J Pathol Transl Med.
2016 Jul;50(4):251-257. 10.4132/jptm.2016.03.30.
Aquaporin 1 Is an Independent Marker of Poor Prognosis in Lung Adenocarcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. chungjh@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China.
- 4Department of Pathology, Fudan University, Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China.
- 5Department of Pathology, Kangwon National University Hospital, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2345546
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.03.30
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Aquaporin 1 (AQP1) overexpression has been shown to be associated with uncontrolled cell replication, invasion, migration, and tumor metastasis. We aimed to evaluate AQP1 expression in lung adenocarcinomas and to examine its association with clinicopathological features and prognostic significance. We also investigated the association between AQP1 overexpression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers.
METHODS
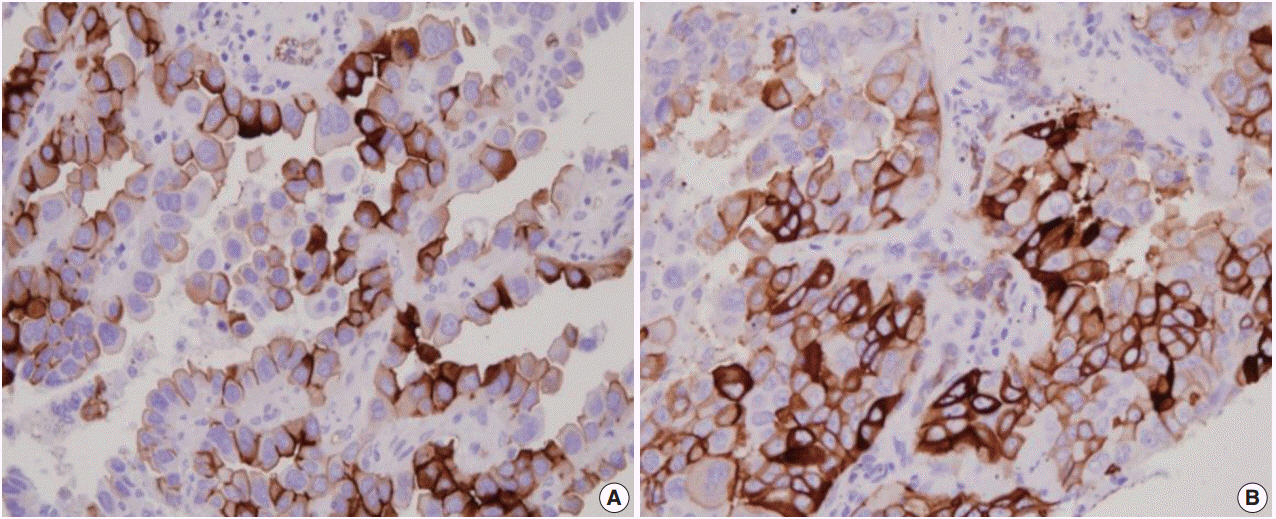
We examined AQP1 expression in 505 cases of surgically resected lung adenocarcinomas acquired at the Seoul National University Bundang Hospital from 2003 to 2012. Expression of AQP1 and EMT-related markers, including Ecadherin and vimentin, were analyzed by immunohistochemistry and tissue microarray.
