J Korean Diabetes Assoc.
2006 Nov;30(6):416-427.
High Glucose Modulates Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation Through Activation of PKC-sigma-dependent NAD(P)H oxidase
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Pusan National University, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Busan St.Mary's Medical Center, Korea.
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Oxidative stress is thought to be one of the causative factors contributing to macrovascular complications in diabetes. However, the mechanisms of development and progression of diabetic vascular complications are poorly understood. We hypothesized that PKC-sigma isozyme contributes to ROS generation and determined their roles in the critical intermediary signaling events in high glucose-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle (VSM) cells.
METHODS
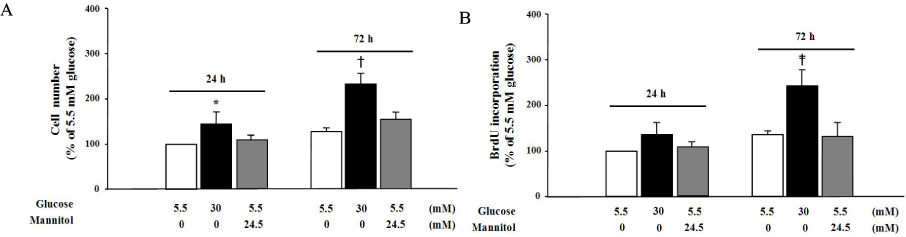
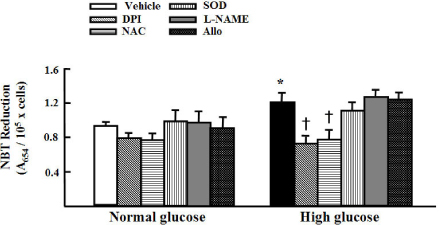
We treated primary cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells for 72 hours with medium containing 5.5 mmol/L D-glucose (normal glucose), 30 mmol/L D-glucose (high glucose) or 5.5 mmol/L D-glucose plus 24.5 mmol/L mannitol (osmotic control). We then measured cell number, BrdU incorporation, cell cycle and superoxide production in VSM cells. Immunoblotting of PKC isozymes using phoshospecific antibodies was performed, and PKC activity was also measured.
RESULTS
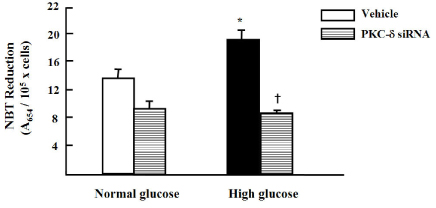
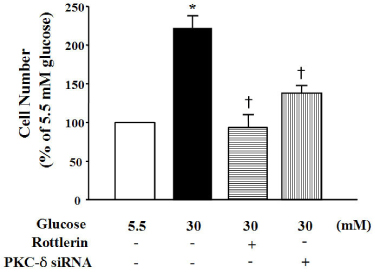
High glucose increased VSM cell number and BrdU incorporation and displayed significantly greater percentages of S and G2/M phases than compared to 5.5 mmol/L glucose and osmotic control. The nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) staining in high glucose-treated VSM cell was more prominent compared with normal glucose-treated VSM cell, which was significantly inhibited by DPI (10 micrometer), but not by inhibitors for other oxidases. High glucose also markedly increased activity of PKC-sigma isozyme. When VSM cells were treated with rottlerin, a specific inhibitor of PKC-sigma or transfected with PKC-sigma siRNA, NBT staining and NAD(P)H oxidase activity were significantly attenuated in the high glucose-treated VSM cells. Furthermore, inhibition of PKC-sigma markedly decreased VSM cell number by high glucose.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that high glucose-induced VSM cell proliferation is dependent upon activation of PKC-sigma, which may responsible for elevated intracellular ROS production in VSM cells, and this is mediated by NAD(P)H oxidase.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Antibodies
Bromodeoxyuridine
Cell Count
Cell Cycle
Cell Proliferation*
Diabetic Angiopathies
Glucose*
Immunoblotting
Isoenzymes
Mannitol
Muscle, Smooth, Vascular*
Myocytes, Smooth Muscle
NADPH Oxidase*
Nitroblue Tetrazolium
Oxidative Stress
Oxidoreductases
Rats
RNA, Small Interfering
Superoxides
Antibodies
Bromodeoxyuridine
Glucose
Isoenzymes
Mannitol
NADPH Oxidase
Nitroblue Tetrazolium
Oxidoreductases
RNA, Small Interfering
Superoxides
Figure
Reference
-
1. DeFranzo RA, Ferrannini E. Insulin resistance. A multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care. 1991. 14:173–194.2. Ross R. Cell biology of atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995. 57:791–804.3. Tanner FC, Boehm M, Akyurek LM, San H, Yang ZY, Tashiro J, Nabel GJ, Nabel EG. Differential effects of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p27(KIP1), p21(CIP1), and 16(Ink4) on vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Circulation. 2000. 10:2022–2025.4. Bruemmer D, Berger JP, Liu J, Kintscher U, Wakino S, Fleck E, Moller DE, Law RE. A non-thiazolidinedione partial peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor ligand inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell growth. Eur J Pharm. 2003. 466:225–234.5. Brownlee M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature. 2001. 414:813–820.6. Griendling KK, Taubman MB, Akers M, Mendlowitz M, Alexander RW. Characterization of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1991. 266:15498–15504.8. Beckman JA, Creager MA, Libby P. Diabetes and atherosclerosis: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. JAMA. 2002. 87:2570–2581.9. Creager MA, Luscher TF, Cosentino F, Beckman JA. Diabetes and vascular disease: pathophysiology, clinical consequences, and medical therapy. Part I. Circulation. 2003. 108:1527–1532.10. Barsness GW, Peterson ED, Ohman EM, Nelson CL, DeLong ER, Reves JG, Smith PK, Anderson RD, Jones RH, Mark DB, Califf RM. Relationship between diabetes mellitus and long-term survival after coronary bypass and angioplasty. Circulation. 1997. 96:2551–2556.11. King GL, Kunisaki M, Nishi N, Inoguchi T, Shiba T, Xia P. Biochemical and molecular mechanisms in the development of diabetic vascular complications. Diabetes. 1996. 45:Suppl 3. S105–S108.12. Lee HS, Son SM, Kim YK, Hong KW, Kim CD. NAD(P)H oxidase participates in the signaling events in high glucose-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Life Sci. 2003. 