J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2013 Oct;39(5):224-230.
Immunohistochemical study on the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 2 and high-risk human papilloma virus in the malignant progression of papillomas
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea. vocaleo@knu.ac.kr
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Papilloma frequently develops as a benign tumor of the head and neck area, but its potential for malignant transformation has yet to be studied. This study aims to provide basic information for papillomas using the immunohistochemical staining of matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) and human papilloma virus (HPV) 16 and 18.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
To evaluate the malignant transformation of papillomas, the selected tissue samples were serially diagnosed with pre-cancerous papilloma (with epithelial dysplasia, pseudo-epitheliomatous hyperplasia) or malignant lesion (squamous cell carcinoma, SCC) after the first diagnosis (squamous papilloma, inverted papilloma). The selected tissues were stained with an antibody to MMP-2 and HPV 16-E7, HPV 18-L1. A statistical analysis was performed according to each transformation step.
RESULTS
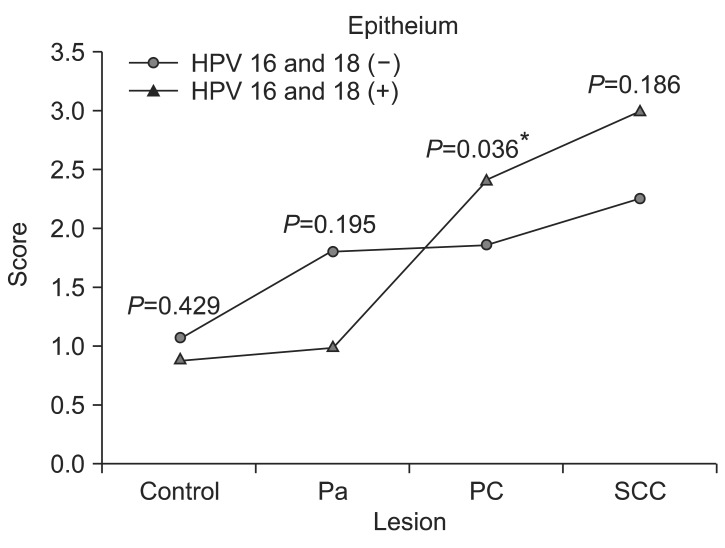
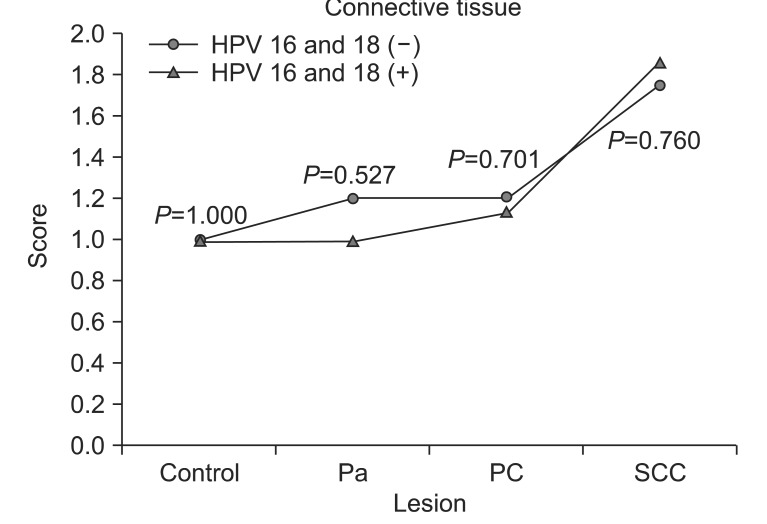
The epithelial layer of papilloma and pre-cancerous papilloma lesions had a similar MMP-2 expression, but that of the malignant lesion had a significantly increased MMP-2 expression. HPV 16 and 18 infection rates were 28.6%, 33.3% and 63.6% in papillomas, pre-cancerous papilloma lesions, and SCC.
CONCLUSIONS
A relatively high MMP-2 expression and HPV 16 or 18 infection of papillomas may be associated with early events in the multistep processes of malignant transformation of papillomas.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sapp JP, Eversole LR, Wysocki GP. Contemporary oral and maxillofacial pathology. St. Louis: Mosby;1997.2. Underbrink MP, Hoskins SL, Pou AM, Albrecht T. Viral interaction: a possible contributing factor in head and neck cancer progression. Acta Otolaryngol. 2008; 128:1361–1369. PMID: 18607925.
Article3. Atula S, Auvinen E, Grenman R, Syrjänen S. Human papillomavirus and Epstein-Barr virus in epithelial carcinomas of the head and neck region. Anticancer Res. 1997; 17:4427–4433. PMID: 9494545.4. Umudum H, Rezanko T, Dag F, Dogruluk T. Human papillomavirus genome detection by in situ hybridization in fine-needle aspirates of metastatic lesions from head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer. 2005; 105:171–177. PMID: 15822131.
