J Menopausal Med.
2014 Aug;20(2):52-56. 10.6118/jmm.2014.20.2.52.
Comparison of Buckling Ratio and Finite Element Analysis of Femoral Necks in Post-menopausal Women
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Engineering, National University of Singapore, Singapore.
- 2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University Health System, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Medical Biotechnology, Dongguk University, Seoul, Korea. tlee@dongguk.edu
- KMID: 2325442
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6118/jmm.2014.20.2.52
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Osteoporosis is a prevalent problem amongst the elderly. Bone mineral density (BMD) obtained from dual X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is the gold standard in diagnosing osteopenia (-1.0 < t < -2.5) and osteoporosis (t > -2.5). However, following osteoporosis therapy, increases in BMD may be unreliable. Although hip fracture risk can be reduced with the aid of drugs, treated patients still face considerable risk as most people who sustain hip fracture do not have generalized osteoporosis. A study of the local distribution of bone mass was necessary as they contribute to the geometry and consequently the bone strength.
METHODS
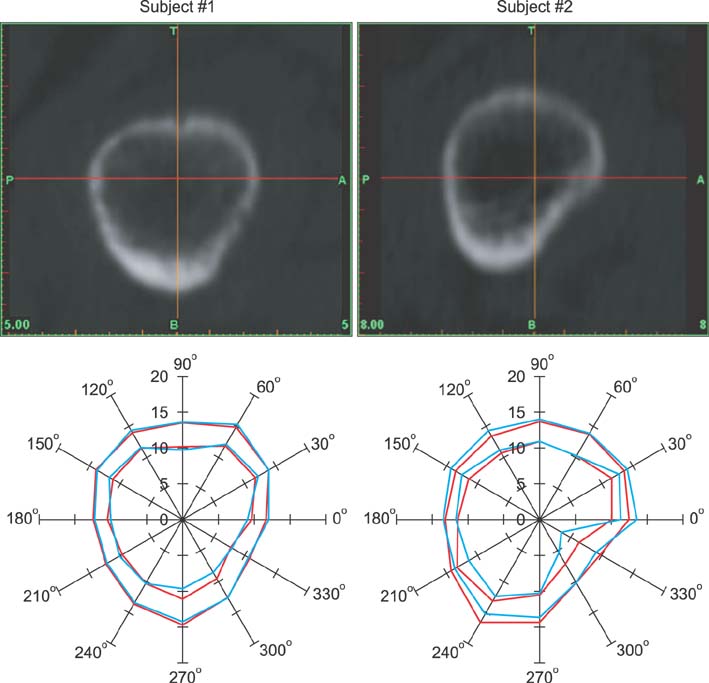
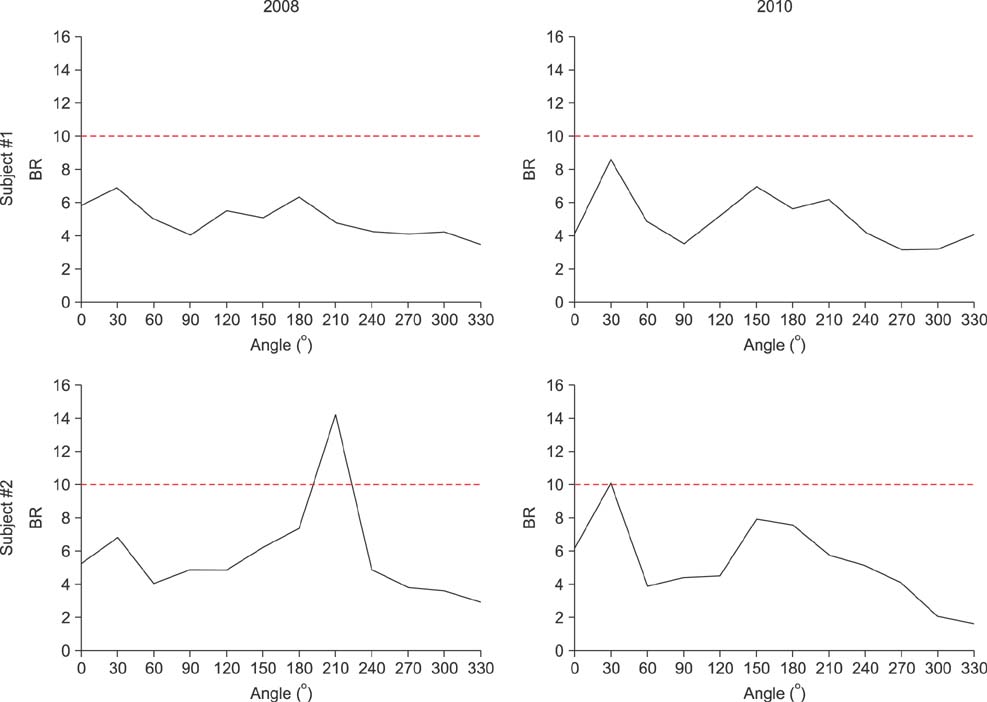
By identifying the respective regions in the femoral neck, the geometric changes were localized and differed between each patient, proving that drug treatment elicits local changes in mean outer radius and mean cortical thickness. Numerical analysis also validated the above findings, where critical strain regions were predicted at similar zones and this is coherent with the fact that reduced thickness of the cortical bone has been related to increased risk of fracture initiation.
