J Lipid Atheroscler.
2016 Jun;5(1):27-36. 10.12997/jla.2016.5.1.27.
Usefulness of Cardiac Biomarkers in the Evaluation of Prognosis and Cardiac Involvement in Patients with Acute Aortic Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1The Heart Center, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. christiankyehun@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2328836
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12997/jla.2016.5.1.27
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the usefulness of cardiac biomarkers in the evaluation of prognosis and cardiac involvement (CI) in patients with acute aortic syndrome (AAS).
METHODS
A total of 260 AAS patients with the measurements of cardiac biomarkers were divided into 2 groups; the survived (n=215, 60.6±13.7 years, 110 males) vs the dead (n=45, 64.5±13.6 years, 19 males). N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), cardiac specific troponin-I (cTnI), C-reactive protein (CRP), creatinine kinase (CK), MB fraction of CK (CK-MB), and D-dimer were compared.
RESULTS
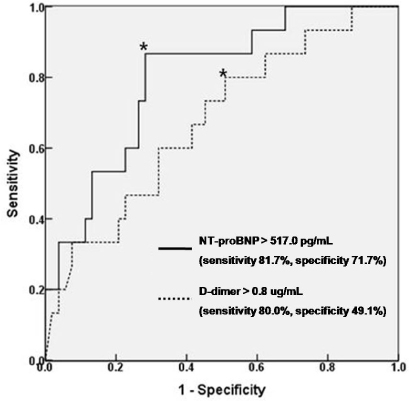
NT-proBNP and D-dimer were significantly elevated in the dead group than in the survived group (3558.7±5497.2 vs 949.9±2307.3 pg/mL, p<0.001, 4.5±5.1 vs 2.0±3.2 ug/mL, p<0.001, respectively). CI was observed in 59 patients (22.7%), and NT-proBNP was significantly elevated in patients with CI than in patients without CI (2497.7±4671.3 vs 722.5±1489.1 pg/mL, p=0.034). In univariate analysis, Stanford type A, CI, NT-proBNP, and D-dimer were significantly associated with mortality, but NT-proBNP was the only significant independent predictor of mortality in multivariate analysis. By receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, the optimal cut-off value to predict mortality was 517.0 pg/mL for NT-proBNP (area under the curve 0.797, sensitivity 86.7%, specificity 71.7%).
CONCLUSION
The elevation of cardiac biomarkers is not infrequent in patients with AAS. NT-proBNP is significantly associated with CI and is an independent predictor of mortality in patients with AAS. The measurement of NT-proBNP would be useful in the risk stratification of AAS.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Golledge J, Eagle KA. Acute aortic dissection. Lancet. 2008; 372:55–66.
Article2. Song JK, Kang SJ, Song JM, Kang DH, Song H, Chung CH, et al. Factors associated with in-hospital mortality in patients with acute aortic syndrome involving the ascending aorta. Int J Cardiol. 2007; 115:14–18.
Article3. Vasan RS. Biomarkers of cardiovascular disease: molecular basis and practical considerations. Circulation. 2006; 113:2335–2362.4. McLean AS, Huang SJ. Cardiac biomarkers in the intensive care unit. Ann Intensive Care. 2012; 2:8–18.
Article5. Mir MA. Aortic dissection--in pursuit of a serum marker. Am J Emerg Med. 2008; 26:942–945.
Article6. Wen D, Zhou XL, Li JJ, Hui RT. Biomarkers in aortic dissection. Clin Chim Acta. 2011; 412:688–695.
Article7. Sugano Y, Anzai T, Yoshikawa T, Satoh T, Iwanaga S, Hayashi T, et al. Serum C-reactive protein elevation predicts poor clinical outcome in patients with distal type acute aortic dissection: association with the occurrence of oxygenation impairment. Int J Cardiol. 2005; 102:39–45.
Article8. Linder N, Treitl M, Nikolaou K, Juchem G, Pichlmaier M, Reiser MF, et al. Acute aortic syndrome. Radiologe. 2012; 52:844–848.9. Parthenakis F, Koutalas E, Patrianakos A, Koukouvas M, Nyktari E, Vardas P. Diagnosing acute aortic syndromes: the role of specific biochemical markers. Int J Cardiol. 2010; 145:3–8.
