J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2012 Sep;52(3):193-199.
Incidence and Risk Factors for Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis in Breast Cancer Patients with Parenchymal Brain Metastases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Cancer Biostatistics Branch, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- 4Neuro-Oncology Clinic, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea. nsghs@ncc.re.kr
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The objective of study is to evaluate the incidence of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis (LMC) in breast cancer patients with parenchymal brain metastases (PBM) and clinical risk factors for the development of LMC.
METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed 27 patients who had undergone surgical resection (SR) and 156 patients with whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) as an initial treatment for their PBM from breast cancer in our institution and compared the difference of incidence of LMC according to clinical factors. The diagnosis of LMC was made by cerebrospinal fluid cytology and/or magnetic resonance imaging.
RESULTS
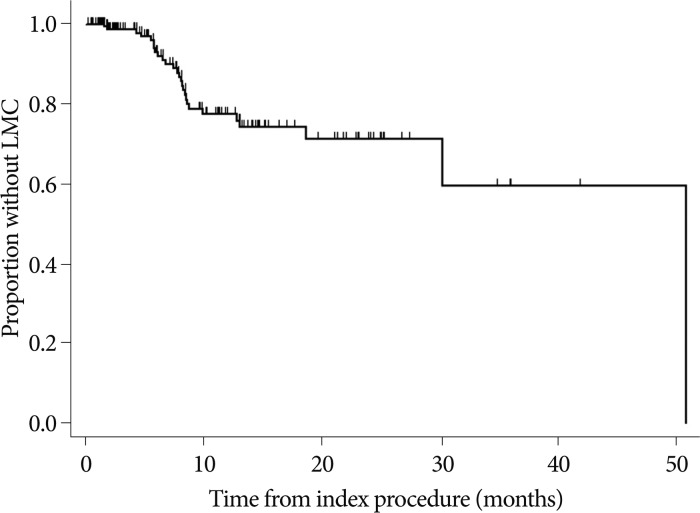
A total of 27 patients (14%) in the study population developed LMC at a median of 6.0 months (range, 1.0-50). Ten of 27 patients (37%) developed LMC after SR, whereas 17 of 156 (11%) patients who received WBRT were diagnosed with LMC after the index procedure. The incidence of LMC was significantly higher in the SR group compared with the WBRT group and the hazard ratio was 2.95 (95% confidence interval; 1.33-6.54, p<0.01). Three additional factors were identified in the multivariable analysis : the younger age group (<40 years old), the progressing systemic disease showed significantly increased incidence of LMC, whereas the adjuvant chemotherapy reduce the incidence.
CONCLUSION
There is an increased risk of LMC after SR for PBM from breast cancer compared with WBRT. The young age (<40) and systemic burden of cancer in terms of progressing systemic disease without adjuvant chemotherapy could be additional risk factors for the development of LMC.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ahn JH, Lee SH, Kim S, Joo J, Yoo H, Lee SH, et al. Risk for leptomeningeal seeding after resection for brain metastases : implication of tumor location with mode of resection. J Neurosurg. 2012; 116:984–993. PMID: 22339161.
Article2. Bae JS, Yang SH, Yoon WS, Kang SG, Hong YK, Jeun SS. The clinical features of spinal leptomeningeal dissemination from malignant gliomas. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2011; 49:334–338. PMID: 21887390.
Article3. Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Sloan AE, Davis FG, Vigneau FD, Lai P, Sawaya RE. Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:2865–2872. PMID: 15254054.
Article4. Beadle BM, Woodward WA, Buchholz TA. The impact of age on outcome in early-stage breast cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2011; 21:26–34. PMID: 21134651.
Article5. Chamberlain MC. Leptomeningeal metastasis. Curr Opin Oncol. 2010; 22:627–635. PMID: 20689429.
Article6. Cheng X, Hung MC. Breast cancer brain metastases. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007; 26:635–643. PMID: 17717635.
Article7. Collins LC, Marotti JD, Gelber S, Cole K, Ruddy K, Kereakoglow S, et al. Pathologic features and molecular phenotype by patient age in a large cohort of young women with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012; 131:1061–1066. PMID: 22080245.
Article8. DeAngelis LM. Current diagnosis and treatment of leptomeningeal metastasis. J Neurooncol. 1998; 38:245–252. PMID: 9696379.9. DeAngelis LM, Mandell LR, Thaler HT, Kimmel DW, Galicich JH, Fuks Z, et al. The role of postoperative radiotherapy after resection of single brain metastases. Neurosurgery. 1989; 24:798–805. PMID: 2473409.
Article10. Dosoretz DE, Blitzer PH, Russell AH, Wang CC. Management of solitary metastasis to the brain : the role of elective brain irradiation following complete surgical resection. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1980; 6:1727–1730. PMID: 7239992.
Article11. Fortner JG. Inadvertent spread of cancer at surgery. J Surg Oncol. 1993; 53:191–196. PMID: 8331942.
Article12. Fox BD, Cheung VJ, Patel AJ, Suki D, Rao G. Epidemiology of metastatic brain tumors. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2011; 22:1–6. vPMID: 21109143.
Article13. Freilich RJ, Krol G, DeAngelis LM. Neuroimaging and cerebrospinal fluid cytology in the diagnosis of leptomeningeal metastasis. Ann Neurol. 1995; 38:51–57. PMID: 7611725.
Article14. Gauthier H, Guilhaume MN, Bidard FC, Pierga JY, Girre V, Cottu PH, et al. Survival of breast cancer patients with meningeal carcinomatosis. Ann Oncol. 2010; 21:2183–2187. PMID: 20430906.