RESULTS
Hence, from individual radar plots, we can determine if the effect of drugs had outweighed the effect of aging. We can then propose a course of treatment drug better suited for the patient in the clinical scenario.
CONCLUSION
Clinically, little conclusion can be drawn from just the BMD in osteopenic / osteoporotic patients. This emphasizes the necessity of using geometry and structure to predict fracture risk. Focusing on a patient specific analysis at a local level will improve diagnosis of osteoporosis and ultimately fracture prediction.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effect of Fennel on the Health Status of Menopausal Women: A Systematic and Meta-analysis
Talat Khadivzadeh, Mona Najaf Najafi, Leila Kargarfard, Masumeh Ghazanfarpour, Fatemeh Rajab Dizavandi, Imaneh Khorsand
J Menopausal Med. 2018;24(1):67-74. doi: 10.6118/jmm.2018.24.1.67.
Reference
-
1. Melton LJ 3rd. Hip fractures: a worldwide problem today and tomorrow. Bone. 1993; 14:Suppl 1. S1–S8.2. Schott AM, Cormier C, Hans D, Favier F, Hausherr E, Dargent-Molina P, et al. How hip and whole-body bone mineral density predict hip fracture in elderly women: the EPIDOS Prospective Study. Osteoporos Int. 1998; 8:247–254.3. McClung MR, Geusens P, Miller PD, Zippel H, Bensen WG, Roux C, et al. Hip Intervention Program Study Group. Effect of risedronate on the risk of hip fracture in elderly women. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:333–340.4. Anitha D, Kim KJ, Lim SK, Lee T. Implications of local osteoporosis on the efficacy of anti-resorptive drug treatment: a 3-year follow-up finite element study in risedronate-treated women. Osteoporos Int. 2013; 24:3043–3051.5. Kim TH, Lee HH, Chung SH, Lee WS, Park J, Lee S. Routine application of the Korean FRAX model in women: a single-center study. Korean J Bone Metab. 2012; 19:29–34.6. Kanis JA, Melton LJ 3rd, Christiansen C, Johnston CC, Khaltaev N. The diagnosis of osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 1994; 9:1137–1141.7. Carpenter RD, Sigurdsson S, Zhao S, Lu Y, Eiriksdottir G, Sigurdsson G, et al. Effects of age and sex on the strength and cortical thickness of the femoral neck. Bone. 2011; 48:741–747.8. Young WC. Elastic stability formulas for stress and strain. In : Crawford H, Thomas S, editors. Roark's formulas for stress and strain. 6th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill;1989. p. 688.9. Keyak JH. Improved prediction of proximal femoral fracture load using nonlinear finite element models. Med Eng Phys. 2001; 23:165–173.10. Ruff C, Holt B, Trinkaus E. Who's afraid of the big bad Wolff?: "Wolff's law" and bone functional adaptation. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2006; 129:484–498.11. Pisharody S, Phillips R, Langton CM. Sensitivity of proximal femoral stiffness and areal bone mineral density to changes in bone geometry and density. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2008; 222:367–375.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A study on the stress analysis of three root-form implants with finite element analysis
- Finite element analysis of osseointegrated implant
- Finite element analysis of stresses induced by osteointegrated prosthesis with or without connection between natural tooth and osseointegrated abutments
- Three dimensional finite element analysis of mandibular stresses of complete denture occlusion
- Biomechanical analysis of the Effect of Debondign of Cement - Femoral Stem Interface to the Cement - Bone Interface - three - dimensional non - linear finite element analysis -