J Korean Rheum Assoc.
2007 Dec;14(4):322-330.
The Blocking of TNF-alpha by RNA Interference and Its Influence on Synovial Fibroblast and Chondrocytes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Intenal Medicine, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Anyang, Korea. kimha@hallym.ac.kr
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Small interfering RNA (siRNA) triggers RNA interference in mammalian somatic cells. TNF-alpha is a proinflammatory cytokine implicated in the pathogenesis of inflammatory arthritis including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This study was to use TNF receptor 1 (TNFRI)- specific siRNA to inhibit the TNF-alpha mediated signaling in RA fibroblast like synoviocytes (FLS) and chondrocytes.
METHODS
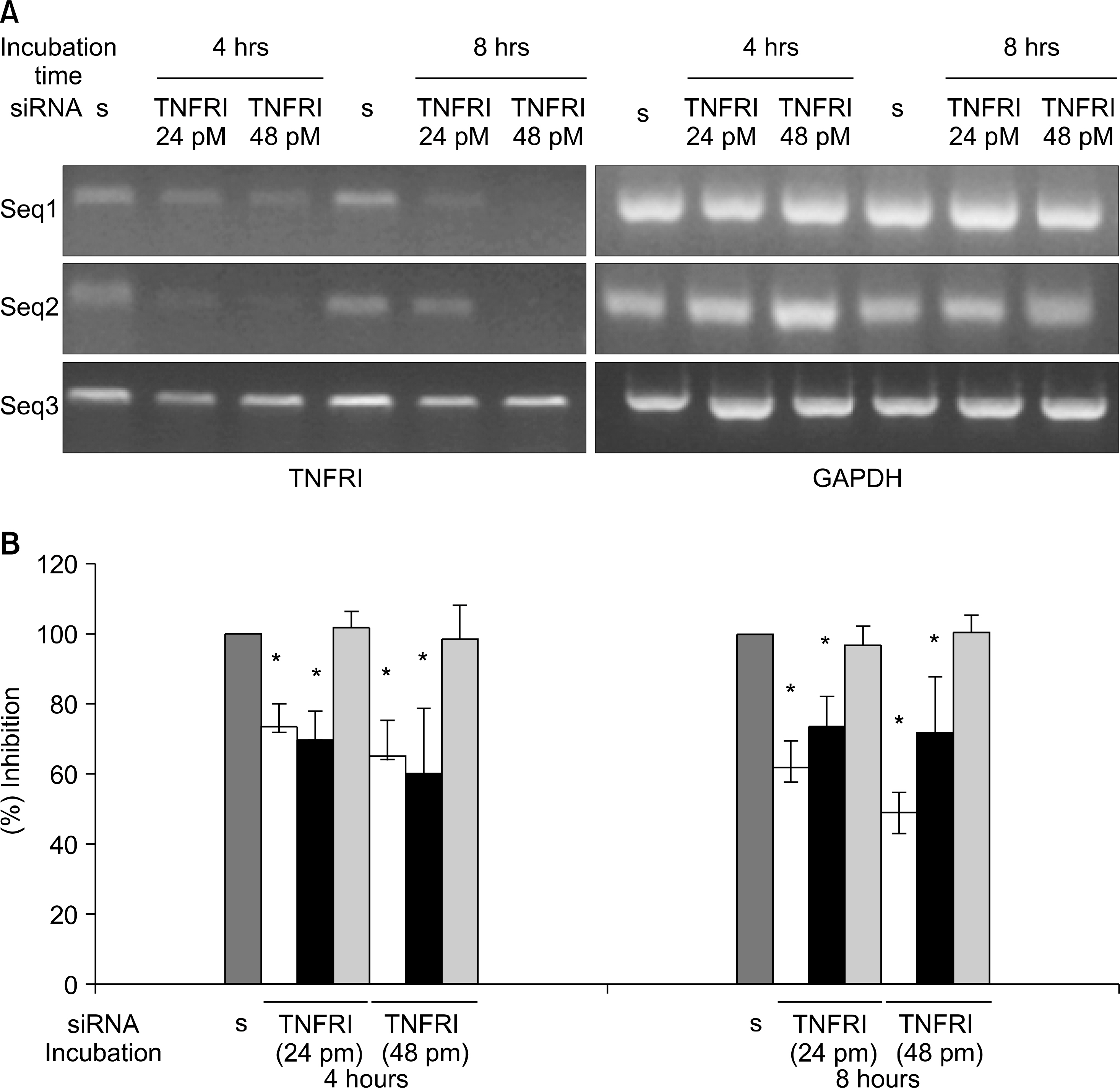
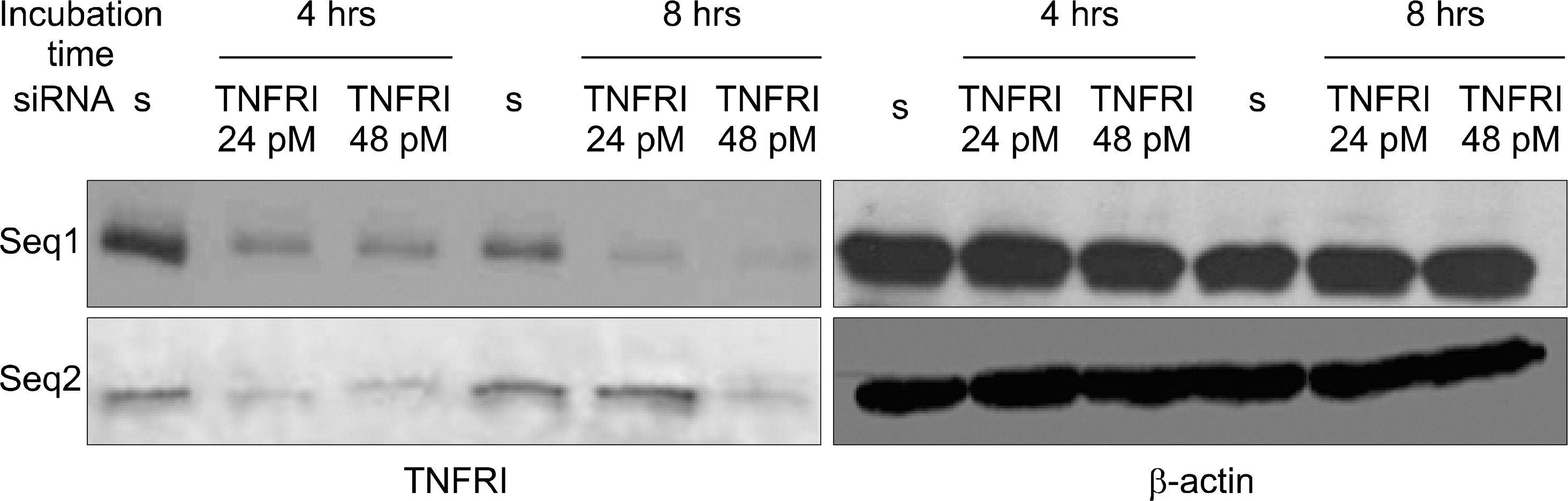
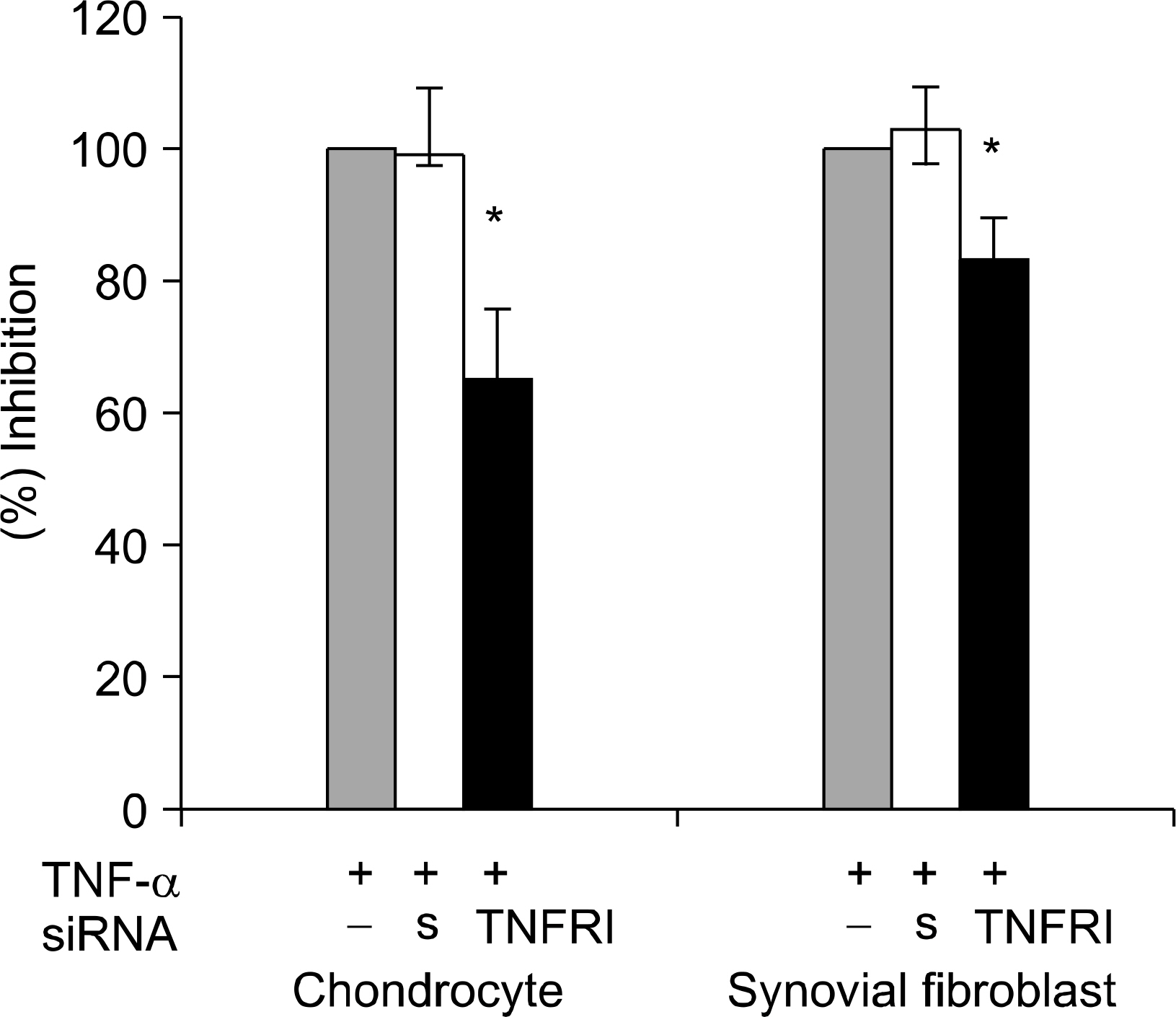
TNFRI specific siRNA was produced by targeting 3 nucleotide sequences at 474~494, 562~582 and 668~688. Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and Western blot were performed to optimize the silencing effects of TNFRI siRNA in cultured FLS and chondrocytes. The inhibition of TNF-alpha mediated signaling was determined by ELISA assay of metalloproteinase 1 secretion induced by TNF-alpha.
RESULTS
The TNFRI siRNA inhibited the expression of TNFRI mRNA and protein in both RA FLS and chondrocytes. MMP-1 secretion induced by TNF-alpha was significantly downregulated by TNFRI siRNA.
CONCLUSION
TNFRI siRNA can inhibit the expression and signaling downstream of TNFRI in both RA FLS and chondrocytes efficiently. This suggests that RNA interference technique by siRNA could be considered as a potential therapeutic target for RA.
MeSH Terms
-
Arthritis
Arthritis, Rheumatoid
Base Sequence
Blotting, Western
Chondrocytes*
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Fibroblasts*
Receptors, Tumor Necrosis Factor
Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction
RNA Interference*
RNA*
RNA, Messenger
RNA, Small Interfering
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha*
RNA
RNA, Messenger
RNA, Small Interfering
Receptors, Tumor Necrosis Factor
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Reference
-
1). Choy EH., Panayi GS. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2001. 344:907–16.