Article15. Glass JP, Melamed M, Chernik NL, Posner JB. Malignant cells in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) : the meaning of a positive CSF cytology. Neurology. 1979; 29:1369–1375. PMID: 573381.
Article16. Grabb PA, Albright AL, Pang D. Dissemination of supratentorial malignant gliomas via the cerebrospinal fluid in children. Neurosurgery. 1992; 30:64–71. PMID: 1738457.
Article17. Kim HJ, Im SA, Keam B, Kim YJ, Han SW, Kim TM, et al. Clinical outcome of central nervous system metastases from breast cancer : differences in survival depending on systemic treatment. J Neurooncol. 2012; 106:303–313. PMID: 21938531.
Article18. Lee S, Ahn HK, Park YH, Nam do H, Lee JI, Park W, et al. Leptomeningeal metastases from breast cancer : intrinsic subtypes may affect unique clinical manifestations. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011; 129:809–817. PMID: 21785952.
Article19. Lin NU, Claus E, Sohl J, Razzak AR, Arnaout A, Winer EP. Sites of distant recurrence and clinical outcomes in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer : high incidence of central nervous system metastases. Cancer. 2008; 113:2638–2645. PMID: 18833576.
Article20. Lin NU, Winer EP. Brain metastases : the HER2 paradigm. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13:1648–1655. PMID: 17363517.21. Mahajan A, Borden J, Tsai JS. Carcinomatous meningitis : are surgeryand gamma knife radiosurgery treatment risk factors? J Neurosurg. 2002; 97:441–444. PMID: 12507072.
Article22. Mayo WJ. Grafting and traumatic dissemination of carcinoma in the course of operations for malignant disease. JAMA. 1913; 60:512–513.
Article23. Mirimanoff RO, Choi NC. Intradural spinal metastases in patients with posterior fossa brain metastases from various primary cancers. Oncology. 1987; 44:232–236. PMID: 3039433.
Article24. Mirimanoff RO, Choi NC. The risk of intradural spinal metastases in patients with brain metastases from bronchogenic carcinomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986; 12:2131–2136. PMID: 3793550.
Article25. Norris LK, Grossman SA, Olivi A. Neoplastic meningitis following surgical resection of isolated cerebellar metastasis : a potentially preventable complication. J Neurooncol. 1997; 32:215–223. PMID: 9049883.26. Pace A, Fabi A. Chemotherapy in neoplastic meningitis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2006; 60:194–200. PMID: 16949298.
Article27. Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Walsh JW, Dempsey RJ, Maruyama Y, Kryscio RJ, et al. A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastases to the brain. N Engl J Med. 1990; 322:494–500. PMID: 2405271.
Article28. Pavlidis N. The diagnostic and therapeutic management of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Ann Oncol. 2004; 15(Suppl 4):iv285–iv291. PMID: 15477323.
Article29. Rosen ST, Aisner J, Makuch RW, Matthews MJ, Ihde DC, Whitacre M, et al. Carcinomatous leptomeningitis in small cell lung cancer : a clinicopathologic review of the National Cancer Institute experience. Medicine (Baltimore). 1982; 61:45–53. PMID: 6276648.30. Seute T, Leffers P, ten Velde GP, Twijnstra A. Leptomeningeal metastases from small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer. 2005; 104:1700–1705. PMID: 16080173.
Article31. Siomin VE, Vogelbaum MA, Kanner AA, Lee SY, Suh JH, Barnett GH. Posterior fossa metastases : risk of leptomeningeal disease when treated with stereotactic radiosurgery compared to surgery. J Neurooncol. 2004; 67:115–121. PMID: 15072456.
Article32. Suki D, Abouassi H, Patel AJ, Sawaya R, Weinberg JS, Groves MD. Comparative risk of leptomeningeal disease after resection or stereotactic radiosurgery for solid tumor metastasis to the posterior fossa. J Neurosurg. 2008; 108:248–257. PMID: 18240919.
Article33. Suki D, Hatiboglu MA, Patel AJ, Weinberg JS, Groves MD, Mahajan A, et al. Comparative risk of leptomeningeal dissemination of cancer after surgery or stereotactic radiosurgery for a single supratentorial solid tumor metastasis. Neurosurgery. 2009; 64:664–674. discussion 674-676. PMID: 19197219.
Article34. Umpleby HC, Williamson RC. Anastomotic recurrence in large bowel cancer. Br J Surg. 1987; 74:873–878. PMID: 3311277.
Article35. van der Ree TC, Dippel DW, Avezaat CJ, Sillevis Smitt PA, Vecht CJ, van den Bent MJ. Leptomeningeal metastasis after surgical resection of brain metastases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999; 66:225–227. PMID: 10071105.
Article36. Waki F, Ando M, Takashima A, Yonemori K, Nokihara H, Miyake M, et al. Prognostic factors and clinical outcomes in patients with leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumors. J Neurooncol. 2009; 93:205–212. PMID: 19043775.
Article37. Wasserstrom WR, Glass JP, Posner JB. Diagnosis and treatment of leptomeningeal metastases from solid tumors : experience with 90 patients. Cancer. 1982; 49:759–772. PMID: 6895713.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis Presenting as a Neurological Complication of Stomach Cancer
- Intrathecal Trastuzumab Treatment in Patients with Breast Cancer and Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis
- Effects of Postoperative Radiotherapy on Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis or Dural Metastasis after Resection of Brain Metastases in Breast Cancer Patients
- Brain Metastasis and Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis in Breast Cancer
- Response of Leptomeningeal Dissemination of Anaplastic Glioma to Temozolomide: Experience of Two Cases