RESULTS
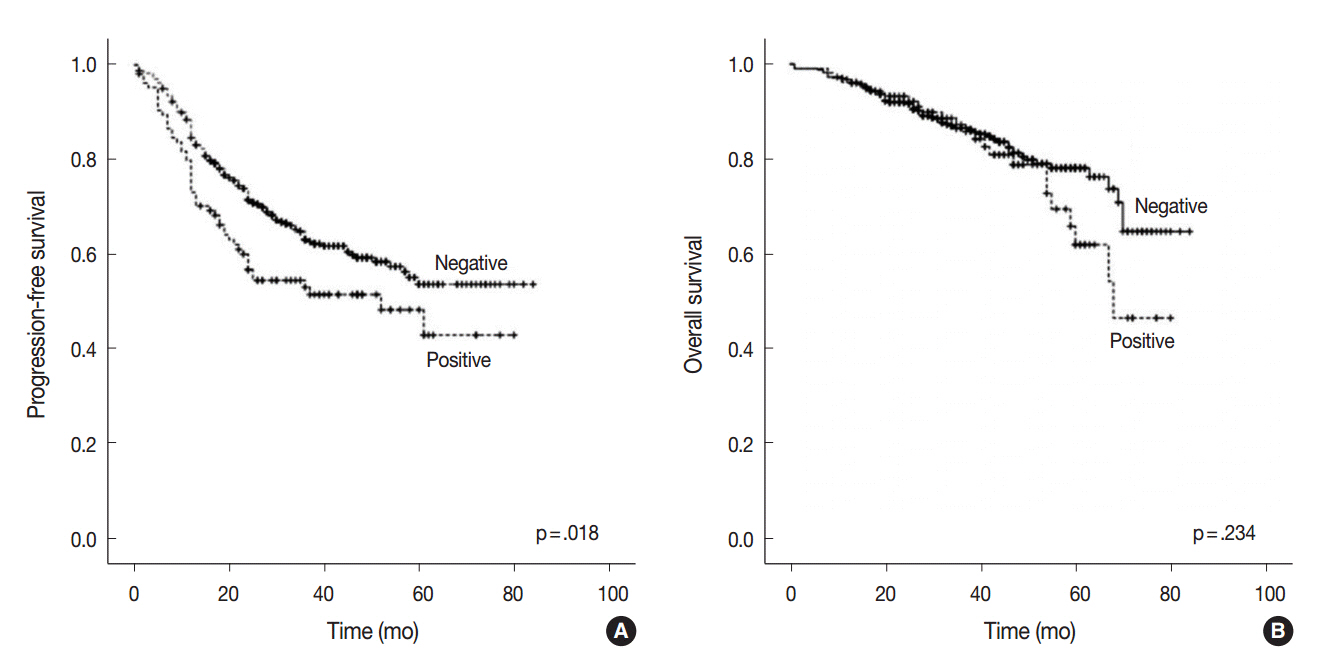
AQP1 overexpression was associated with several aggressive pathological parameters, including venous invasion, lymphatic invasion, and tumor recurrence. AQP1 overexpression tended to be associated with higher histological grade, advanced pathological stage, and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) translocation; however, these differences were not statistically significant. In addition, AQP1 overexpression positively correlated with loss of E-cadherin expression and acquired expression of vimentin. Lung adenocarcinoma patients with AQP1 overexpression showed shorter progression-free survival (PFS, 46.1 months vs. 56.2 months) compared to patients without AQP1 overexpression. Multivariate analysis confirmed that AQP1 overexpression was significantly associated with shorter PFS (hazard ratio, 1.429; 95% confidence interval, 1.033 to 1.977; p=.031).
CONCLUSIONS
AQP1 overexpression was thereby concluded to be an independent factor of poor prognosis associated with shorter PFS in lung adenocarcinoma. These results suggested that AQP1 overexpression might be considered as a prognostic biomarker of lung adenocarcinoma.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim JE, Kim H, Choe JY, Sun P, Jheon S, Chung JH. High expression of Sonic hedgehog signaling proteins is related to the favorable outcome, EGFR mutation, and lepidic predominant subtype in primary lung adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013; 20 Suppl 3:S570–6.2. Seo AN, Yang JM, Kim H, et al. Clinicopathologic and prognostic significance of c-MYC copy number gain in lung adenocarcinomas. Br J Cancer. 2014; 110:2688–99.
Article3. Pao W, Girard N. New driver mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2011; 12:175–80.
Article4. Cuddapah VA, Sontheimer H. Ion channels and transporters [corrected] in cancer. 2. Ion channels and the control of cancer cell migration. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011; 301:C541–9.5. Verkman AS. More than just water channels: unexpected cellular roles of aquaporins. J Cell Sci. 2005; 118(Pt 15):3225–32.
Article6. Wang J, Feng L, Zhu Z, et al. Aquaporins as diagnostic and therapeutic targets in cancer: how far we are? J Transl Med. 2015; 13:96.
Article7. Nico B, Ribatti D. Aquaporins in tumor growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2010; 294:135–8.
Article8. Hoque MO, Soria JC, Woo J, et al. Aquaporin 1 is overexpressed in lung cancer and stimulates NIH-3T3 cell proliferation and anchorage-independent growth. Am J Pathol. 2006; 168:1345–53.
Article9. López-Campos JL, Sánchez Silva R, Gómez Izquierdo L, et al. Overexpression of aquaporin-1 in lung adenocarcinomas and pleural mesotheliomas. Histol Histopathol. 2011; 26:451–9.10. Machida Y, Ueda Y, Shimasaki M, et al. Relationship of aquaporin 1, 3, and 5 expression in lung cancer cells to cellular differentiation, invasive growth, and metastasis potential. Hum Pathol. 2011; 42:669–78.