Article2). Clark IA. How TNF was recognized as a key mechanism of disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007. 18:335–43.
Article3). Lipsky PE., van der Heijde DM., St ., Clair EW., Furst DE., Breedveld FC., Kalden JR, et al. Infliximaband methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: anti-tumor necrosis factor trial in rheumatoid arthritis with concomitant therapy study group. N Engl J Med. 2000. 343:1594–602.4). Weinblatt ME., Kremer JM., Bankhurst AD., Bulpitt KJ., Fleischmann RM., Fox RI, et al. A trial of etanercept, a recombinant tumor necrosis factor receptor: Fc fusion protein, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate. N Engl J Med. 1999. 340:253–9.5). Hannon GJ. RNA interference. Nature. 2002. 418:244–51.
Article6). Elbashir SM., Harborth J., Lendeckel W., Yalcin A., Weber K., Tuschl T. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature. 2001. 411:494–8.
Article7). Harborth J., Elbashir SM., Bechert K., Tuschl T., Weber K. Identification of essential genes in cultured mammalian cells using small interfering RNAs. J Cell Sci. 2001. 114:4557–65.
Article8). Kim HA., Kim S., Chang SH., Hwang HJ., Choi YN. Anti-arthritic effect of ginsenoside Rb1 on collagen induced arthritis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2007. 7:1286–91.
Article9). Bernstein E., Caudy AA., Hammond SM., Hannon GJ. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature. 2001. 409:363–6.
Article10). Manche L., Green SR., Schmedt C., Mathews MB. Interactions between double-stranded RNA regulators and the protein kinase DAI. Mol Cell Biol. 1992. 12:5238–48.
Article11). Saito F., Yokota H., Sudo Y., Yakabe Y., Takeyama H., Matsunaga T. Application of RNAi inducible TNFRI knockdown cells to the analysis of TNFalpha-induced cytotoxicity. Toxicol In Vitro. 2006. 20:1343–53.12). Zhou HW., Lou SQ., Zhang K. Recovery of function in osteoarthritic chondrocytes induced by p16INK4a-specific siRNA in vitro. Rheumatology. 2004. 43:555–68.
Article13). Lianxu C., Hongti J., Changlong Y. NF-kappaB p65-specific siRNA inhibits expression of genes of COX-2, NOS-2 and MMP-9 in rat IL-1 beta-induced and TNF-alpha-induced chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006. 14:367–76.14). Klatt AR., Klinger G., Zech D., Paul-Klausch B., Renno JH., Schmidt J, et al. RNAi in primary human chondrocytes: Efficiencies, kinetics, and non-specific effects of siRNA-mediated gene suppression. Biologicals. 2007. 35:321–8.
Article15). Robbins PD., Evans CH., Chernajovsky Y. Gene therapy for arthritis. Gene Ther. 2003. 10:902–11.
Article16). Schiffelers RM., Xu J., Storm G., Woodle MC., Scaria PV. Effects of treatment with small interfering RNA on joint inflammation in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005. 52:1314–8.
Article17). Chen LX., Lin L., Wang HJ., Wei XL., Fu X., Zhang JY, et al. Suppression of early experimental osteoarthritis by in vivo delivery of the adenoviral vector-mediated NF-kappaBp65-specific siRNA. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007. doi: 10.1016/j.biologicals.2007.06.006.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Screening of Genes Regulating TNF-alpha-mediated Synovial Hyperplasia in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Crosstalk between FLS and chondrocytes is regulated by HIF-2alpha-mediated cytokines in arthritis
- Synovial Cell Migration is Associated with B Cell Activating Factor Expression Increased by TNFα or Decreased by KR33426
- The time-course and RNA interference of TNF-alpha, IL-6, and IL-1beta expression on neuropathic pain induced by L5 spinal nerve transection in rats
- Effect of Zoledronate on the Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A by Articular Chondrocytes and Synovial Cells: An in Vitro Study