72:2719–2730.13. Inoguchi T, Li P, Umeda F, Yu HY, Kakimoto M, Imamura M, Aoki T, Etoh T, Hashimoto T, Naruse M, Sano H, Utsumi H, Nawata H. High glucose level and free fatty acid stimulate reactive oxygen species production through protein kinase C-dependent activation of NAD(P)H oxidase in cultured vascular cells. Diabetes. 2000. 49:1939–1944.14. Graier WF, Grubenthal I, Dittrich P, Wascher TC, Kostner GM. Intracellular mechanism of high D-glucose-induced modulation of vascular cell proliferation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995. 294:221–229.15. Nakamura J, Kasuya Y, Hamada Y, Nakashima E, Naruse K, Yasuda Y, Kato K, Hotta N. Glucose-induced hyperproliferation of cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells through polyol pathway hyperactivity. Diabetologia. 2001. 44:480–487.16. Natarajan R, Gonzales N, Xu L, Nadler JL. Vascular smooth muscle cells exhibit increased growth in response to elevated glucose. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992. 187:552–560.17. Sheetz MJ, King GL. Molecular understanding of hyperglycemia's adverse effects for diabetes complications. JAMA. 2002. 288:2579–2588.18. Igarashi M, Wakasaki H, Takahara N, Ishii H, Jiang ZY, Yamauchi T, Kuboki K, Meier M, Rhodes CJ, King GL. Glucose or diabetes activates p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase via different pathways. J Clin Invest. 1999. 103:185–195.19. Haller H, Baur E, Quass P, Behrend M, Lindschau C, Distler A, Luft FC. High glucose concentrations and protein kinase C isoforms in vascular smooth muscle cells. Kidney Int. 1995. 47:1057–1067.20. Konishi H, Tanaka M, Takemura Y, Matsuzaki H, Ono Y, Kikkawa U, Nishizuka Y. Activation of protein kinase C by tyrosine phosphorylation in response to H2O2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997. 94:11233–11237.21. Lagaud GJ, Masih-Khan E, Kai S, van Breemen C, Dube GP. Influence of type II diabetes on arterial tone and endothelial function in murine mesenteric resistance arteries. J Vasc Res. 2001. 38:578–589.22. Park JY, Takahara N, Gabriele A, Chou E, Naruse K, Suzuma K, Yamauchi T, Ha SW, Meier M, Rhodes CJ, King GL. Induction of endothelin-1 expression by glucose: an effect of protein kinase C activation. Diabetes. 2000. 49:1239–1248.23. Suzuma K, Takahara N, Suzuma I, Isshiki K, Ueki K, Leitges M, Aiello LP, King GL. Characterization of protein kinase C isoform's action on retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation, vascular endothelial growth factor-induced endothelial cell proliferation, and retinal neovascularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002. 99:721–726.24. Fukumoto S, Nishizawa Y, Hosoi M, Koyama H, Yamakawa K, Ohno S, Morii H. Protein kinase C inhibits the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells by suppressing G1 cyclin expression. J Biol Chem. 1997. 272:13816–13822.25. Ueda Y, Hirai S, Osada S, Suzuki A, Mizuno K, Ohno S. Protein kinase C activates the MEK-ERK pathway in a manner independent of Ras and dependent on Raf. J Biol Chem. 1996. 271:23512–23519.26. Guo JH, Wang H, Malbon CC. Conditional, tissue-specific expression of Q205L Gi2 in vivo mimics insulin activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and p38 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1998. 273:16487–16493.27. Sweeney G, Somwar R, Ramlal T, Volchuk A, Ueyama A, Klip A. An inhibitor of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase prevents insulin-stimulated glucose transport but not glucose transporter translocation in 3T3L1 adipocytes and L6 myotubes. J Biol Chem. 1999. 274:10071–10078.28. Igarashi M, Yamaguchi H, Hirata A, Tsuchiya H, Susa S, Tominaga M, Daimon M, Kato T. Insulin activates p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase via a MAP kinase kinase (MKK) 3/MKK 6 pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. Eur J Clin Invest. 2000. 30:668–677.29. MacFarlene WM, Smith SB, James RFL, Clifton AD, Doza YN, Cohen P, Docherty K. The p38/reactivating kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade mediates the activation of the transcription factor insulin upstream factor 1 and insulin gene transcription by high glucose in pancreatic β-cells. J Biol Chem. 1997. 272:20936–20944.30. Stein B, Brady H, Yang MX, Young DB, Barbosa MS. Cloning and characterization of MEK6, a novel member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. J Biol Chem. 1996. 271:11427–11433.31. Krump E, Sanghera JS, Pelech SL, Furuya W, Grinstein S. Chemotactic peptide N-formyl-met-leu-phe activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and MAPK-activated protein kinase-2 in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1997. 272:937–944.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Migration of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells by High Glucose is Reactive Oxygen Dependent
- The Effect of High Glucose on the Proliferation and Migration of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
- Involvement of NAD (P) H Oxidase in a Potential Link between Diabetes and Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation
- The Role of Janus Kinase in Superoxide-mediated Proliferation of Diabetic Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
- The Role of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Vascular Complications