Article10. Tokita Y, Kusama Y, Kodani E, Tadera T, Nakagomi A, Atarashi H, et al. Utility of rapid D-dimer measurement for screening of acute cardiovascular disease in the emergency setting. J Cardiol. 2009; 53:334–340.
Article11. Evangelista Masip A. Progress in the acute aortic syndrome. Rev Esp Cardiol. 2007; 60:428–439.
Article12. D'Aloia A, Faggiano P, Brentana L, DeiCas L. D-dimer serum levels in a case of type B aortic dissection A rapid test for the early diagnosis of acute aortic disease? J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2006; 7:216–218.13. Wen D, Wu HY, Jiang XJ, Zhang HM, Zhou XL, Li JJ, et al. Role of plasma C-reactive protein and white blood cell count in predicting in-hospital clinical events of acute type A aortic dissection. Chin Med J (Engl). 2011; 124:2678–2682.14. Sbarouni E, Georgiadou P, Marathias A, Geroulanos S, Kremastinos DT. D-dimer and BNP levels in acute aortic dissection. Int J Cardiol. 2007; 122:170–172.
Article15. Sodeck G, Domanovits H, Schillinger M, Janata K, Thalmann M, Ehrlich MP, et al. Pre-operative N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide predicts outcome in type A aortic dissection. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008; 51:1092–1097.
Article16. Cho JR, Shin S, Kim JS, Ko YG, Hong MK, Jang Y, et al. Clinical characteristics of acute aortic syndrome in Korean patients: from the Korean multi-center registry of acute aortic syndrome. Korean Circ J. 2012; 42:528–537.
Article17. Tsai TT, Nienaber CA, Eagle KA. Acute aortic syndromes. Circulation. 2005; 112:3802–3813.
Article18. Yamashita T, Seino Y, Ogawa A, Ogata K, Fukushima M, Tanaka K, et al. N-terminal pro-BNP is a novel biomarker for integrated cardio-renal burden and early risk stratification in patients admitted for cardiac emergency. J Cardiol. 2010; 55:377–383.
Article19. Emdin M, Vittorini S, Passino C, Clerico A. Old and new biomarkers of heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 2009; 11:331–335.
Article20. Tschöpe C, Kasner M, Westermann D, Gaub R, Poller WC, Schultheiss HP. The role of NT-proBNP in the diagnostics of isolated diastolic dysfunction: correlation with echocardiographic and invasive measurements. Eur Heart J. 2005; 26:2277–2284.
Article21. Kehl DW, Iqbal N, Fard A, Kipper BA, De La Parra Landa A, Maisel AS. Biomarkers in acute myocardial injury. Transl Res. 2012; 159:252–264.
Article22. Bonnefoy E, Godon P, Kirkorian G, Chabaud S, Touboul P. Significance of serum troponin I elevation in patients with acute aortic dissection of the ascending aorta. Acta Cardiol. 2005; 60:165–170.
Article23. Nienaber CA, Powell JT. Management of acute aortic syndromes. Eur Heart J. 2012; 33:26–35b.
Article24. Imoto K, Uchida K, Karube N, Yasutsune T, Cho T, Kimura K, et al. Risk analysis and improvement of strategies in patients who have acute type A aortic dissection with coronary artery dissection. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2013; 44:419–424.
Article25. Ohlmann P, Faure A, Morel O, Petit H, Kabbaj H, Meyer N, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating D-dimers in patients with acute aortic dissection. Crit Care Med. 2006; 34:1358–1364.
Article26. Ranasinghe AM, Bonser RS. Biomarkers in acute aortic dissection and other aortic syndromes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010; 56:1535–1541.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Usefulness of Cardiac Biomarker in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke
- Novel Biomarkers for Cardio-renal Syndrome
- Cardiac Tamponade during Endovascular Repair of Thoracic Aortic Dissection
- Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Cardiac Involvement in Behcet's Disease
- Using CT to Evaluate Cardiac Function