Article11. Xie Y, Wen X, Jiang Z, Fu HQ, Han H, Dai L. Aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 4 are involved in invasion of lung cancer cells. Clin Lab. 2012; 58:75–80.12. Wei X, Dong J. Aquaporin 1 promotes the proliferation and migration of lung cancer cell in vitro. Oncol Rep. 2015; 34:1440–8.13. Sato M, Shames DS, Hasegawa Y. Emerging evidence of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in lung carcinogenesis. Respirology. 2012; 17:1048–59.
Article14. Kase S, Sugio K, Yamazaki K, Okamoto T, Yano T, Sugimachi K. Expression of E-cadherin and beta-catenin in human non-small cell lung cancer and the clinical significance. Clin Cancer Res. 2000; 6:4789–96.15. Shi Y, Wu H, Zhang M, Ding L, Meng F, Fan X. Expression of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related proteins and their clinical significance in lung adenocarcinoma. Diagn Pathol. 2013; 8:89.
Article16. Yoshida T, Hojo S, Sekine S, et al. Expression of aquaporin-1 is a poor prognostic factor for stage II and III colon cancer. Mol Clin Oncol. 2013; 1:953–8.
Article17. Jiang Y. Aquaporin-1 activity of plasma membrane affects HT20 colon cancer cell migration. IUBMB Life. 2009; 61:1001–9.
Article18. Yin T, Yu S, Xiao L, Zhang J, Liu C, Lu Y. Correlation between the expression of aquaporin 1 and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in breast cancer tissues. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2008; 28:346–8.
Article19. Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M, et al. International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 2011; 6:244–85.20. Travis WD, Brambilla E, Burke AP, Marx A, Nicholson AG. WHO classification of tumours of the lung, pleura, thymus and heart. Lyon: IARC Press;2015.21. Li XQ, Yang XL, Zhang G, et al. Nuclear beta-catenin accumulation is associated with increased expression of Nanog protein and predicts poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. J Transl Med. 2013; 11:114.
Article22. Kim H, Yoo SB, Sun P, et al. Alteration of the E-cadherin/beta-catenin complex is an independent poor prognostic factor in lung adenocarcinoma. Korean J Pathol. 2013; 47:44–51.23. Chung JH, Choe G, Jheon S, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation and pathologic-radiologic correlation between multiple lung nodules with ground-glass opacity differentiates multicentric origin from intrapulmonary spread. J Thorac Oncol. 2009; 4:1490–5.
Article24. Deb P, Pal S, Dutta V, Boruah D, Chandran VM, Bhatoe HS. Correlation of expression pattern of aquaporin-1 in primary central nervous system tumors with tumor type, grade, proliferation, microvessel density, contrast-enhancement and perilesional edema. J Cancer Res Ther. 2012; 8:571–7.
Article25. Bartis D, Mise N, Mahida RY, Eickelberg O, Thickett DR. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung development and disease: does it exist and is it important? Thorax. 2014; 69:760–5.
Article26. Monzani E, Bazzotti R, Perego C, La Porta CA. AQP1 is not only a water channel: it contributes to cell migration through Lin7/beta-catenin. PLoS One. 2009; 4:e6167.
Article27. Hu J, Verkman AS. Increased migration and metastatic potential of tumor cells expressing aquaporin water channels. FASEB J. 2006; 20:1892–4.
Article28. Johnson MD, O’Connell M. Na-K-2Cl cotransporter and aquaporin 1 in arachnoid granulations, meningiomas, and meningiomas invading dura. Hum Pathol. 2013; 44:1118–24.
Article29. Oshio K, Binder DK, Liang Y, et al. Expression of the aquaporin-1 water channel in human glial tumors. Neurosurgery. 2005; 56:375–81.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Eyeball Metastasis of Lung Adenocarcinoma Confirmed by Enucleation
- Human Leukocyte Antigen Class I and Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Coexpression Is an Independent Poor Prognostic Factor in Adenocarcinoma of the Lung
- p40 Immunohistochemistry Is an Excellent Marker in Primary Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- An Adenocarcinoma of Lung with Unusual Very Slow Growth : A case report
- Prognostic Significance of Cigarette Smoking in Association with Histologic Subtypes of Resected Lung Adenocarcinoma