Article5. Capone RB, Pai SI, Koch WM, Gillison ML, Danish HN, Westra WH, et al. Detection and quantitation of human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA in the sera of patients with HPV-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2000; 6:4171–4175. PMID: 11106228.6. Gillison ML, Koch WM, Capone RB, Spafford M, Westra WH, Wu L, et al. Evidence for a causal association between human papillomavirus and a subset of head and neck cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000; 92:709–720. PMID: 10793107.
Article7. Scheckenbach K, Lieven O, Götte K, Bockmühl U, Zotz R, Bier H, et al. p53 codon 72 polymorphic variants, loss of allele-specific transcription, and human papilloma virus 16 and/or 18 E6 messenger RNA expression in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004; 13:1805–1809. PMID: 15533911.8. Kähäri VM, Saarialho-Kere U. Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in tumour growth and invasion. Ann Med. 1999; 31:34–45. PMID: 10219712.9. Mook OR, Frederiks WM, Van Noorden CJ. The role of gelatinases in colorectal cancer progression and metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004; 1705:69–89. PMID: 15588763.
Article10. Roomi MW, Ivanov V, Kalinovsky T, Niedzwiecki A, Rath M. Modulation of human renal cell carcinoma 786-0 MMP-2 and MMP-9 activity by inhibitors and inducers in vitro. Med Oncol. 2006; 23:245–250. PMID: 16720925.
Article11. Thomas GT, Lewis MP, Speight PM. Matrix metalloproteinases and oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 1999; 35:227–233. PMID: 10621841.
Article12. Kim MK, Lee EH, Kim J, Lee EW, Cha IH. Immunohistochemical study on expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in irritation fibroma, oral leukoplakia and oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006; 32:352–359.13. da Silva Cardeal LB, Brohem CA, Corrêa TC, Winnischofer SM, Nakano F, Boccardo E, et al. Higher expression and activity of metalloproteinases in human cervical carcinoma cell lines is associated with HPV presence. Biochem Cell Biol. 2006; 84:713–719. PMID: 17167534.14. Katori H, Nozawa A, Tsukuda M. Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and 9 and human papilloma virus infection are associated with malignant transformation of sinonasal inverted papilloma. J Surg Oncol. 2006; 93:80–85. PMID: 16353190.
Article15. Chambers AF, Matrisian LM. Changing views of the role of matrix metalloproteinases in metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1997; 89:1260–1270. PMID: 9293916.
Article16. Curran S, Murray GI. Matrix metalloproteinases in tumour invasion and metastasis. J Pathol. 1999; 189:300–308. PMID: 10547590.
Article17. Davies B, Miles DW, Happerfield LC, Naylor MS, Bobrow LG, Rubens RD, et al. Activity of type IV collagenases in benign and malignant breast disease. Br J Cancer. 1993; 67:1126–1131. PMID: 8494711.
Article18. Tokuraku M, Sato H, Murakami S, Okada Y, Watanabe Y, Seiki M. Activation of the precursor of gelatinase A/72 kDa type IV collagenase/MMP-2 in lung carcinomas correlates with the expression of membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase (MT-MMP) and with lymph node metastasis. Int J Cancer. 1995; 64:355–359. PMID: 7591310.
Article19. Duffy MJ, Maguire TM, Hill A, McDermott E, O'Higgins N. Metalloproteinases: role in breast carcinogenesis, invasion and metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 2000; 2:252–257. PMID: 11250717.
Article20. Jones JL, Walker RA. Control of matrix metalloproteinase activity in cancer. J Pathol. 1997; 183:377–379. PMID: 9496252.
Article21. Gissmann L, Diehl V, Schultz-Coulon HJ, zur Hausen H. Molecular cloning and characterization of human papilloma virus DNA derived from a laryngeal papilloma. J Virol. 1982; 44:393–400. PMID: 6292500.
Article22. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Human papillomaviruses. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum. 1995; 64:1–378. PMID: 16755705.23. Arndt O, Johannes A, Zeise K, Brock J. High-risk HPV types in oral and laryngeal papilloma and leukoplakia. Laryngorhinootologie. 1997; 76:142–149. PMID: 9213402.24. Miller CS, White DK. Human papillomavirus expression in oral mucosa, premalignant conditions, and squamous cell carcinoma: a retrospective review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1996; 82:57–68. PMID: 8843455.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Malignant inverted papilloma of the urinary bladder: the histopathological aspect of malignant potential of inverted papilloma
- The Effects of Hantaan Virus on Fibronectin and Matrix Metalloproteinase-3
- Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase and Tissue Inhibitors of Matrix Metalloproteinase in Malignant Lymphoma
- Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Correlates with Poor Prognosis in Human Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma
- Matrix metalloproteinases in human gliomas: activation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) may be correlated with membrane-type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) expression