resistance to chemotherapy. Curr Med Chem. 2014; 21:3021–3028.
Article21. Zerilli M, Zito G, Martorana A, Pitrone M, Cabibi D, Cappello F, et al. BRAF(V600E) mutation influences hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression levels in papillary thyroid cancer. Mod Pathol. 2010; 23:1052–1060.
Article22. Kim CH, Kwon S, Bahn JH, Lee K, Jun SI, Rack PD, et al. Effects of atmospheric nonthermal plasma on invasion of colorectal cancer cells. Appl Phys Lett. 2010; 96:243701.
Article23. Chang JW, Kang SU, Choi JW, Shin YS, Baek SJ, Lee SH, et al. Tolfenamic acid induces apoptosis and growth inhibition in anaplastic thyroid cancer: involvement of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene-1 expression and intracellular reactive oxygen species generation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014; 67:115–130.
Article24. Yang J, Mani SA, Donaher JL, Ramaswamy S, Itzykson RA, Come C, et al. Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell. 2004; 117:927–939.
Article25. Carpenter RL, Paw I, Dewhirst MW, Lo HW. Akt phosphorylates and activates HSF-1 independent of heat shock, leading to Slug overexpression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2015; 34:546–557.
Article26. Chen L, Shi Y, Yuan J, Han Y, Qin R, Wu Q, et al. HIF-1 alpha overexpression correlates with poor overall survival and disease-free survival in gastric cancer patients post-gastrectomy. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e90678.
Article27. Friday BB, Adjei AA. Advances in targeting the Ras/Raf/MEK/Erk mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade with MEK inhibitors for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2008; 14:342–346.
Article28. Vasko V, Ferrand M, Di Cristofaro J, Carayon P, Henry JF, de Micco C. Specific pattern of RAS oncogene mutations in follicular thyroid tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003; 88:2745–2752.
Article29. Nikiforova MN, Lynch RA, Biddinger PW, Alexander EK, Dorn GW 2nd, Tallini G, et al. RAS point mutations and PAX8-PPAR gamma rearrangement in thyroid tumors: evidence for distinct molecular pathways in thyroid follicular carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003; 88:2318–2326.
Article30. Burrows N, Babur M, Resch J, Ridsdale S, Mejin M, Rowling EJ, et al. GDC-0941 inhibits metastatic characteristics of thyroid carcinomas by targeting both the phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K) and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) pathways. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011; 96:E1934–E1943.
Article31. Sandrini F, Matyakhina L, Sarlis NJ, Kirschner LS, Farmakidis C, Gimm O, et al. Regulatory subunit type I-alpha of protein kinase A (PRKAR1A): a tumor-suppressor gene for sporadic thyroid cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2002; 35:182–192.
Article32. Jubb AM, Pham TQ, Hanby AM, Frantz GD, Peale FV, Wu TD, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor, hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha, and carbonic anhydrase IX in human tumours. J Clin Pathol. 2004; 57:504–512.
Article33. Zundel W, Schindler C, Haas-Kogan D, Koong A, Kaper F, Chen E, et al. Loss of PTEN facilitates HIF-1-mediated gene expression. Genes Dev. 2000; 14:391–396.34. Maxwell PJ, Coulter J, Walker SM, McKechnie M, Neisen J, McCabe N, et al. Potentiation of inflammatory CXCL8 signalling sustains cell survival in PTEN-deficient prostate carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2013; 64:177–188.
Article35. Franco-Chuaire ML, Magda Carolina SC, Chuaire-Noack L. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT): principles and clinical impact in cancer therapy. Invest Clin. 2013; 54:186–205.36. Gravdal K, Halvorsen OJ, Haukaas SA, Akslen LA. A switch from E-cadherin to N-cadherin expression indicates epithelial to mesenchymal transition and is of strong and independent importance for the progress of prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13:7003–7011.
Article37. Fan M, Liu Y, Xia F, Wang Z, Huang Y, Li J, et al. Increased expression of EphA2 and E-N cadherin switch in primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumori. 2013; 99:689–696.
Article38. Cano A, Pérez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I, Locascio A, Blanco MJ, del Barrio MG, et al. The transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol. 2000; 2:76–83.
Article39. Hajra KM, Chen DY, Fearon ER. The SLUG zinc-finger protein represses E-cadherin in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2002; 62:1613–1618.40. Grooteclaes ML, Frisch SM. Evidence for a function of CtBP in epithelial gene regulation and anoikis. Oncogene. 2000; 19:3823–3828.
Article41. Comijn J, Berx G, Vermassen P, Verschueren K, van Grunsven L, Bruyneel E, et al. The two-handed E box binding zinc finger protein SIP1 downregulates E-cadherin and induces invasion. Mol Cell. 2001; 7:1267–1278.
Article42. Perez-Moreno MA, Locascio A, Rodrigo I, Dhondt G, Portillo F, Nieto MA, et al. A new role for E12/E47 in the repression of E-cadherin expression and epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:27424–27431.43. Yang MH, Wu KJ. TWIST activation by hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1): implications in metastasis and development. Cell Cycle. 2008; 7:2090–2096.
Article44. Khan MA, Chen HC, Zhang D, Fu J. Twist: a molecular target in cancer therapeutics. Tumour Biol. 2013; 34:2497–2506.
Article45. Yang MH, Wu MZ, Chiou SH, Chen PM, Chang SY, Liu CJ, et al. Direct regulation of TWIST by HIF-1alpha promotes metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 2008; 10:295–305.
Article46. Stoletov K, Kato H, Zardouzian E, Kelber J, Yang J, Shattil S, et al. Visualizing extravasation dynamics of metastatic tumor cells. J Cell Sci. 2010; 123(Pt 13):2332–2341.
Article47. Eckert MA, Yang J. Targeting invadopodia to block breast cancer metastasis. Oncotarget. 2011; 2:562–568.
Article48. Hung JJ, Yang MH, Hsu HS, Hsu WH, Liu JS, Wu KJ. Prognostic significance of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, TWIST1 and Snail expression in resectable non-small cell lung cancer. Thorax. 2009; 64:1082–1089.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Relationship between the Endogenous Hypoxic Markers Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1alpha, Carbonic Anhydrase IX, and Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition Regulator TWIST Expression in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- The Role of TWIST in Ovarian Epithelial Cancers
- Wheatgrass extract inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in A549 cells
- The role of hypoxia on the acquisition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stemness: a possible link to epigenetic regulation
- Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1alpha Directly Induces the Expression of Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-kappaB Ligand in MLO-Y4 Osteocytes